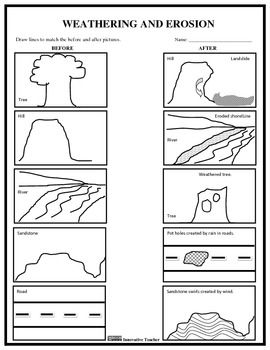
Weathering Erosion Worksheets Grade 4
If you're a Grade 4 teacher looking for comprehensive and engaging worksheets to teach your students about weathering and erosion, you've come to the right place. We understand the importance of providing students with hands-on activities that reinforce their understanding of these scientific concepts. With our specially designed worksheets, you can ensure that your students grasp the key principles of weathering and erosion while having fun in the process.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is weathering?
Weathering is the process by which rocks and other earth materials are broken down or worn away by the effects of natural elements such as water, wind, temperature changes, and living organisms. This gradual process can lead to the physical and chemical breakdown of rocks, creating soil and sediment that contributes to the shaping of Earth's surface over time.
Give an example of physical weathering.
One example of physical weathering is freeze-thaw weathering. This process occurs when water seeps into cracks in rocks, freezes, expands, and then thaws. The constant freezing and thawing cycle gradually wears away the rock, eventually causing it to break apart.
What is erosion?
Erosion is the process by which soil, rock, or sediment is gradually worn away by natural forces such as water, wind, or ice. It typically occurs over a long period of time and can be caused by factors such as weathering, gravitational forces, and human activities. Erosion can lead to the formation of landforms such as valleys, canyons, and coastlines, but it can also have negative impacts such as loss of fertile soil and damage to infrastructure.
How does erosion differ from weathering?
Erosion refers to the process of wearing away or moving rock, soil, or other particles from one location to another through the action of wind, water, or ice. Weathering, on the other hand, is the process of breaking down rocks, soil, and minerals into smaller pieces through physical, chemical, or biological means without necessarily moving them from one place to another. Weathering is the precursor to erosion, as it weakens rocks and makes them more susceptible to being eroded away by natural forces.
Describe the processes involved in chemical weathering.
Chemical weathering refers to the breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions. The processes involved include hydrolysis, where minerals react with water to form new minerals; oxidation, where minerals combine with oxygen to create new compounds; and dissolution, where minerals are dissolved in water. These reactions weaken the rock, leading to its eventual breakdown and formation of new materials like clays and oxides. Factors such as temperature, moisture, and the presence of acids can accelerate chemical weathering.
What is mechanical weathering?
Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces by physical processes such as temperature changes, frost action, and the growth of plant roots. This type of weathering does not change the composition of the rock but instead breaks it down into smaller fragments.
Explain how ice can contribute to weathering.
Ice can contribute to weathering through a process known as frost wedging. When water seeps into cracks in rocks and freezes, it expands, putting pressure on the surrounding rock and causing it to break apart. This repeated cycle of freezing and thawing can gradually break down rocks into smaller pieces, ultimately contributing to the weathering of the Earth's surface over time.
Give an example of erosion caused by water.
An example of erosion caused by water is the Grand Canyon in Arizona, USA. The Colorado River has been carving through the rock formations for millions of years, creating the vast and beautiful canyon that we see today. The force of the water has eroded the rock layers, creating cliffs, slopes, and unique rock formations along the river banks.
How does wind contribute to erosion?
Wind contributes to erosion by picking up and carrying loose particles such as sand and soil from the Earth's surface. As the wind moves across the land, these particles can be transported over long distances and deposited elsewhere, wearing down and smoothing out surfaces. This process of wind erosion can result in the loss of fertile soil, the formation of sand dunes, and the reshaping of landscapes over time.
Describe the role of gravity in erosion.
Gravity plays a significant role in erosion by exerting a downward force that pulls debris and sediments downhill. In steep terrain, gravity causes rocks and sediments to be dislodged and transported downhill through processes like mass wasting and landslides. Additionally, gravity influences the speed and direction of moving water and ice, facilitating their ability to transport sediment and carve into the landscape through processes like river erosion and glacial erosion. Ultimately, gravity acts as a driving force for erosional processes, shaping the Earth's surface over time.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments