What Causes Seasons Worksheet
Understanding the causes of seasons is an essential concept in earth science education. This blog post provides a descriptive and declarative introduction to a worksheet designed to aid students in comprehending the fundamental concepts behind the changing seasons. Whether you are a teacher seeking educational resources or a student looking to reinforce your knowledge, this worksheet offers an engaging and informative way to explore the fascinating phenomenon of seasons.
Table of Images 👆
- Earth Seasons Diagram Worksheet
- Bill Nye Earth Seasons Worksheet
- Earth Tilt and Seasons Worksheet
- Reasons for Seasons Worksheet Answers
- Earths Seasons Diagram Worksheet
- Sun Earth and Seasons Worksheet
- Sun Earth and Seasons Worksheet
- Four Seasons Kindergarten Worksheets Science
- Hemisphere 5th Grade Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the main cause of the changing seasons on Earth?
The changing seasons on Earth are mainly caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis as it orbits around the Sun. This tilt results in different parts of the Earth receiving more or less direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to variations in temperature and weather patterns that we experience as the four seasons: spring, summer, fall, and winter.
How does the tilt of the Earth's axis affect the seasons?
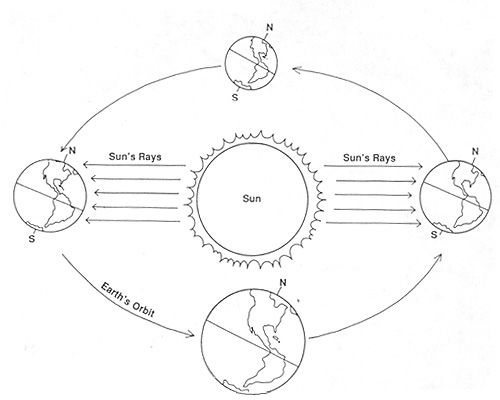
The tilt of the Earth's axis is responsible for the changing seasons. When a hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it receives more direct sunlight and experiences summer, while the opposite hemisphere is tilted away and has winter. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight, resulting in spring and autumn. This tilt creates the unique patterns of temperature and daylight that define the seasons on Earth.
Why do different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year?
Different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year due to the tilt of the Earth's axis as it orbits the sun. This tilt causes different parts of the planet to be angled towards or away from the sun at different times, creating the changing seasons and variations in sunlight levels. Areas near the equator receive more consistent sunlight year-round, while regions closer to the poles experience dramatic differences in daylight hours between summer and winter.
How does the angle at which sunlight reaches the Earth affect the seasons?
The angle at which sunlight reaches the Earth affects the seasons by varying the intensity of sunlight received in different parts of the planet throughout the year. When sunlight hits the Earth at a more direct angle, the region receives more energy and heat, leading to warmer temperatures and longer days, thus creating summer. Conversely, when sunlight hits at a shallower angle, the region receives less energy and heat, resulting in cooler temperatures and shorter days, leading to winter. This changing angle of sunlight causes the Earth's tilt and its position in orbit around the Sun to influence the length and intensity of each season experienced in different hemispheres.
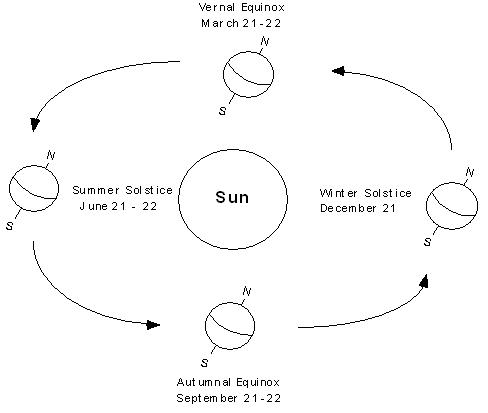
What is the difference between the summer and winter solstice?
The summer solstice occurs around June 21st in the Northern Hemisphere when the North Pole is tilted towards the sun, making it the longest day of the year with the most daylight. In contrast, the winter solstice occurs around December 21st in the Northern Hemisphere when the North Pole is tilted away from the sun, making it the shortest day of the year with the least amount of daylight. The solstices mark the point at which the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky, leading to the longest or shortest day of the year.
Why do regions near the equator experience relatively consistent climates throughout the year?
Regions near the equator experience relatively consistent climates throughout the year because they receive consistent direct sunlight due to the Earth's tilt and the position of the equator. This results in consistent high temperatures and a lack of distinct seasons compared to regions further away from the equator. Additionally, the equatorial regions have a higher humidity level due to the warm temperatures, which contributes to the consistent climate patterns throughout the year.
How do the changing seasons affect plant and animal life?
The changing seasons significantly impact plant and animal life by influencing behavior, reproduction, growth, and availability of food and shelter. Plants adapt to seasonal changes by altering their growth patterns, flowering, and seed production. Animals respond to the changing seasons by hibernating, migrating, or changing their diet to suit the available food sources. The seasonal variations in temperature, light, and precipitation also play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems and influencing the overall biodiversity of an area.
Can the distance between the Earth and the Sun influence the seasons?
Yes, the distance between the Earth and the Sun can influence the seasons. However, the primary reason for the seasons is the tilt of the Earth's axis in relation to its orbit around the Sun, rather than the distance between them. The changing distance, due to the Earth's elliptical orbit, does affect the intensity of sunlight received by the Earth, but this effect is relatively minor compared to the impact of the axial tilt.
What role do atmospheric conditions play in the seasonal changes?
Atmospheric conditions play a significant role in seasonal changes by influencing factors such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns. Changes in the Earth's axial tilt relative to the sun create variations in sunlight intensity, affecting the distribution of heat across different latitudes. This, in turn, drives shifts in atmospheric pressure, leading to changes in weather patterns that define the different seasons experienced in various regions. The interaction between the atmosphere, oceans, and land surfaces is critical in shaping the climate and weather patterns that contribute to seasonal changes.
How have human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, impacted the natural seasons?
Human activities like deforestation and urbanization have significantly impacted the natural seasons by disrupting the balance and rhythm of ecosystems. Deforestation can alter local climates, leading to changes in temperature and precipitation patterns that affect the timing and duration of seasons. Urbanization, with its large expanses of concrete and asphalt, can create "heat islands" that raise temperatures in cities, further altering seasonal patterns. These activities can also harm biodiversity, leading to disruptions in plant and animal life cycles that are closely tied to seasonal changes. Overall, human activities have accelerated climate change, contributing to shifts in seasons and affecting ecosystem functions worldwide.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments