Star Formation Worksheet
Star formation is an exciting and fundamental concept in astronomy that captivates the minds of both beginners and enthusiasts alike. Understanding the intricacies of how stars form can be a challenging yet rewarding journey. If you're eager to delve into the fascinating world of star formation, then this worksheet is perfect for you. Designed to cater to both students and astronomy lovers, this worksheet will guide you through the essential concepts and processes involved in the birth of stars.
Table of Images 👆
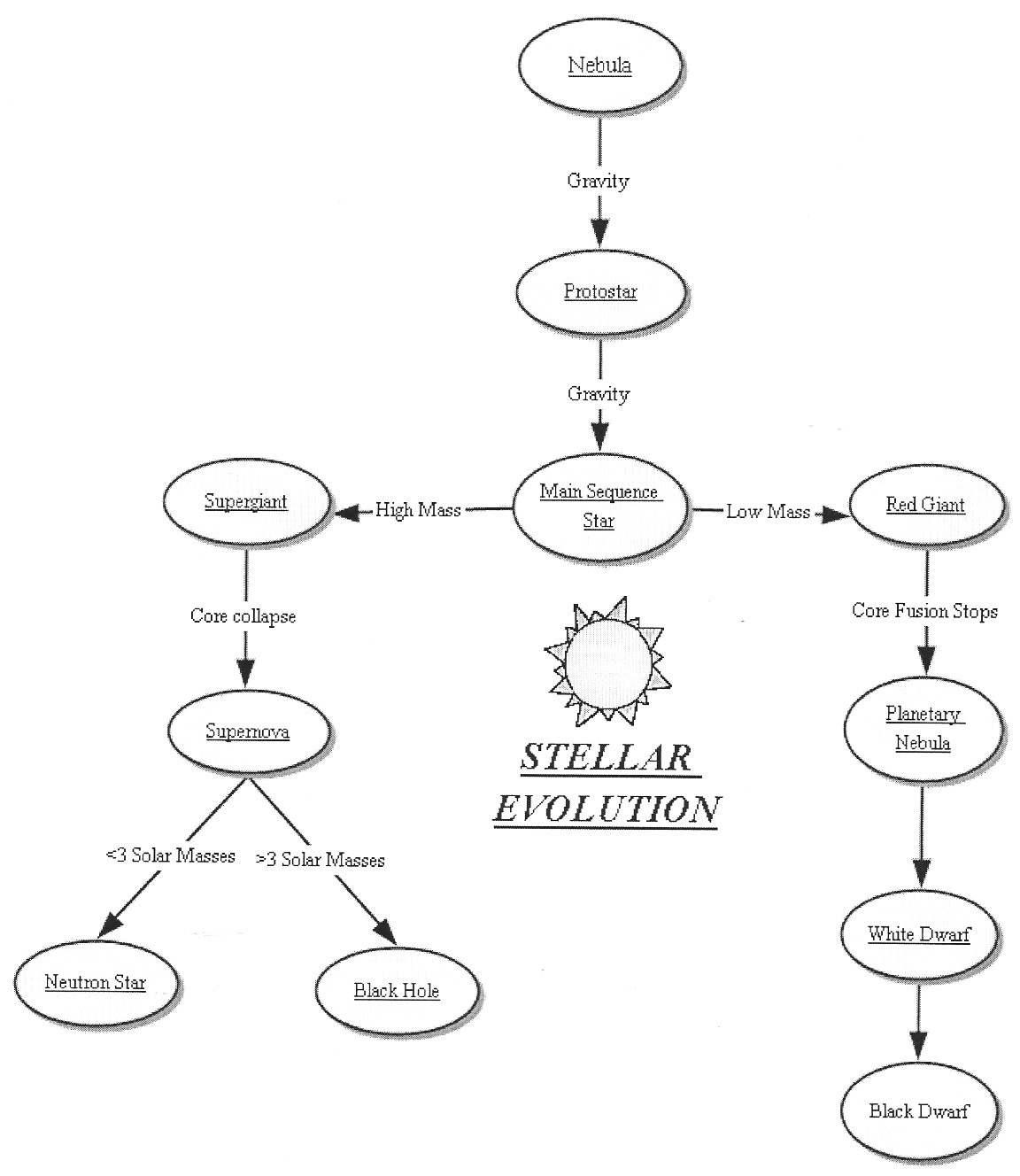
- Star Stellar Evolution Stages Chart
- Evolution of Stars Worksheet Answers
- Star Life Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Printable Star Shape Worksheets
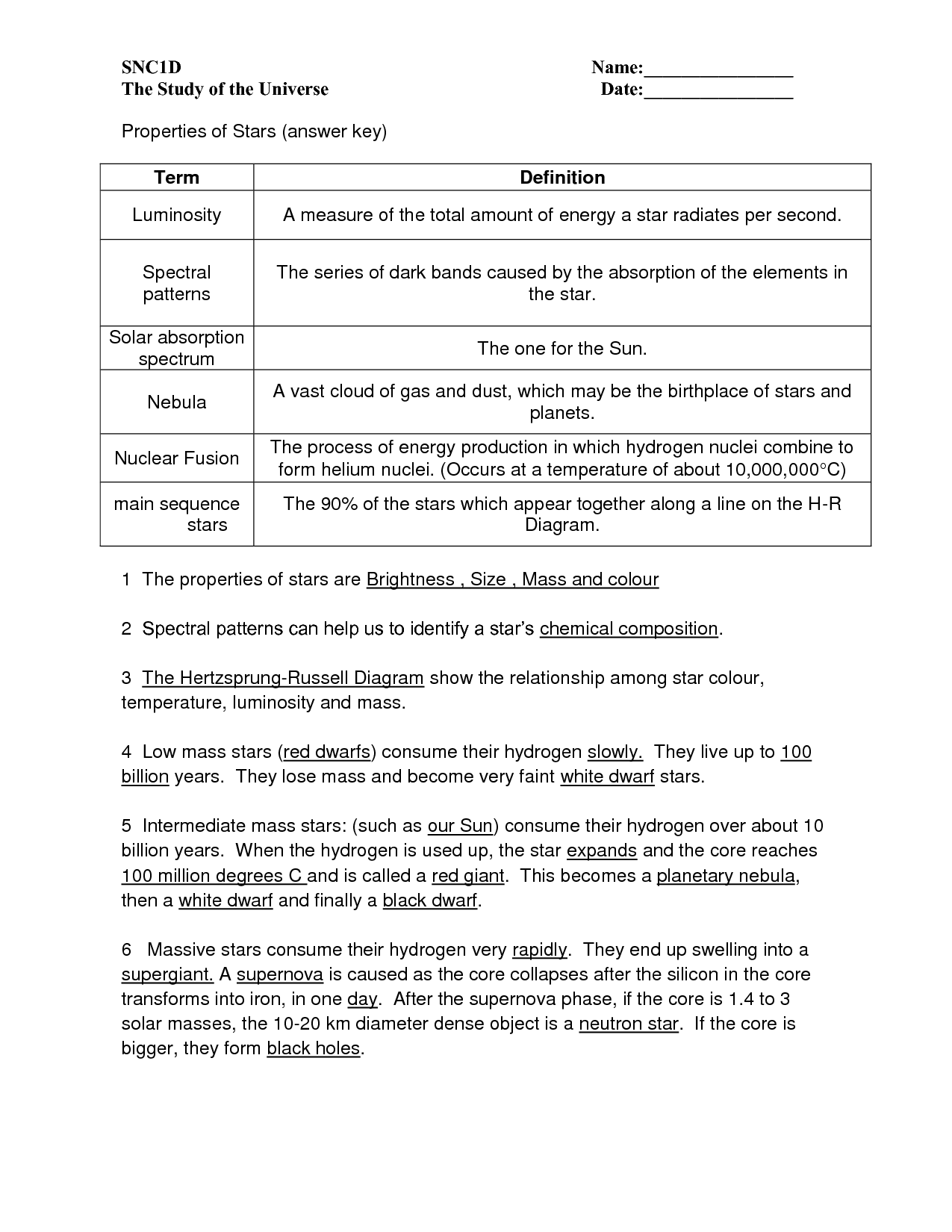
- Stars and the HR Diagram Worksheet Answer Key
- Handwriting Practice Writing Letters
- Stars Math Worksheet Count
- Sun Moon Stars Worksheets
- Scientific Notation Standard Form Worksheet
- Lump Sum Promissory Note Form Template Free
- Evolution Concept Map Worksheet
- Star Tracing Worksheets
- Star Shape Tracing Worksheet
- Evolution of Stars Worksheet
- Printable Polygon Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is star formation?
Star formation is the process by which molecular clouds of gas and dust collapse under their own gravity, leading to the birth of new stars. As the cloud collapses, it heats up and becomes denser, eventually reaching temperatures and pressures high enough for nuclear fusion to begin in its core, which is the process that powers a star. The newly formed star will then shine and evolve over millions to billions of years, depending on its mass.
What are the main components needed for star formation?
The main components needed for star formation are a large cloud of gas and dust, typically made up of hydrogen and helium, and the force of gravity. The cloud needs to be dense enough to allow gravity to overcome the outward pressure and collapse in on itself, leading to the formation of a dense core. As the core contracts and heats up, nuclear fusion reactions begin, producing energy and causing the core to shine brightly as a new star.
How do clouds of gas and dust play a role in star formation?
Clouds of gas and dust play a crucial role in star formation by providing the raw materials needed for the process. Gravity causes these clouds to condense and collapse, increasing the density and temperature at the core. As the core becomes more compact and dense, it eventually reaches a point where nuclear fusion reactions can occur, leading to the birth of a new star. The gas and dust in the cloud also help to regulate the rate of star formation by influencing the size and mass of the resulting stars.
What is the process of gravitational collapse and how does it contribute to star formation?
Gravitational collapse is the process in which a cloud of gas and dust collapses under its own gravity, leading to the formation of a star. As the cloud collapses, it heats up and the pressure and temperature at its center increase, eventually triggering nuclear fusion and igniting as a star. The collapse of material within the cloud also leads to the formation of a protostar, which continues to accrete more material until it reaches a stable state. Overall, gravitational collapse is essential for the formation of stars because it concentrates matter and initiates the processes that allow a star to form and shine.
What are protostars and how do they form?
Protostars are young, forming stars that are in the earliest stage of their lifecycle. They form from collapsing clouds of gas and dust in interstellar space due to gravitational forces overcoming outward gas pressure. As the cloud collapses, it heats up and becomes more dense, eventually leading to the formation of a protostar. These protostars continue to accrete matter from their surrounding disk, eventually becoming a fully-fledged star through nuclear fusion in their cores.
How does the temperature and pressure inside a protostar influence its evolution?
The temperature and pressure inside a protostar play crucial roles in its evolution. As the protostar compresses due to gravitational forces, the temperature and pressure increase, eventually leading to nuclear fusion in the star's core once it reaches the necessary conditions. This fusion process allows the star to generate energy, which counteracts gravitational collapse, maintaining stability and leading to its evolution into a main-sequence star. Temperature and pressure variations during this process also impact the star's size, luminosity, and overall lifespan.
What is the role of nuclear fusion in star formation?
Nuclear fusion is the process that powers stars, including during their formation. As a star forms from a cloud of gas and dust, gravity causes the core to become increasingly dense and hot. Eventually, the pressure and temperature in the core become high enough to ignite nuclear fusion, primarily converting hydrogen into helium. This fusion process releases energy in the form of light and heat, which counteract the force of gravity trying to pull the star's material inwards. Thus, nuclear fusion plays a crucial role in both initiating and sustaining the energy output of a star during its formation.
What factors determine the final size and mass of a star?
The final size and mass of a star are determined primarily by the amount of matter present in a molecular cloud that collapses to form the star. Factors such as the initial size of the cloud, the density of the material, and the rate of rotation can all influence the size and mass of the resulting star. Additionally, the composition of the cloud, particularly the abundance of heavy elements, can affect the final characteristics of the star.
How do stars reach the main sequence stage?
Stars reach the main sequence stage by undergoing a process known as stellar formation. This occurs when a cloud of gas and dust in space collapses under its own gravity, causing the center to become hotter and denser until nuclear fusion reactions begin, primarily converting hydrogen into helium. Once the star's core reaches a temperature and pressure where nuclear fusion can sustain itself, the star settles into the main sequence stage of its life cycle, where it will remain stable for the majority of its lifespan.
What happens to the remaining gas and dust after a star is formed?
The remaining gas and dust after a star is formed can either remain in the form of a circumstellar disk around the star, eventually forming into planets and other celestial bodies, or it can be blown away into space by powerful stellar winds or a supernova explosion. This gas and dust can be recycled into new stars and planetary systems, contributing to the ongoing cycle of star formation in the universe.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments