Worksheet Reaction Rates Answer
When it comes to understanding and mastering the concept of reaction rates, having the right tools is key. This is where worksheets can play a crucial role. Designed to provide practice and reinforcement, worksheets offer a structured and organized approach to learning. By focusing on the entity and subject of reaction rates, worksheets can cater to students who are seeking clarity and comprehension in this specific area of study.
Table of Images 👆
- Worksheet Measuring Reaction Rate
- Worksheet Reaction Rates Answer Key
- Exothermic Reaction Worksheet
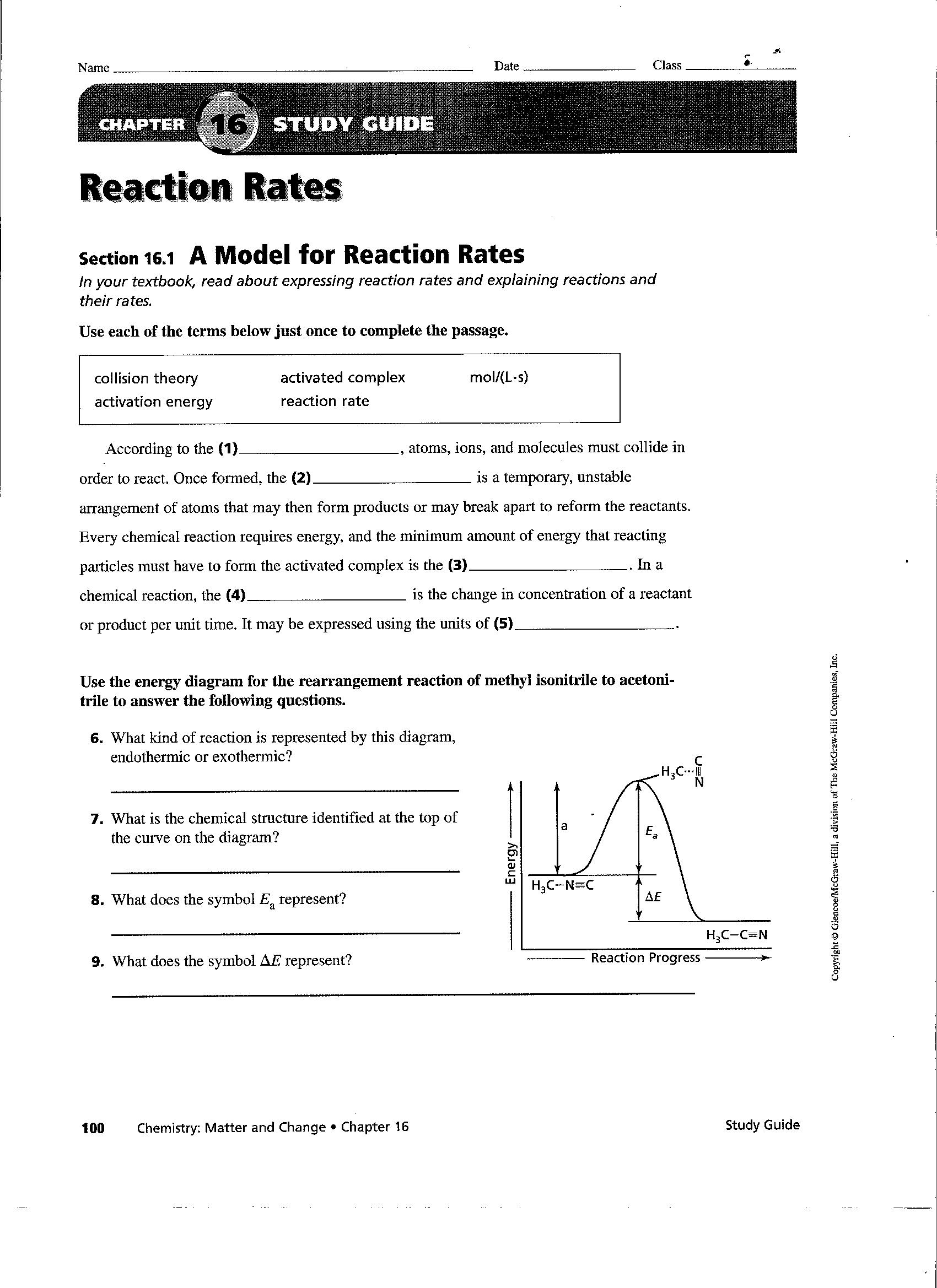
- Worksheet Reaction Rates Answer Key
- Rate Photosynthesis Worksheet
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
- Chemistry Reaction Rates Worksheet Answers
- AP Chemistry Kinetics Worksheet
- Chemical Reaction Types Worksheet
- Chemical Kinetics Worksheet
- Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Worksheet
- Reaction Rates Answers Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a reaction rate?
A reaction rate is the measure of how quickly a reaction takes place, typically expressed as the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time. It describes the speed at which reactants are consumed and products are formed in a chemical reaction, and can be influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, and the presence of catalysts.
How is reaction rate defined mathematically?
The reaction rate is typically defined as the change in concentration of a reactant or product over time. Mathematically, it is often expressed as the negative of the rate of change of reactants divided by their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. This is usually denoted as d[A]/dt for reactants and d[B]/dt for products, where [A] and [B] are the concentrations of reactants and products, respectively, and t represents time.
What factors can affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
Several factors can affect the rate of a chemical reaction including temperature, concentration of reactants, surface area of reactants, presence of a catalyst, and the nature of the reactants or the type of reaction. Temperature generally increases the rate of reaction by providing more energy for the molecules to collide and react. Higher concentrations of reactants increase the frequency of collisions, while a larger surface area of reactants allows for more exposed areas for collisions to occur. Catalysts can speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. Additionally, the nature of the reactants and the type of reaction being performed influence the rate at which chemical reactions occur.
What is the role of temperature in reaction rates?
Temperature plays a critical role in reaction rates by influencing the speed at which reactant molecules collide and the energy with which they collide. Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions that are more likely to result in a successful reaction. This increases the rate at which reactions occur, as described by the Arrhenius equation, which states that reaction rates generally double for every 10-degree Celsius increase in temperature.
How does concentration influence the rate of a reaction?
Concentration directly influences the rate of a reaction by affecting the frequency of collisions between reactant molecules. When the concentration of reactants is increased, there are more reactant molecules present in a given volume, leading to a higher likelihood of collisions. This increased frequency of collisions results in more successful collisions that can lead to the formation of products, ultimately speeding up the reaction rate. Conversely, decreasing the concentration of reactants reduces the number of collisions and slows down the reaction rate.
What is the significance of catalysts in speeding up reactions?
Catalysts are significant in speeding up reactions because they lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. By providing an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy, catalysts enable reactions to happen more quickly by increasing the frequency of successful collisions between reacting molecules. This ultimately leads to faster reaction rates and more efficient conversion of reactants into products.
How does surface area affect the rate of a reaction?
Surface area affects the rate of a reaction by increasing the number of collision between reactant particles. A higher surface area means more exposed area for particles to come into contact with each other, leading to more frequent collisions and a faster reaction rate. This is especially true for reactions that involve solid reactants, as breaking the solid into smaller pieces increases the surface area and accelerates the reaction.
What is the difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction in terms of rate?
In terms of rate, the main difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction is that exothermic reactions typically occur at a faster rate than endothermic reactions. This is because exothermic reactions release energy in the form of heat, which provides additional activation energy to speed up the reaction process. On the other hand, endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, which can slow down the rate of the reaction since additional energy is needed for the reaction to proceed.
What is meant by a rate-determining step in a reaction mechanism?
The rate-determining step in a reaction mechanism is the slowest step in the overall process, which determines the overall rate of the reaction. It is the step that has the highest activation energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to proceed. The rate of the entire reaction cannot exceed the rate of this particular step, making it crucial in determining the overall speed of the reaction.
How can reaction rates be measured experimentally?
Reaction rates can be measured experimentally by monitoring changes in the concentration of reactants or products over time. Common techniques include spectroscopy, chromatography, and titration. For example, measuring the color intensity of a solution, tracking the release of gases, or monitoring changes in pH are all ways to determine how quickly a reaction is proceeding. By analyzing these measurements and plotting them against time, scientists can determine the rate at which a reaction is occurring.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments