Weather and Climate Worksheets 5th Grade
Weather and climate worksheets are a valuable tool for 5th-grade students to enhance their understanding of the subject. These worksheets provide a comprehensive breakdown of the various elements and processes involved in weather and climate. From studying the different types of clouds to exploring the factors that influence climate patterns, these worksheets not only engage students but also deepen their knowledge and appreciation of the fascinating world of weather and climate.
Table of Images 👆
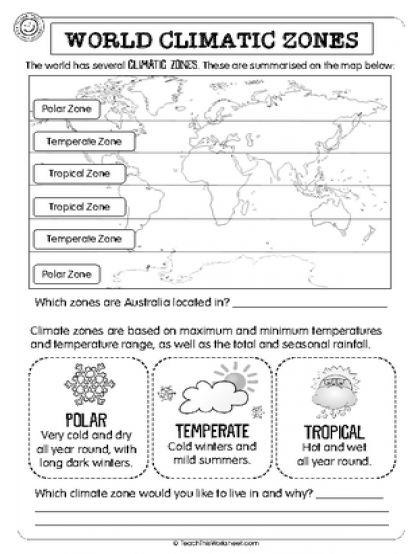
- World Climate Zones Worksheet
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
- 5th Grade Weather Worksheets
- 6th Grade Weather and Climate Worksheets
- 5th Grade Worksheets Reading a Weather Map
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
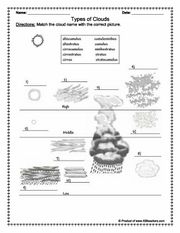
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
- 5th Grade Science Quiz Weather
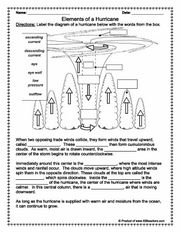
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
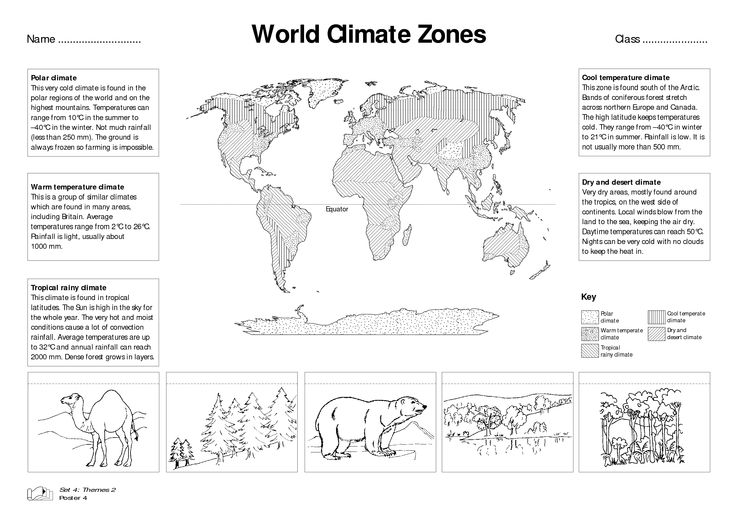
- World Climate Map Worksheet
- Free Printable Weather Word Search
- 5th Grade Science Weather Test
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
- Weather and Climate Worksheets
More 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Math Worksheets PrintableMultiplication Worksheets for 5th Grade
Constitution Worksheets for 5th Grade
5th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Coordinates Worksheets 5th Grade
United States Worksheets 5th Grade
5th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets Printable
Free Division Worksheets for 5th Grade
Long Division Decimal Worksheets 5th Grade
Coordinate Graphing Worksheets 5th Grade
What is weather?
Weather refers to the condition of the atmosphere at a specific place and time, including temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind speed, and cloud cover. It is influenced by factors such as sunlight, air pressure, and air masses, and is recorded and forecasted by meteorologists to help people plan for daily activities and respond to changing conditions.
What are the main factors that affect weather?
The main factors that affect weather include temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind direction and speed, and the presence of weather systems such as high and low-pressure systems, fronts, and air masses. These factors interact with each other to create various weather conditions such as rain, snow, storms, and sunny skies. Additionally, geographical features such as mountains, bodies of water, and urban areas can also influence local weather patterns.
How do temperature and humidity affect weather?
Temperature and humidity are key factors that influence weather. Temperature determines whether air will rise or sink, leading to the formation of different types of weather systems such as high or low-pressure areas. Humidity, on the other hand, affects the amount of moisture in the air, which can lead to the formation of clouds, precipitation, and fog. Together, temperature and humidity play a crucial role in shaping the weather patterns we experience on a day-to-day basis.
What is climate?
Climate refers to the long-term patterns and trends of weather conditions in a specific region, including temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind patterns. It typically describes the average weather conditions in a particular area over a period of time, such as decades or centuries, and is influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, proximity to bodies of water, and topography.
How is climate different from weather?
Climate refers to the long-term patterns and averages of temperature, humidity, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions in a specific region over an extended period of time, typically measured over decades. On the other hand, weather describes the short-term and localized atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation, that can change quickly and are measured over hours or days. In simple terms, weather is what you experience on a day-to-day basis whereas climate is the overall trend of weather patterns in a region over a longer period.
What are the main factors that determine climate?
The main factors that determine climate include the amount of solar radiation received, the Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun, the distribution of land and water on the planet, ocean currents, atmospheric circulation patterns, and greenhouse gas concentrations. These factors influence temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables that shape the long-term average conditions in a particular region.
How does latitude affect climate?
Latitude has a significant impact on climate as it determines the amount of sunlight an area receives. Areas closer to the equator, with lower latitudes, receive more direct sunlight and heat, resulting in warmer temperatures. In contrast, areas closer to the poles, with higher latitudes, receive less direct sunlight and heat, leading to colder temperatures. This leads to the formation of distinct climate zones, such as tropical, temperate, and polar climates, based on the latitude of a region.
How do ocean currents influence climate?
Ocean currents influence climate by redistributing heat around the globe. Warm ocean currents carry heat from the equator to higher latitudes, leading to milder climates in coastal regions. In contrast, cold ocean currents bring cooler temperatures to areas they flow through. Additionally, ocean currents impact weather patterns and can affect the intensity and frequency of storms. Overall, ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate by influencing temperature distribution and influencing weather systems.
How does the elevation of a location impact its climate?
The elevation of a location impacts its climate by affecting temperature, precipitation, and air pressure. Generally, as elevation increases, the air becomes cooler and drier, leading to lower temperatures and decreased humidity. This can result in significant differences in climate between locations at different elevations, even if they are close together geographically. Additionally, the change in air pressure with elevation can also influence weather patterns and atmospheric conditions.
How do prevailing winds affect weather and climate?
Prevailing winds, which are winds that consistently blow in a particular direction over a certain location, play a crucial role in shaping weather and climate. These winds help transport moisture and air masses, influencing temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns across regions. For example, winds blowing from oceans can bring moisture and moderate temperatures, while winds descending from mountains can cause dry and warm conditions in the leeward side. Ultimately, prevailing winds contribute to the overall climate of an area by determining the distribution of heat and moisture.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments