Wavelength Problems and Answers Worksheet
Are you a student or teacher searching for an effective way to strengthen your understanding of wavelength problems? Look no further! This wavelength problems and answers worksheet is designed to provide you with a valuable resource for practice and consolidation. Whether you are studying physics, engineering, or any other subject that involves wave phenomena, this worksheet will guide you through various problems and help you develop a solid grasp of this important concept.
Table of Images 👆
- Speed Frequency Wavelength Worksheet Answers
- Speed Frequency Wavelength Worksheet Answers
- Speed Wavelength Frequency Energy Worksheet
- Wave Speed Frequency Wavelength Worksheet
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Speed Wavelength Frequency Energy Worksheet Answers
- Energy Frequency and Wavelength Worksheet
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Light Energy Wavelength and Frequency Worksheet Answers Key
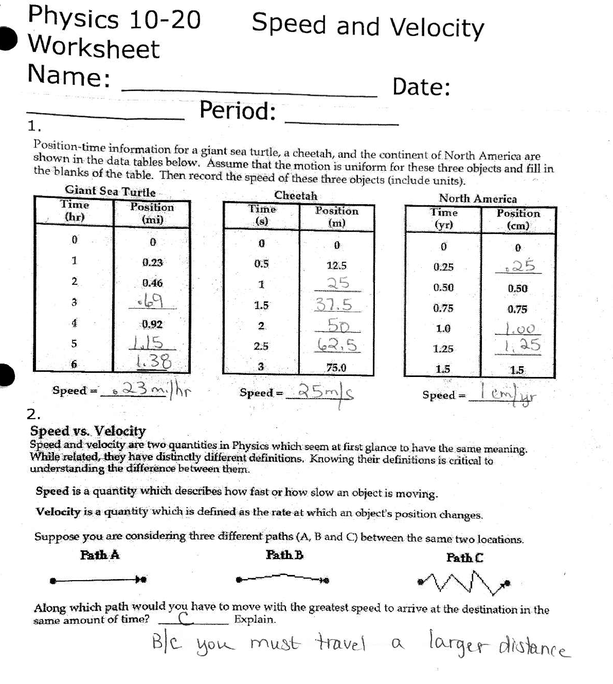
- Speed and Velocity Worksheet Answer Key
- Electromagnetic Radiation Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Frequency
- 17.1 Mechanical Waves Worksheet Answers
- Lab Equipment Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Waves Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Problems Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
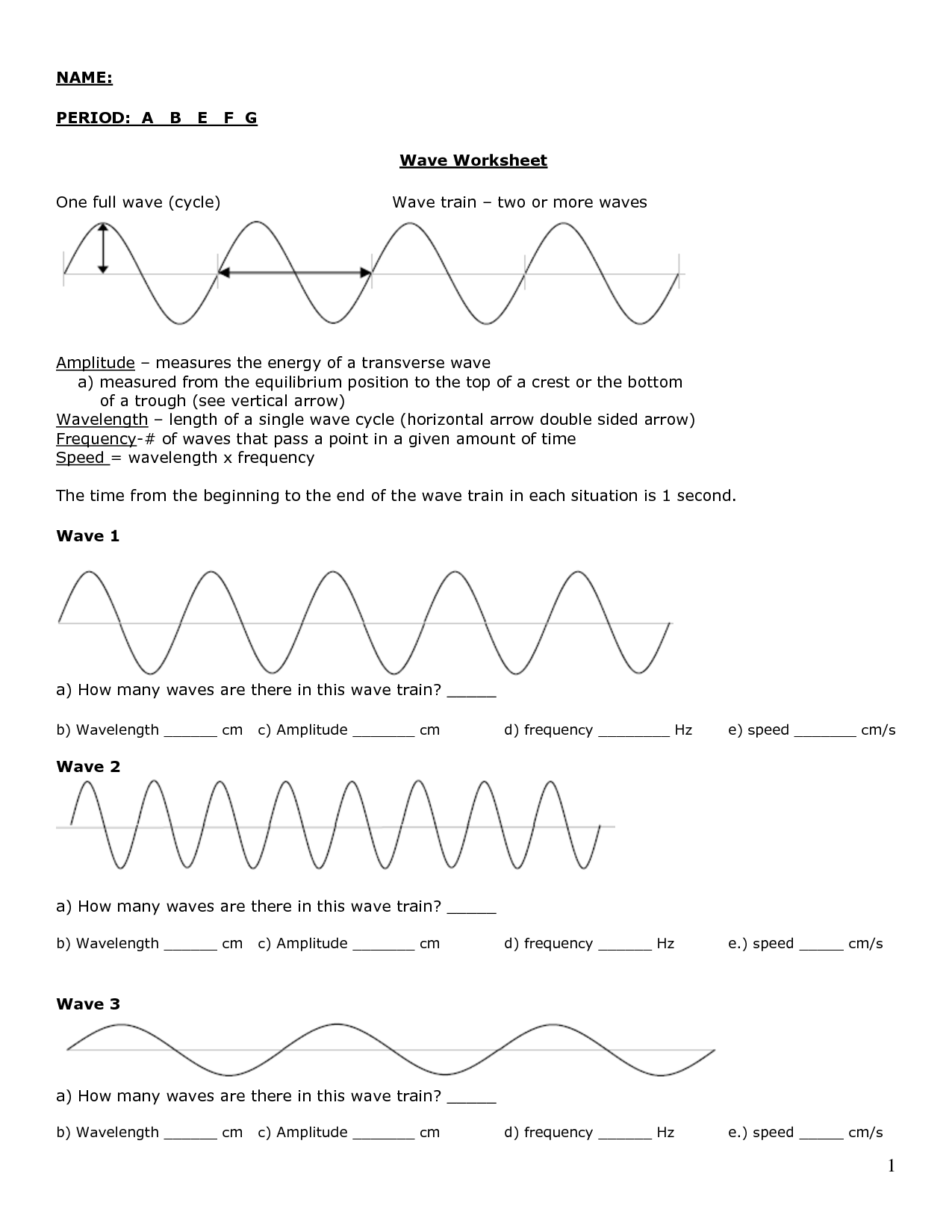
What is a wavelength?
A wavelength is the distance between successive points of a wave that are in phase, such as the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs. It is commonly used to describe the length of a specific wave, such as in the electromagnetic spectrum or sound waves.
How is wavelength measured?
Wavelength can be measured by determining the distance between two consecutive points in a wave that are in phase, such as two peaks or two troughs. This distance is typically measured in meters, nanometers, or other units depending on the scale of the wave being analyzed. Scientists often use techniques like interferometry, diffraction, or spectroscopy to accurately measure wavelengths in various electromagnetic or mechanical waves.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
The relationship between wavelength and frequency is inversely proportional. This means that as the wavelength of a wave increases, its frequency decreases, and vice versa. Mathematically, this relationship is described by the equation: speed of a wave = wavelength x frequency. So, when one parameter changes, the other changes such that their product (speed of the wave) remains constant.
How does wavelength affect the speed of a wave?
The wavelength of a wave does not affect its speed. The speed of a wave is determined by the medium through which it is traveling. In a given medium, the speed of the wave remains constant regardless of changes in wavelength. However, wavelength does affect other properties of a wave, such as its frequency and energy.
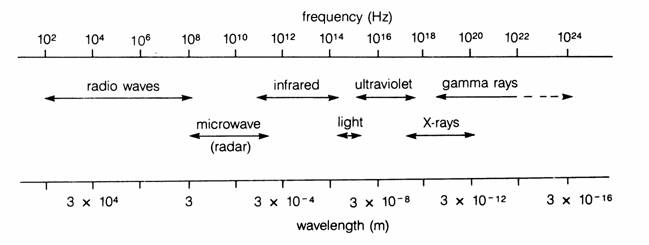
What are the different types of waves that can have a wavelength?
There are various types of waves that can have a wavelength, including electromagnetic waves (such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays), sound waves, water waves, seismic waves, and even brain waves (such as alpha, beta, theta, and delta waves). Each of these waves has a specific wavelength associated with its frequency and speed of propagation through a medium.
How do you calculate the wavelength of a wave?
To calculate the wavelength of a wave, you need to use the formula: wavelength (?) = speed of the wave (v) / frequency of the wave (f). Firstly, determine the speed of the wave, which could be the speed of light in vacuum (c = 3 x 10^8 m/s) for electromagnetic waves, or the speed of sound in a medium for acoustic waves. Then, find the frequency of the wave in hertz (Hz). Finally, divide the speed of the wave by its frequency to calculate the wavelength in meters.
Can the wavelength of a wave change in different mediums? If yes, how?
Yes, the wavelength of a wave can change when it enters different mediums. This is due to a phenomenon called refraction, where the speed of the wave changes as it travels from one medium to another with a different density. This change in speed causes the wavelength to either increase or decrease, depending on the change in the medium's properties.
What is the significance of wavelength in determining the color of light?
The wavelength of light is significant in determining its color because different wavelengths correspond to different colors in the visible spectrum. Shorter wavelengths are associated with colors like blue and violet, while longer wavelengths are associated with reds and oranges. When light enters our eyes, the different wavelengths stimulate our color receptors, allowing us to perceive various colors. This relationship between wavelength and color is foundational in understanding the nature of light and how we perceive the world around us.
How does the wavelength of a wave affect its energy?
The wavelength of a wave is inversely proportional to its energy. This means that as the wavelength of a wave decreases, its energy increases, and vice versa. In other words, shorter wavelengths have higher energy, while longer wavelengths have lower energy. This relationship is described by the equation E = h / ?, where E is the energy of the wave, h is Planck's constant, and ? is the wavelength of the wave.
How can wavelength be used in practical applications, such as in telecommunications or medical imaging?
Wavelength can be used in practical applications such as telecommunications by enabling the transmission of information in the form of data through fiber optic cables. By using different wavelengths of light, multiple streams of data can be sent simultaneously, increasing the overall bandwidth and transmission capacity of the network. In medical imaging, different wavelengths of energy, such as X-rays or ultrasound, can be used to create detailed images of the body's internal structures. By varying the wavelength of the energy source, different tissues can be highlighted or visualized for diagnostic purposes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments