Weather and Climate Worksheets
If you're searching for engaging and educational resources to enhance your understanding of weather and climate, look no further than our collection of worksheets. Designed for students interested in earth sciences and meteorology, these worksheets cover a wide range of topics related to weather patterns, climate change, and atmospheric phenomena. Whether you're an educator looking for supplemental materials or a learner seeking to enhance your knowledge, these worksheets provide a valuable opportunity to delve into the fascinating world of weather and climate.
Table of Images 👆
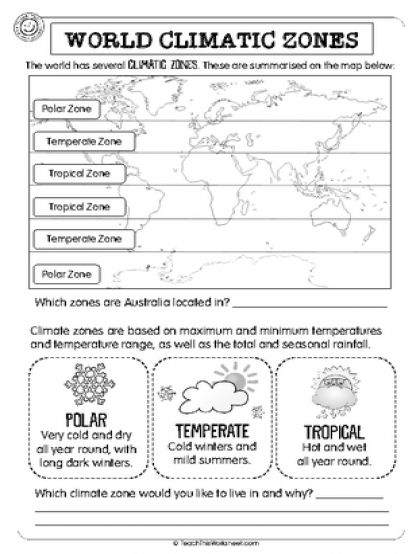
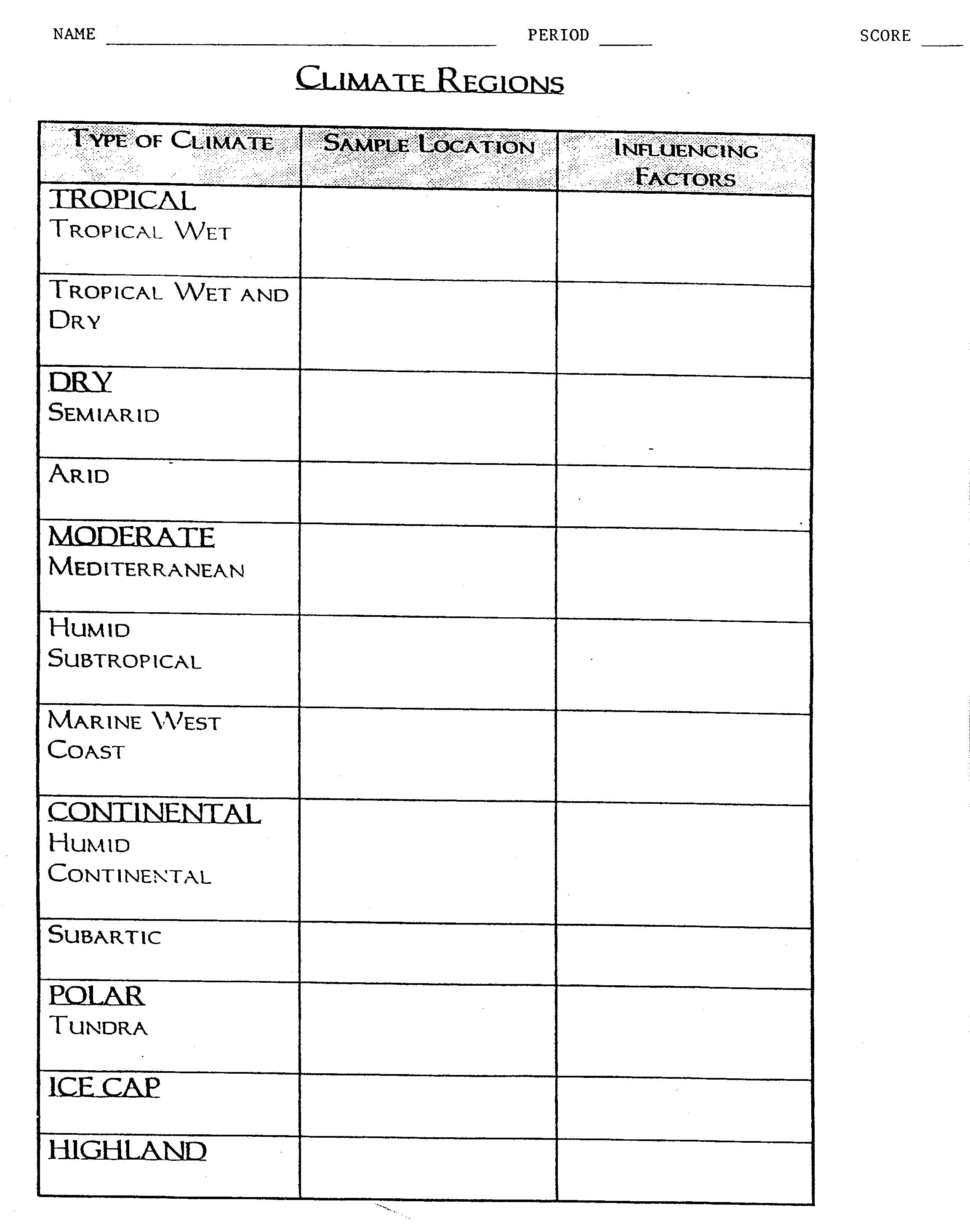
- World Climate Zones Worksheet
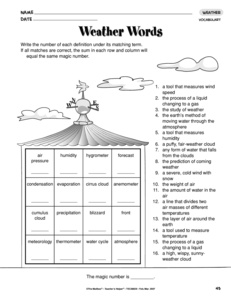
- Weather Map Worksheet
- Elementary Weather Worksheets
- Seasons Science Worksheet Middle School
- World Climate Patterns Worksheets
- Weather Maps for Kids Printable Worksheets
- Science Natural Disasters Worksheet
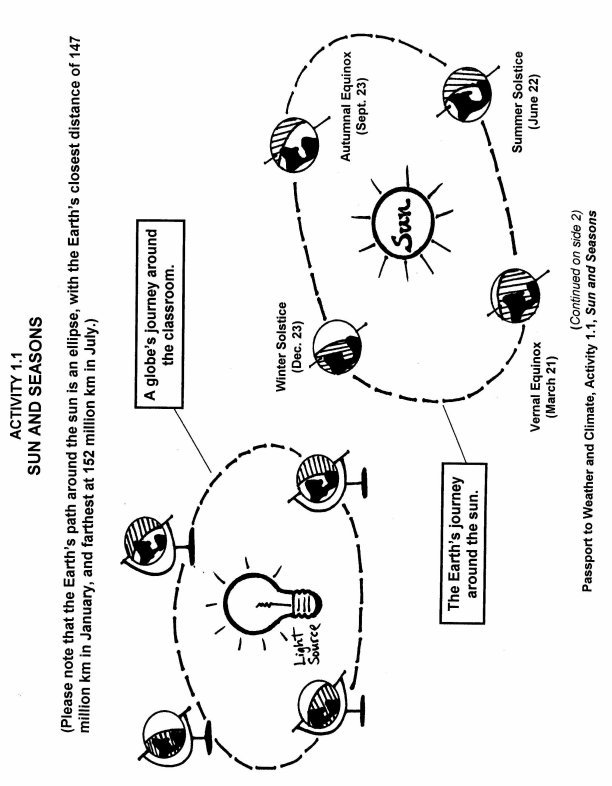
- Sun Earth and Seasons Worksheet
- Weather Air Masses and Fronts Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to the current atmospheric conditions at a specific place and time, such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity. It is short-term and can change quickly. On the other hand, climate is the average weather pattern in a specific region over a long period, typically 30 years or more. Climate encompasses the overall trends, variations, and averages of weather conditions in a particular area, providing a broader perspective on the expected weather patterns over time.
What factors determine weather patterns?
Weather patterns are primarily determined by factors such as temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind patterns, and the presence of atmospheric conditions like high or low-pressure systems. These factors interact to create variations in weather conditions such as temperature fluctuations, precipitation, and cloud formation, ultimately influencing the overall weather patterns in a specific region. Other factors like ocean currents, geography, and Earth's rotation also play a role in determining weather patterns.
How do air masses influence weather conditions?
Air masses influence weather conditions by bringing different temperature, pressure, and moisture content to an area. When an air mass moves into a region, it can affect the temperature, humidity, and likelihood of precipitation. The collision of different air masses can lead to the formation of weather systems such as fronts, which often result in changes in weather patterns like storms or precipitation. The characteristics of an air mass determine the type of weather that will prevail in a particular area, making air masses a key factor in weather forecasting and understanding local climate patterns.
What is the greenhouse effect and its impact on climate?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun, creating a warming effect on the planet. While this phenomenon is crucial for maintaining a habitable climate, human activities have significantly increased the concentration of these greenhouse gases, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect. This has resulted in global warming, causing shifts in climate patterns, rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems and biodiversity.
What causes seasonal variations in temperature and weather?
Seasonal variations in temperature and weather are primarily caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the Sun. As the Earth moves along its orbit, different parts of the planet receive different amounts of sunlight, leading to the changing seasons. This tilt causes the angle at which sunlight hits different regions to vary throughout the year, resulting in variations in temperature and weather patterns such as precipitation and wind.
How do natural disasters such as hurricanes and tornadoes form?
Natural disasters such as hurricanes and tornadoes form due to specific weather conditions. Hurricanes develop over warm ocean waters as low-pressure systems with strong winds that rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. Tornadoes, on the other hand, form within severe thunderstorms when warm, moist air collides with cold, dry air, creating instability and rotation in the atmosphere. Both hurricanes and tornadoes can cause significant damage and devastation when they make landfall.
What is the role of the jet stream in weather systems?
The jet stream is a fast-flowing, narrow air current located in the upper atmosphere. Its role in weather systems is significant as it helps to steer and influence the movement of weather systems around the globe. By dividing contrasting air masses, the jet stream acts as a boundary that can strengthen or weaken storms, as well as impact the intensity and direction of winds and precipitation. Its position and strength can affect the development and movement of weather patterns, making it a crucial factor in forecasting and understanding weather conditions.
How do ocean currents affect weather and climate?
Ocean currents play a significant role in influencing weather and climate by redistributing heat energy and regulating temperature variations across the Earth. Warm ocean currents can transfer heat from the equator towards the poles, affecting air temperatures and influencing weather patterns in coastal areas. Similarly, cold ocean currents can lead to cooler temperatures in adjacent regions. Additionally, ocean currents can impact the distribution of moisture in the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of weather systems such as storms and hurricanes. Overall, ocean currents play a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns by moderating temperatures, influencing precipitation, and driving weather conditions around the world.
What are the primary factors contributing to climate change?
The primary factors contributing to climate change are human activities, specifically the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat and lead to a warming of the Earth's climate. Deforestation, industrial processes, agriculture, and land use changes also play a significant role in increasing greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbating climate change.
How do scientists study and predict long-term climate trends?
Scientists study and predict long-term climate trends through a combination of methods, including analyzing historical data, observing current trends, and using computer models to simulate future climate scenarios. They study various aspects of the climate system, such as temperature, precipitation, and greenhouse gas concentrations, to identify patterns and trends over time. By understanding these factors and their interactions, scientists can make projections about how the climate may change in the future, helping to inform policies and mitigation efforts to address climate change.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments