Solubility Rules Worksheet Answers
Are you a chemistry student struggling to understand the concept of solubility rules? Look no further! This worksheet provides clear and concise explanations, along with answers, to help you master the topic. Whether you're a high school student or a college-level learner, this resource will guide you through the complexities of solubility rules with ease.
Table of Images 👆
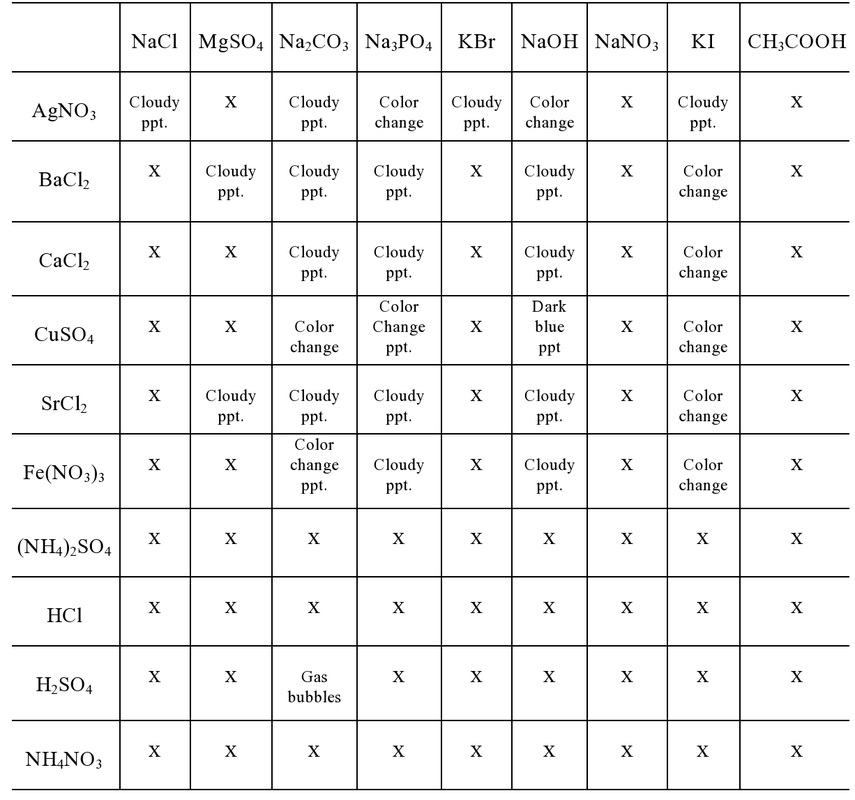
- Precipitation Reactions and Solubility Rules Lab Answers
- Worksheet Solubility Rules Chart
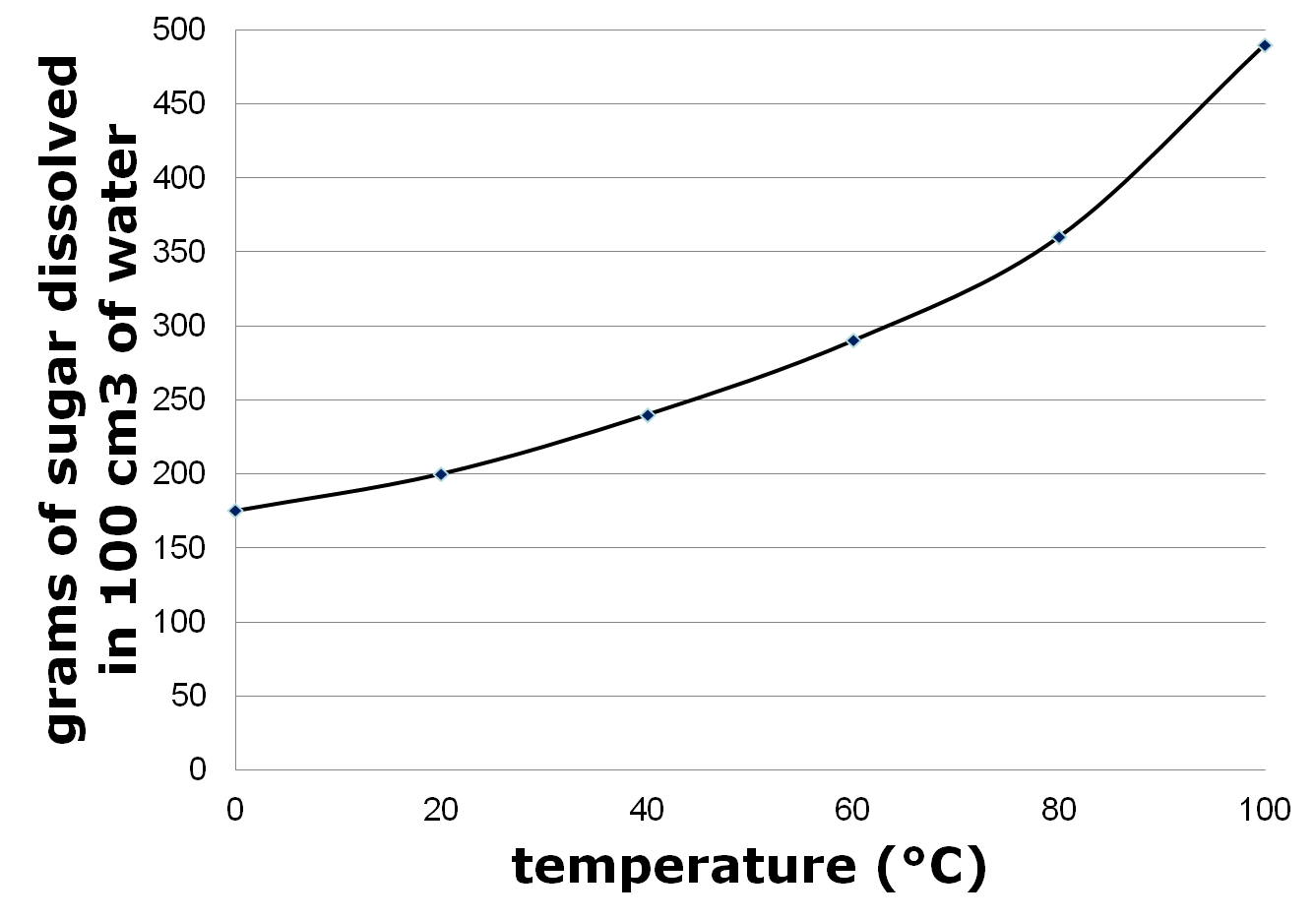
- Graph of Sugar Solubility in Water
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
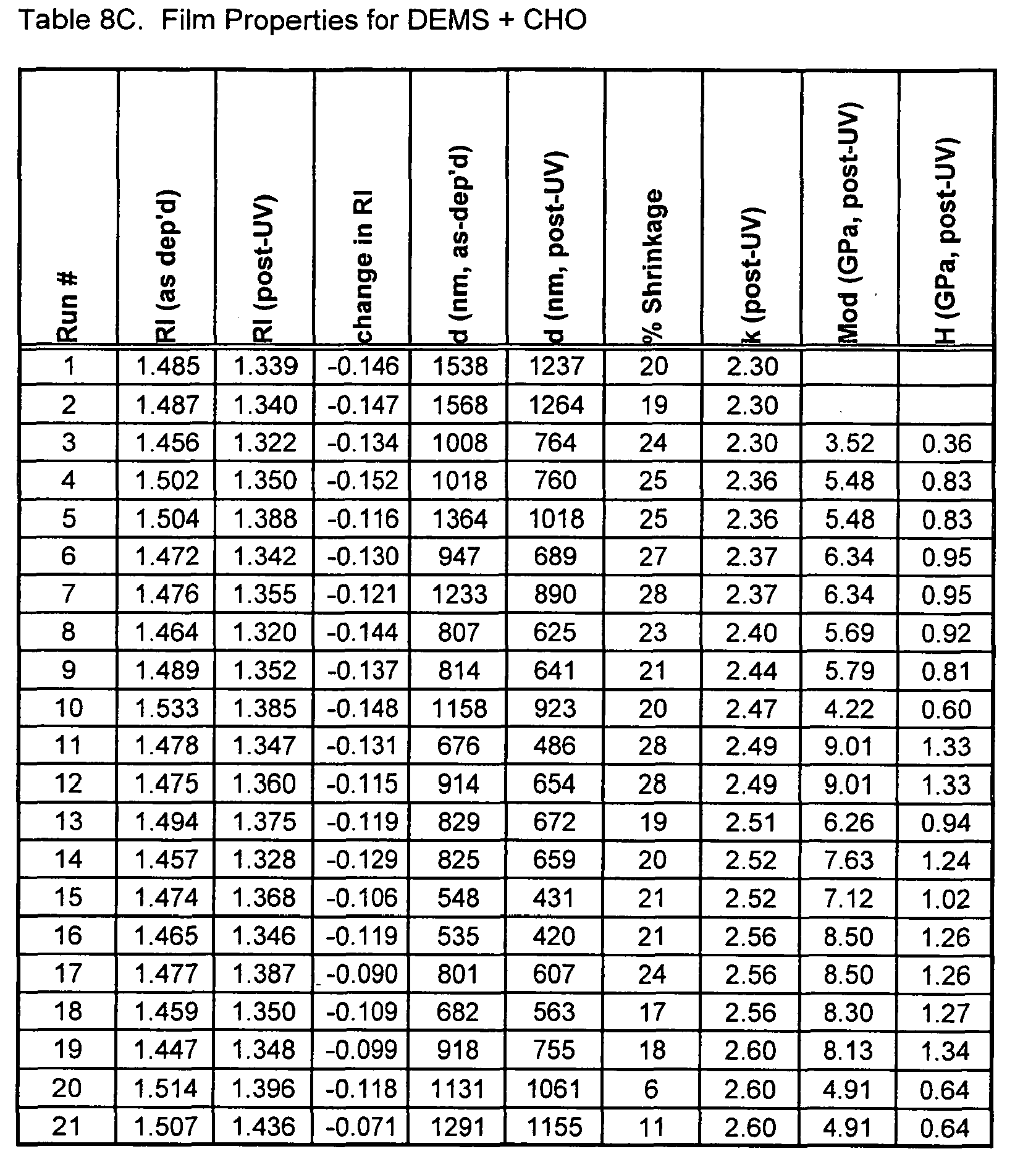
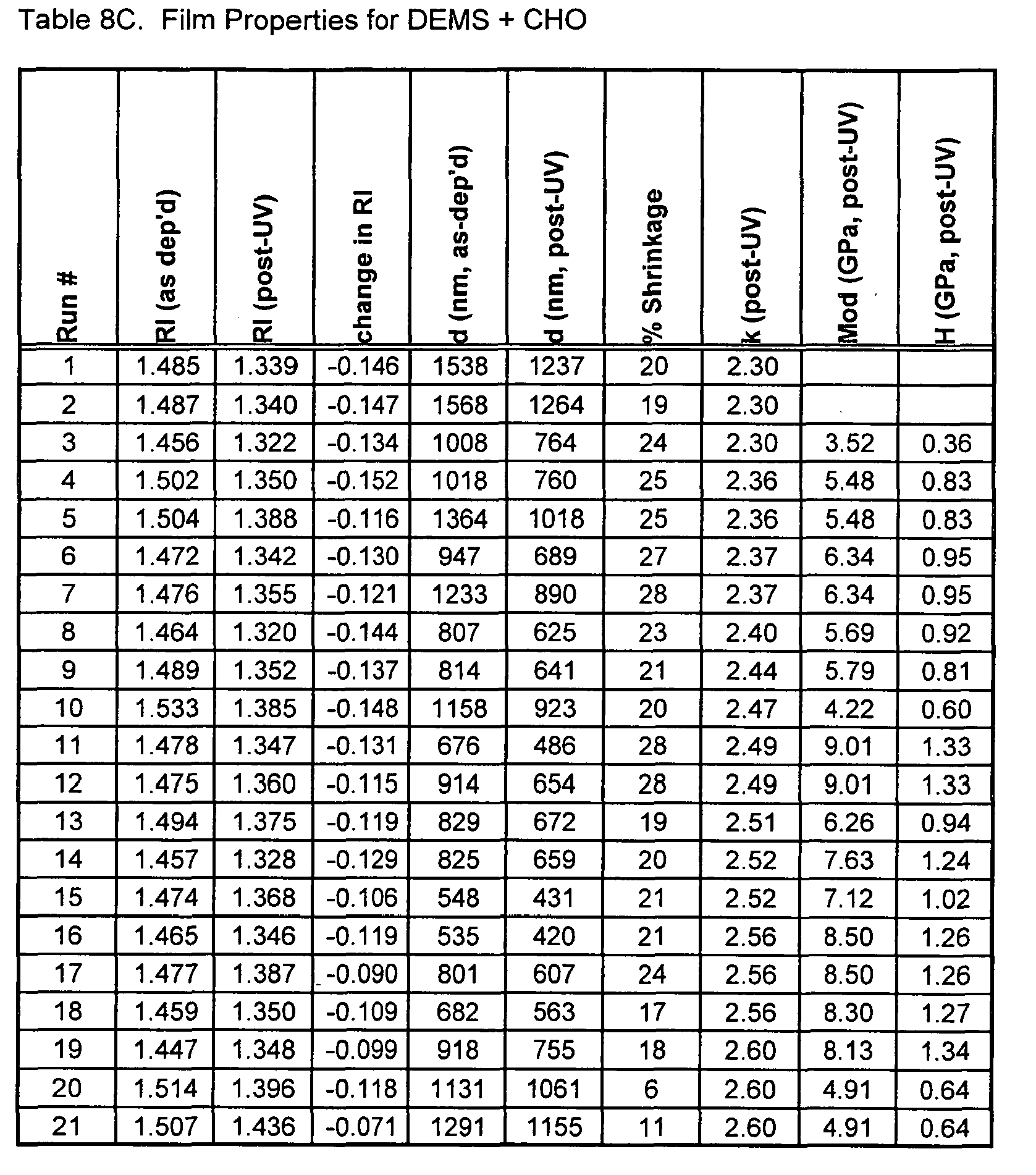
- Dielectric Constant Tables
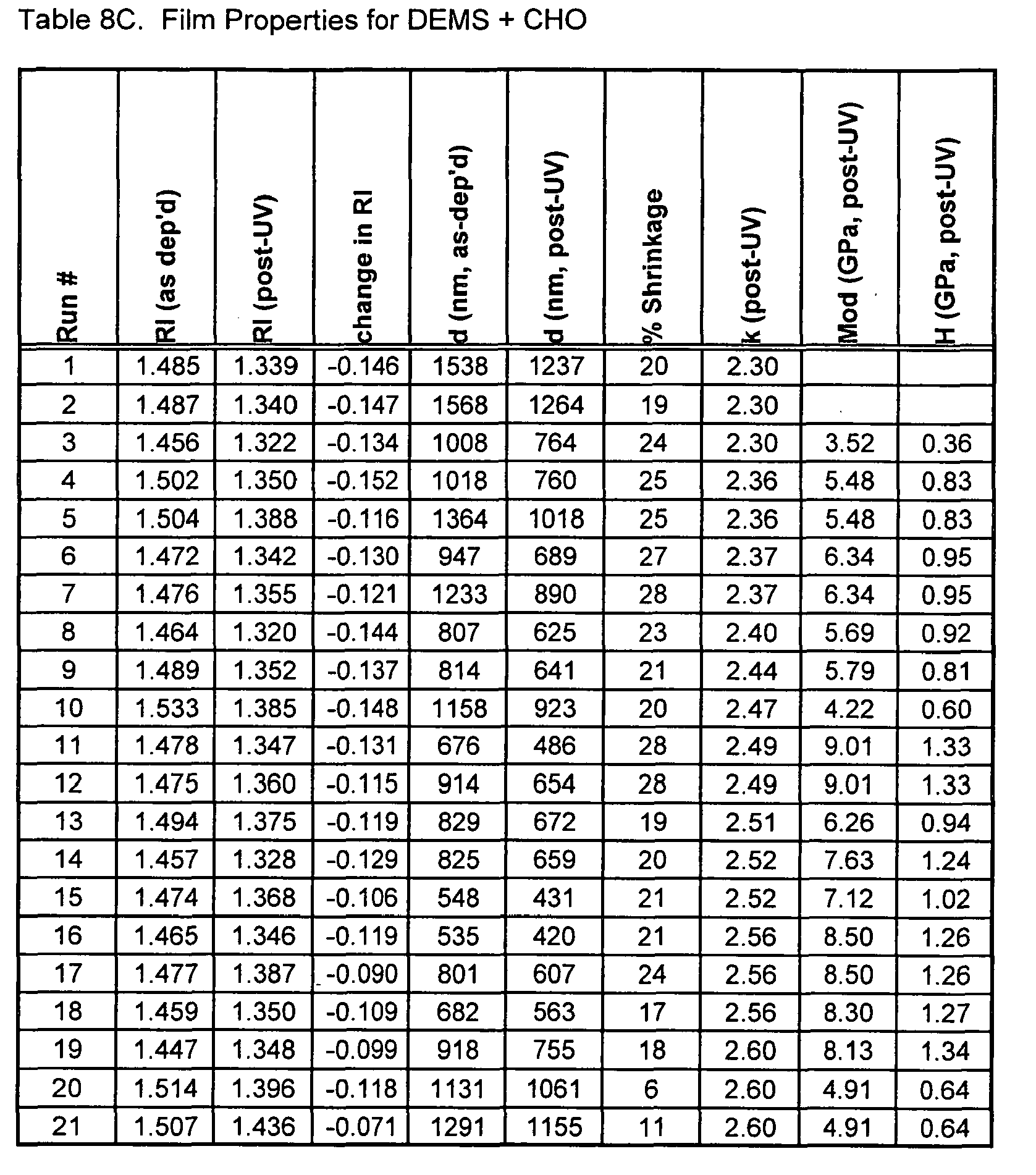
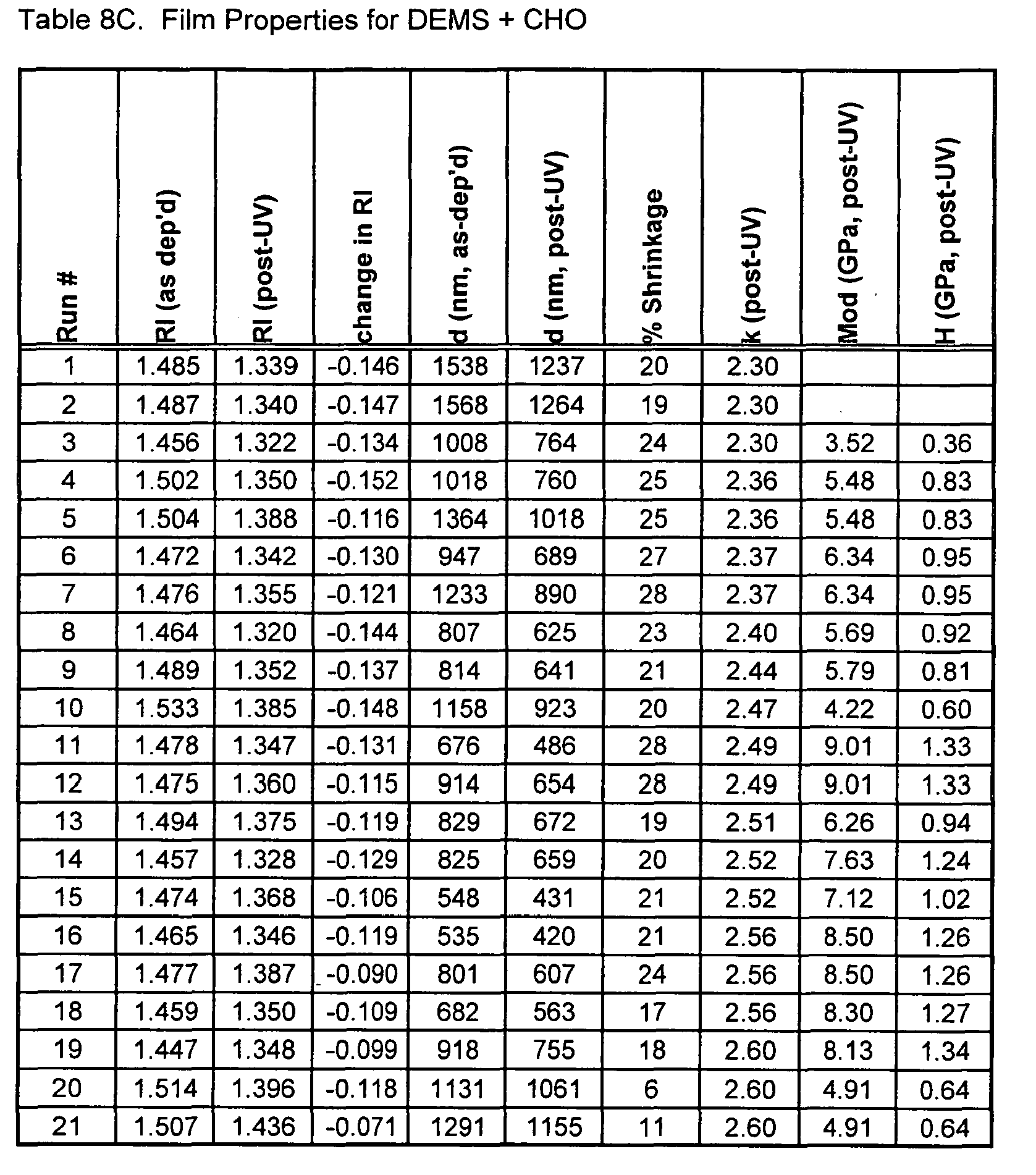
- Dielectric Constant Tables
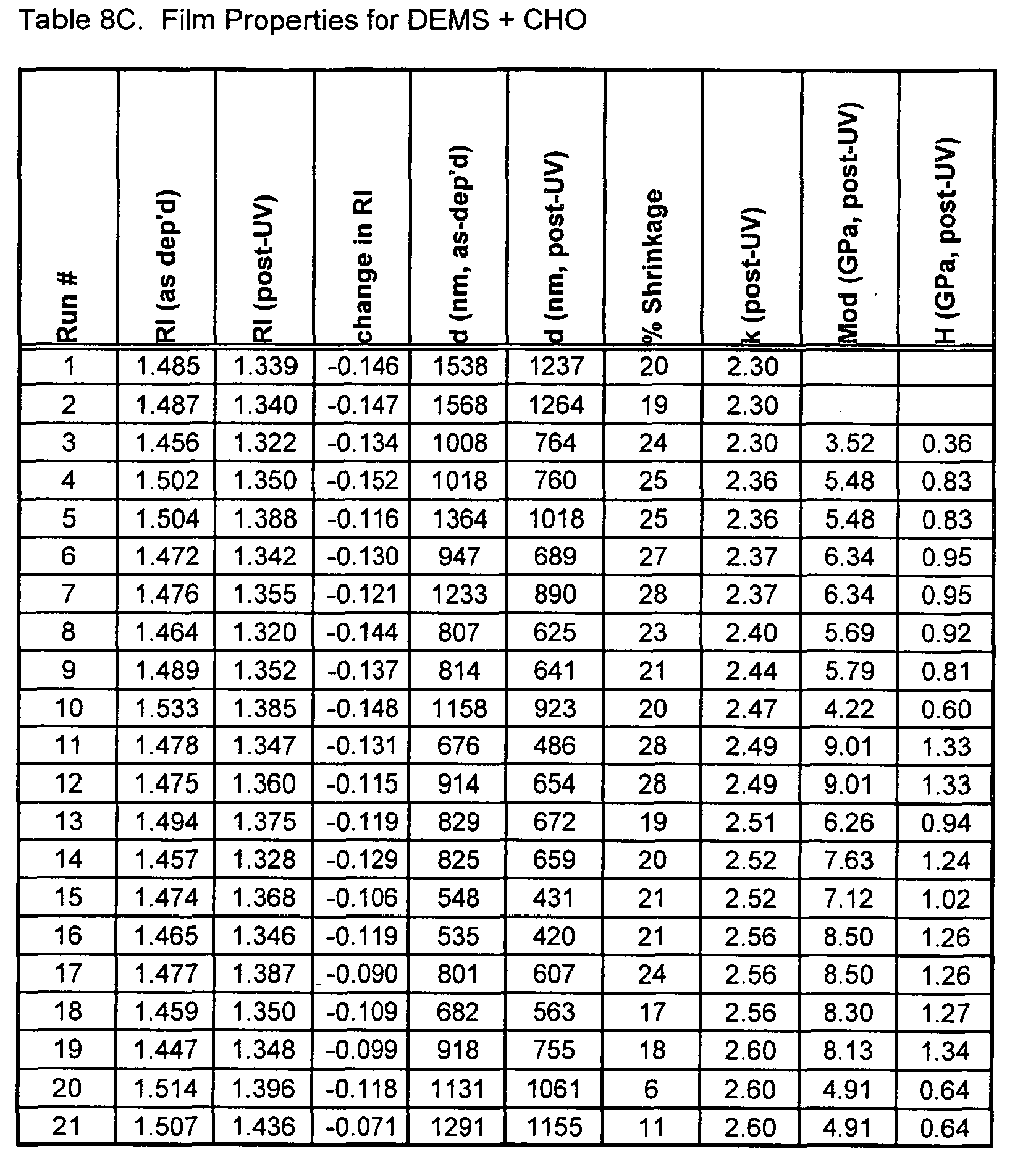
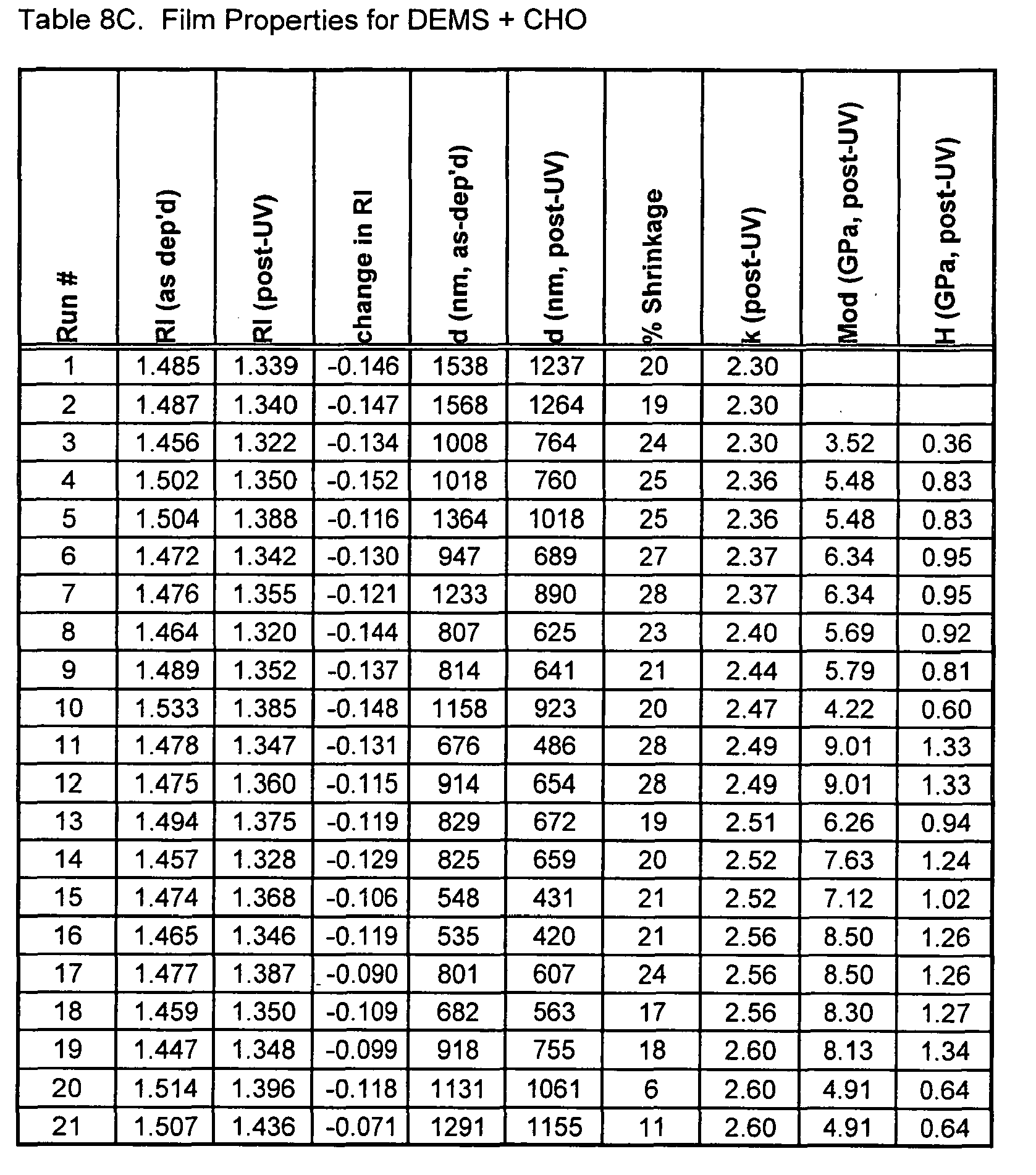
- Dielectric Constant Tables
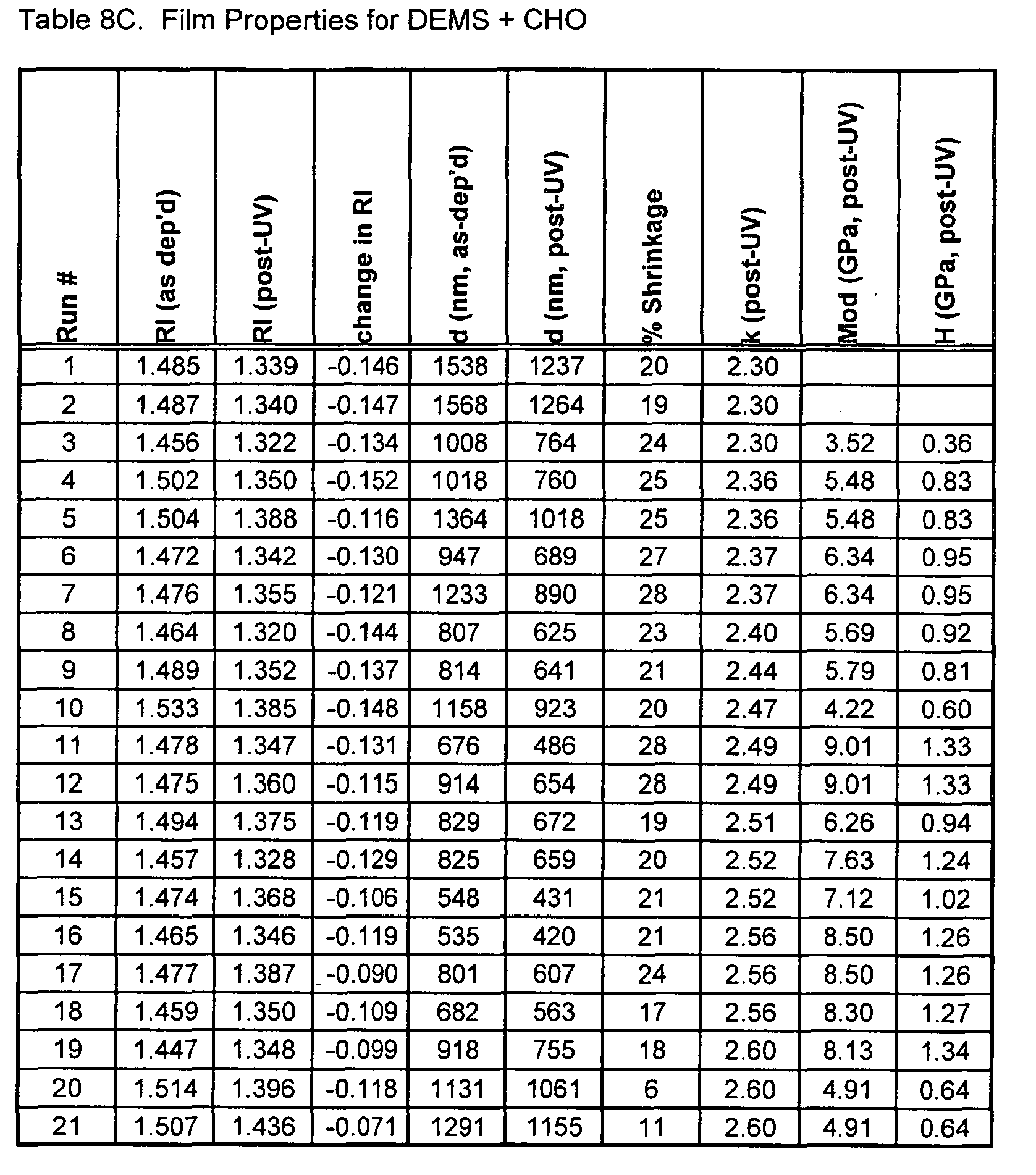
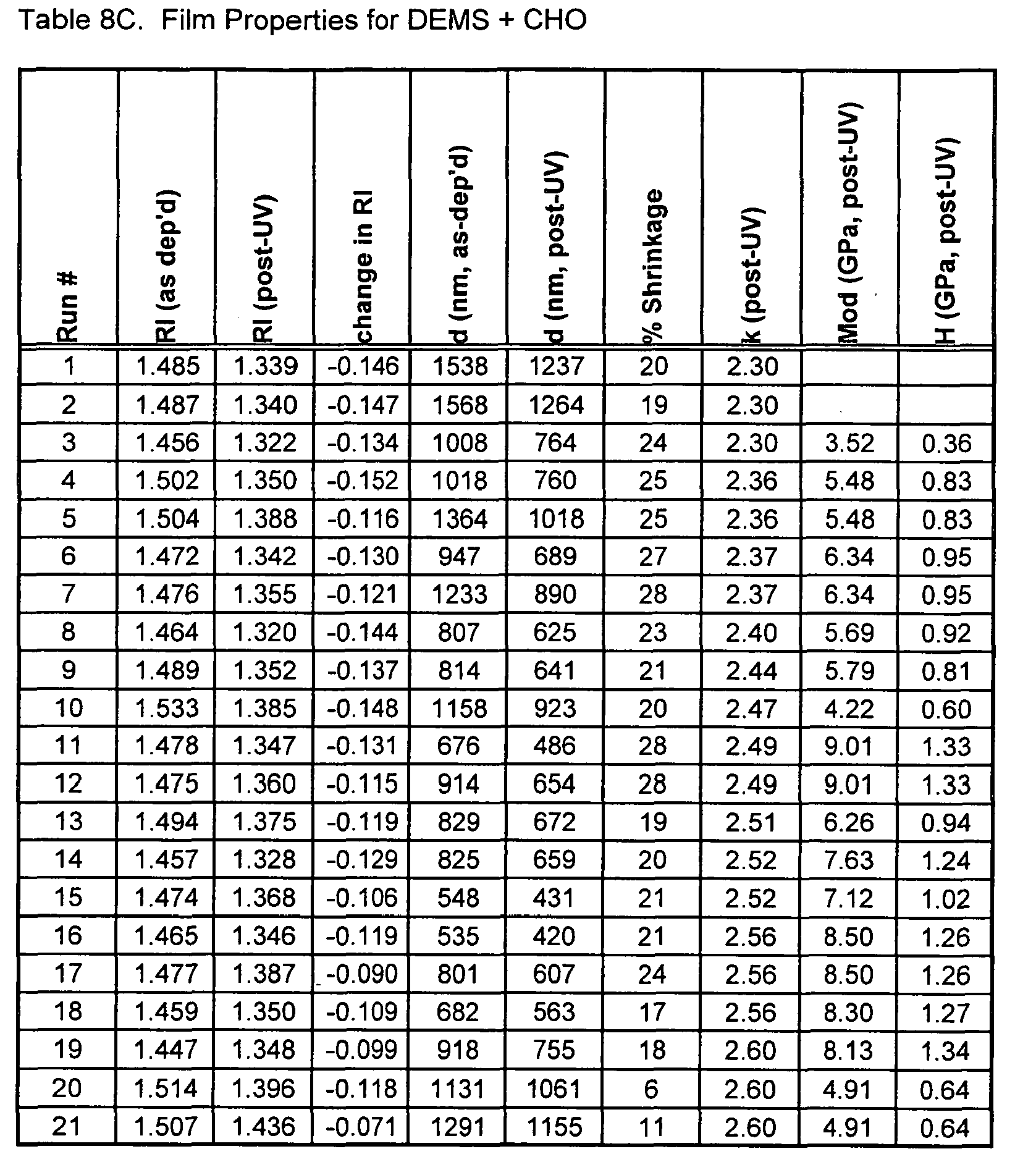
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
- Dielectric Constant Tables
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
How do ionic compounds dissolve in water?
Ionic compounds dissolve in water through a process called dissociation. When an ionic compound is added to water, the water molecules surround the positive and negative ions of the compound, breaking the ionic bonds and separating the ions from each other. This results in the formation of a solution of ions in water, allowing the ions to move freely and conduct electricity. This process is crucial for many chemical reactions and biological processes that occur in aqueous environments.
What is the "like dissolves like" principle?
The "like dissolves like" principle is a concept in chemistry that states that substances with similar polarities or solubilities will mix and dissolve in each other. This means that nonpolar solvents will dissolve nonpolar solutes, and polar solvents will dissolve polar solutes. For example, oil, which is nonpolar, will dissolve in nonpolar solvents like hexane, while salt, which is polar, will dissolve in polar solvents like water.
Explain the concept of "solubility" in chemistry.
Solubility in chemistry refers to the ability of a substance, known as the solute, to dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous solution. It is determined by how well the solute's particles can interact and disperse within the solvent molecules. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and type of solvent can influence the solubility of a substance. Substances with high solubility will dissolve easily, while those with low solubility will form a precipitate when the solvent becomes saturated.
Define the terms "solute" and "solvent.
A solute refers to the substance that is dissolved in a solution, while a solvent is the substance that dissolves the solute to form a homogeneous mixture. The solute is typically present in lesser quantity compared to the solvent, which is usually the abundant component in a solution.
Why do some compounds have high solubility while others are insoluble?
Compounds exhibit different solubilities based on their respective chemical structures and interactions with the solvent. Compounds with strong intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions tend to be more soluble in polar solvents, while compounds with predominantly nonpolar interactions are more soluble in nonpolar solvents. Additionally, the size and shape of molecules can affect solubility, with smaller, more compact molecules often being more soluble than larger, less compact ones. Other factors such as temperature and pressure can also influence solubility. Overall, it is the balance of intermolecular forces and molecular structure that determines whether a compound is soluble or insoluble in a given solvent.
What factors affect the solubility of a substance?
The factors that affect the solubility of a substance include temperature, pressure, type of solvent, and presence of other solutes. Generally, solubility increases with higher temperature for most solid solutes but can vary for gas solutes. Pressure typically only affects the solubility of gases. The type of solvent and the presence of other solutes can also impact solubility through interactions between different substances.
Describe the impact of temperature on solubility.
Temperature has a significant impact on solubility as a general rule, solubility of most solid solutes in liquid solvents increases with an increase in temperature. This is because higher temperatures generally lead to increased kinetic energy, which helps break the intermolecular forces holding the solute particles together, allowing them to dissolve more easily in the solvent. However, this relationship can vary depending on the specific solute and solvent involved, with some solutes showing decreased solubility at higher temperatures.
How do polar and nonpolar solvents affect the solubility of different substances?
Polar solvents tend to dissolve polar solutes, like salts and sugars, due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds or dipole-dipole interactions. Nonpolar solvents, on the other hand, dissolve nonpolar solutes, such as oils and fats, primarily because of London dispersion forces. However, there are exceptions where certain substances may exhibit solubility in both polar and nonpolar solvents depending on their molecular structure and interactions with the solvent molecules.
Explain the solubility rules and why they are important in predicting precipitation reactions.
Solubility rules are guidelines used to predict whether an ionic compound will dissolve in water or precipitate as a solid. They are important in predicting precipitation reactions because they help determine which combinations of ions will form insoluble compounds when mixed together. By following these rules, one can anticipate the formation of a solid precipitate when two solutions containing ions that are likely to form insoluble compounds are combined. This enables chemists to identify and control chemical reactions that result in the formation of solid products, which is crucial for various industrial, research, and educational applications.
Provide an example of a precipitation reaction based on the solubility rules.
An example of a precipitation reaction based on solubility rules is the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) to form silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO3). According to solubility rules, silver chloride is insoluble in water, while sodium nitrate is soluble. Therefore, when aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of the solution as a solid, as it is not soluble, leading to the formation of a white precipitate.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments