Work Power and Energy Worksheet
Are you struggling to understand the concepts of work, power, and energy? Look no further! This blog post will provide you with a helpful and comprehensive worksheet on these topics. Designed for students who are in high school or college, this worksheet is perfect for anyone who wants to practice and reinforce their understanding of work, power, and energy.
Table of Images 👆
- Physics Work and Power Worksheets
- Main Things That Use Electricity and Battery
- Kinetic Energy Worksheet
- Ecosystem Population Worksheet
- Tattoo Artist
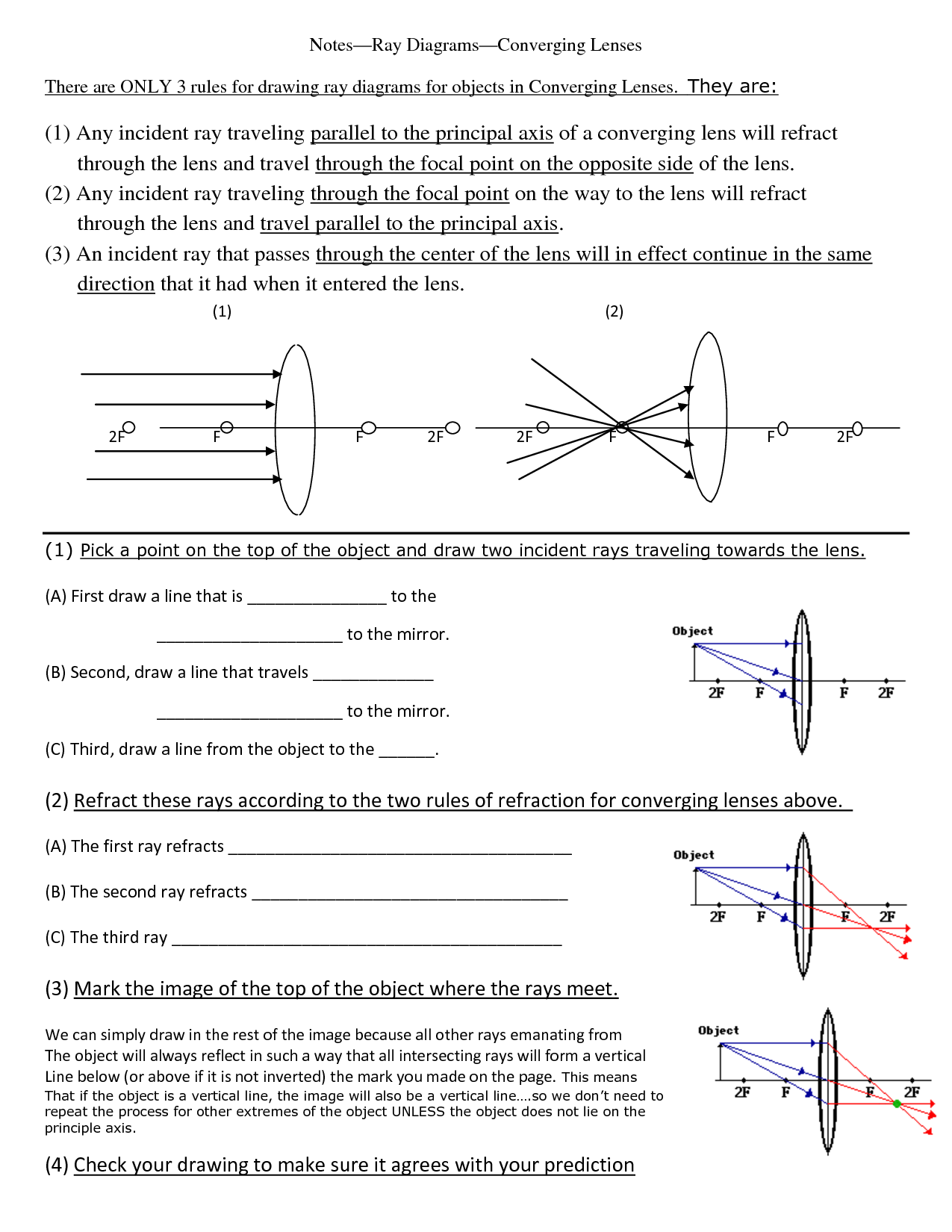
- Converging Lenses Ray Diagrams for Worksheet
- Pressure Problem Worksheet
- Stoichiometry Practice Worksheet Answer Key
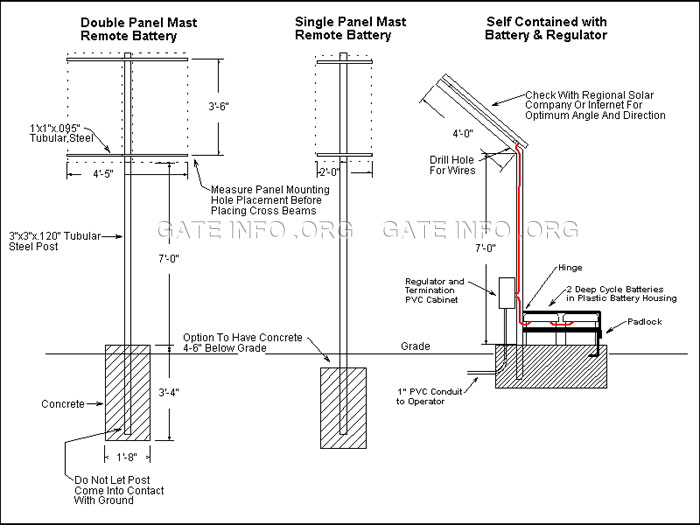
- Solar Panel Installation Diagram
- Three Little Pigs Story
- Three Little Pigs Story
- Three Little Pigs Story
- Three Little Pigs Story
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is work?
Work is the effort exerted by an individual to achieve a particular task or goal, often involving physical or mental activity to produce, accomplish, or achieve a desired outcome. It can encompass a wide range of activities, from manual labor to intellectual or creative endeavors, and is a fundamental part of human existence and productivity.
What is power?
Power is the ability to influence or control people, events, or resources. It can be exerted through various means such as authority, knowledge, wealth, or physical strength, and is often used to achieve specific goals or maintain a position of advantage. Power dynamics can exist on individual, organizational, or societal levels, and can have significant impacts on relationships, decision-making processes, and societal structures.
How is work related to energy?
Work is related to energy through the principle of conservation of energy which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed. In the context of work, energy is required to perform tasks, such as lifting an object, moving a vehicle, or generating electricity. When work is done, energy is transferred from one system to another, either increasing or decreasing the energy of the objects involved in the process. This interaction between work and energy demonstrates the fundamental relationship between the two concepts in the physical world.
What are the units of work and energy?
The units of work and energy are both Joules (symbol: J) in the International System of Units (SI).
What is the formula to calculate work?
The formula to calculate work is W = F * d * cos(theta), where W is the work done, F is the force applied, d is the distance over which the force is applied, and theta is the angle between the force and the direction of movement.
How is power defined and calculated?
Power is defined as the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It is calculated by dividing the amount of work done or energy transferred by the time it took to do that work or transfer that energy. Mathematically, power (P) can be expressed as P = W/t, where P is power, W is work done, and t is time. In the International System of Units (SI), power is measured in watts (W).
What is the unit of power?
The unit of power is the watt, symbolized by W. It measures the rate of energy transfer or the rate at which work is done.
How does power relate to work and time?
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred over time. In other words, power is a measure of how quickly work is being done or how fast energy is being transferred. The greater the power, the faster work can be completed or energy can be transferred in a given amount of time. This relationship between power, work, and time is crucial in understanding and measuring various physical phenomena and processes.
How can the conservation of energy be applied to solve problems?
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed. This principle can be applied to solve problems by accounting for all forms of energy in a system and ensuring that the total energy remains constant. By analyzing the different energy transfers and transformations in a system, one can determine the final state of the system or calculate unknown quantities such as velocity, height, or potential energy. This approach allows for a systematic and comprehensive understanding of the energy dynamics in a given situation, enabling accurate predictions and solutions to a wide range of problems across various fields such as physics, engineering, and environmental science.
What are some real-life applications of work, power, and energy?
Real-life applications of work, power, and energy can be seen in various aspects such as generating electricity from wind turbines or solar panels, designing efficient transportation systems like electric cars or high-speed trains, calculating the energy required for manufacturing processes in industries, understanding the power output of the human body during physical activities like running or lifting weights, and optimizing the work done by machines in construction or agriculture to increase productivity and efficiency.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments