Verb Worksheets for 6th Grade
Are you a 6th-grade teacher or parent looking for helpful resources to reinforce verb skills with your students? Well, you're in luck! In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets as a tool to enhance understanding and proficiency in verbs. Worksheets can provide structured practice that engages students while targeting specific verb concepts, making learning enjoyable and effective.
Table of Images 👆
- Linking Verbs Worksheet 6th Grade
- Subject Verb Agreement Worksheets
- Past Tense Verb Worksheet Grade 2
- Dialogue Worksheet Grade 2
- 3rd Grade Preposition and Prepositional Phrases Worksheet
- Subject and Predicate Worksheets Second Grade
- Subject and Predicate Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Crossword Puzzle Past Present and Future
- Collective Noun Worksheet 6th Grade
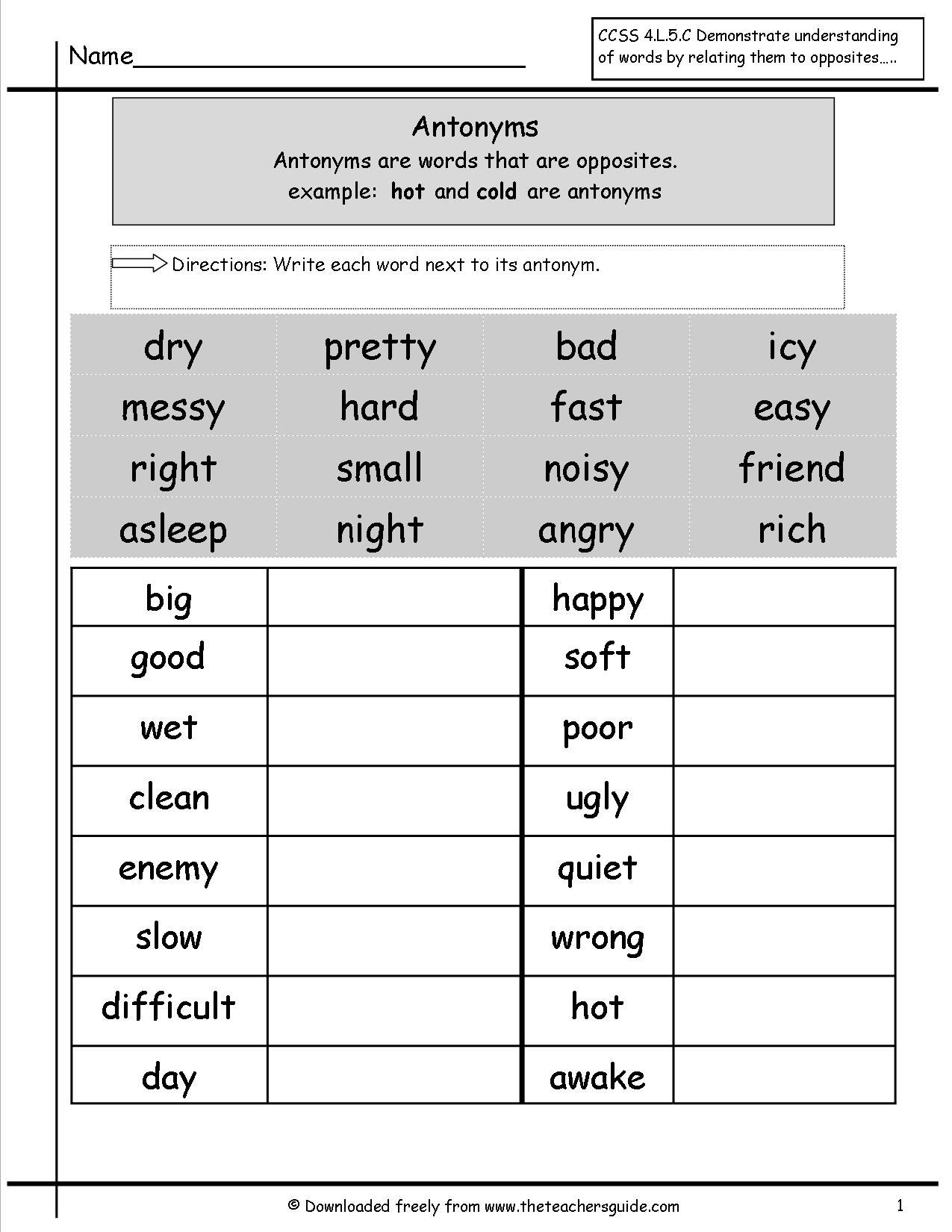
- Synonyms and Antonyms Worksheets
- Adjectives and Adverbs Worksheets 6th Grade
- Haunted House Adjectives
- Fun Long Vowel Worksheet
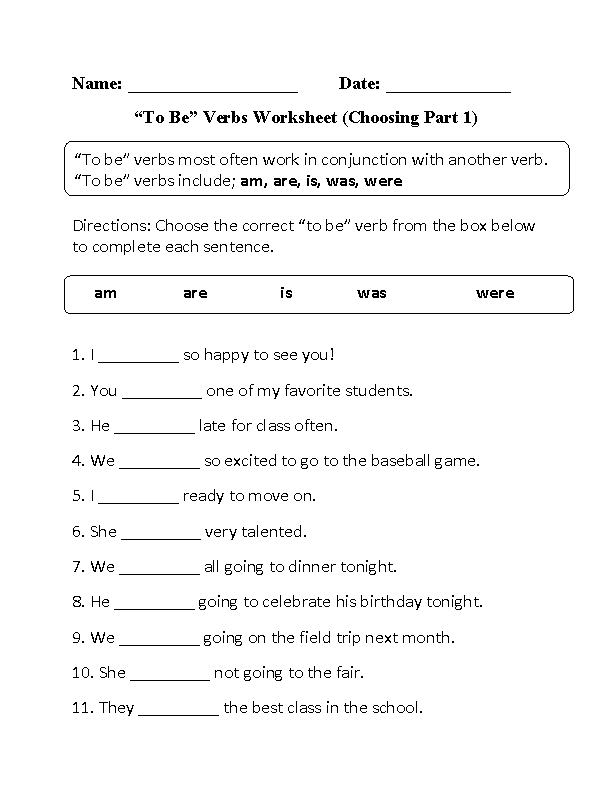
- Verb Be Worksheets
- Singular Possessive Nouns Worksheet
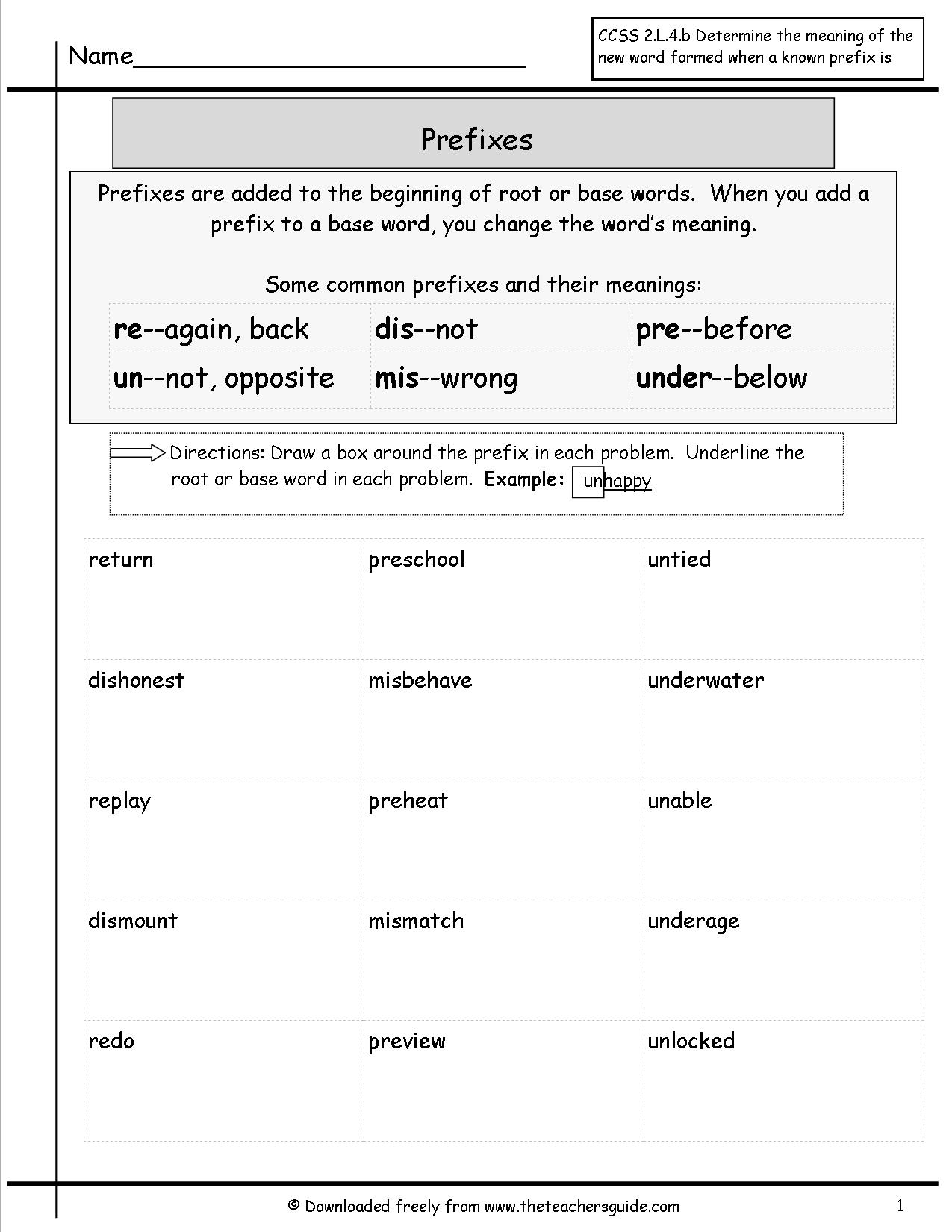
- ROOT-WORDS Prefixes Suffixes Worksheets
- Past Tense for Irregular Verbs Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Worksheets Free 6th Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a verb?
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. It is a fundamental component of sentences and helps to convey the meaning of the sentence by describing what the subject is doing or the state it is in. Verbs can be in different tenses, such as past, present, or future, and can also be conjugated to match the subject in terms of number and person.
What is the difference between a regular verb and an irregular verb?
A regular verb follows a predictable and consistent pattern when conjugated in different tenses, typically by adding -ed to the base form to form the past tense. In contrast, an irregular verb does not follow a regular pattern when conjugated and may change in spelling or form completely when changing tenses, such as "go" changing to "went" in the past tense.
Can a verb function as a noun in a sentence? Give an example.
Yes, a verb can function as a noun in a sentence. This is known as a gerund. For example, in the sentence "Swimming is good exercise," the word "swimming" is a gerund that functions as a noun, representing the action of swimming as the subject of the sentence.
What is a linking verb, and how does it connect the subject to the rest of the sentence?
A linking verb is a verb that connects the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, which provides more information about the subject. Linking verbs do not show action but rather link the subject to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that renames or describes the subject. Examples of linking verbs include "is," "become," "seem," and "appear." The linking verb essentially acts as a bridge that connects the subject to the complement, helping to establish a relationship between the two parts of the sentence.
Identify and list three examples of action verbs.
jump, run, swim
How does the tense of a verb change the meaning of a sentence?
The tense of a verb indicates the time at which an action occurs. It can significantly change the meaning of a sentence by conveying whether the action is happening in the past, present, or future. For example, "She sang" indicates the action happened in the past, while "She sings" indicates it is currently happening. Choosing the appropriate tense is crucial for accurately expressing the timeframe of an action and conveying the intended message of the sentence.
Explain the concept of subject-verb agreement and provide an example.
Subject-verb agreement is a grammatical rule that states that the subject and verb in a sentence must agree in number (singular or plural). This means that a singular subject requires a singular verb, and a plural subject requires a plural verb. For example, in the sentence "The cat is sleeping," the singular subject "cat" agrees with the singular verb "is.
What are transitive and intransitive verbs, and how do they differ?
Transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning, while intransitive verbs do not need a direct object. In other words, transitive verbs act upon something or someone, whereas intransitive verbs do not transfer the action to an object. For example, in the sentence "She ate the cake," "ate" is a transitive verb because it needs the direct object "cake" to make sense, whereas in the sentence "He laughed," "laughed" is an intransitive verb because it does not require a direct object.
How can helping verbs be used to create different verb tenses?
Helping verbs are used in combination with main verbs to create different verb tenses. For example, the helping verb "will" is used with the main verb to form the future tense (e.g., "I will eat"), while the helping verb "was" is used to form the past continuous tense (e.g., "I was eating"). By adding specific helping verbs to main verbs, different tenses can be expressed in English grammar.
Describe the process of changing a sentence from active voice to passive voice using verbs.
To change a sentence from active voice to passive voice using verbs, you need to switch the positions of the subject and the object in the sentence. The object becomes the new subject, while the original subject is either omitted or placed at the end of the sentence with the preposition "by." Additionally, the main verb needs to be changed to its passive form by adding a form of the verb "to be" followed by the past participle of the main verb. This transformation shifts the focus from the doer of the action (subject) to the receiver of the action (object) in the sentence.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments