Soil Worksheets for High School
High school students studying soil science can benefit greatly from engaging and educational worksheets. These worksheets provide a comprehensive understanding of the entity and subject of soil, allowing students to explore its properties, composition, and role in the environment. By utilizing these worksheets, high school students will be equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to further their studies in soil science.
Table of Images 👆
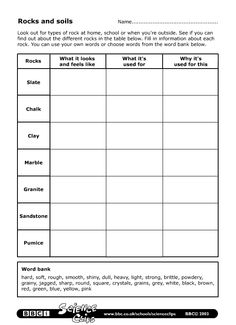
- Rocks and Soil Worksheet
- Middle School Nutrition Worksheets
- Weathering and Soil Formation Worksheet
- Soil Conservation Worksheets Grade 3
- Soil Formation Worksheet Answers
- Soil Classification Worksheet
- Social Studies Worksheets
- AP Environmental Science Worksheets
- High School Interest Inventory Worksheet for Students
- Label Soil Layers Diagram
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Fossil Worksheets Printables
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
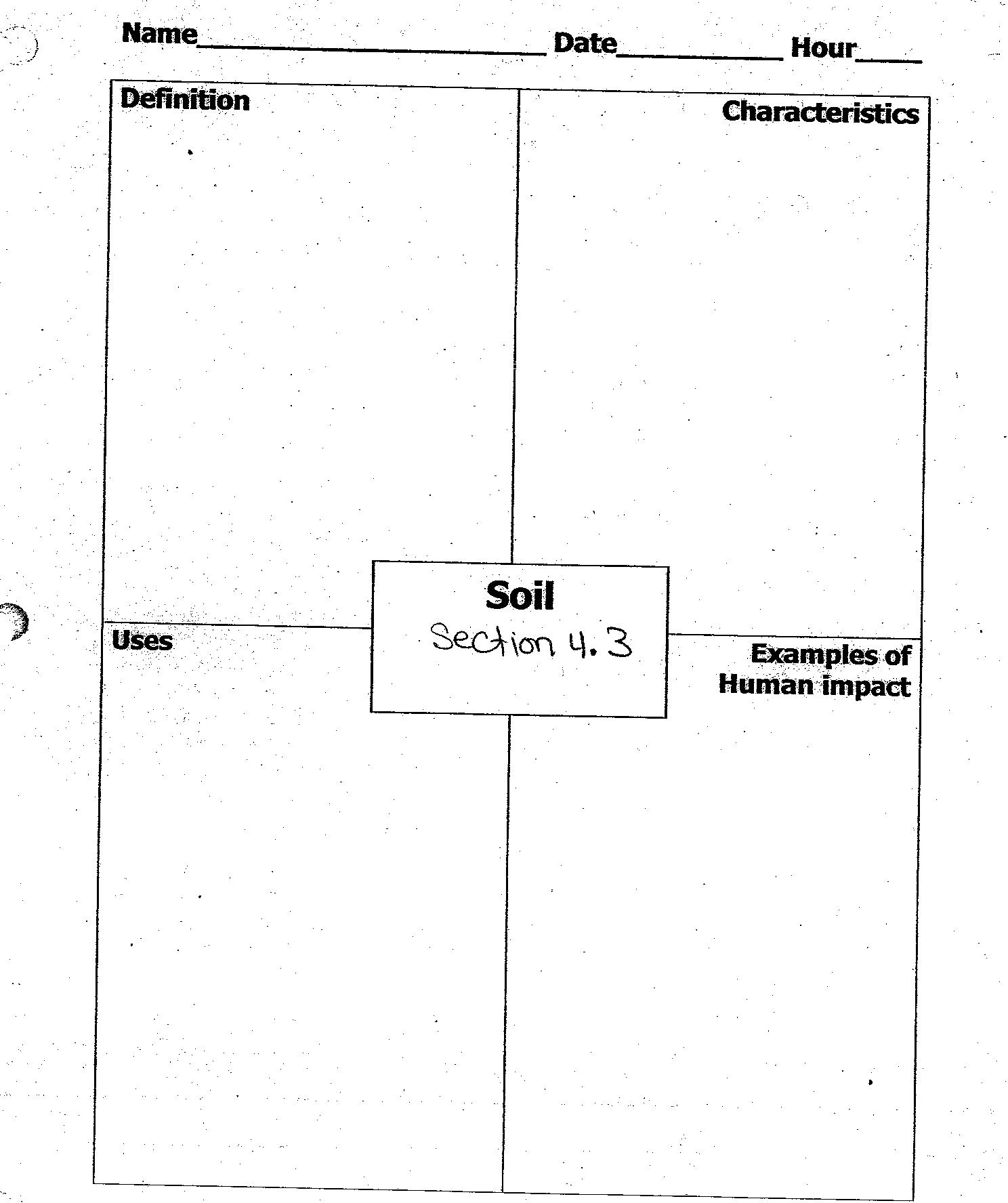
What is soil?
Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. It provides a medium for plant growth, stores carbon, filters water, and serves as a habitat for a diverse range of organisms. Soils vary in composition and properties depending on factors such as climate, vegetation, and geological history.
How is soil formed?
Soil is formed through the weathering of rocks and minerals over long periods of time. Physical, chemical, and biological processes break down rocks into smaller particles, resulting in the formation of soil. Factors such as climate, organisms, topography, and time contribute to the development of different types of soil with varying properties and characteristics.
What are the different layers of soil called?
The different layers of soil are called horizons. The soil profile is typically comprised of several horizons, including the O horizon (organic matter), A horizon (topsoil), E horizon (eluviated layer), B horizon (subsoil), and C horizon (parent material).
What is the importance of soil for plant growth?
Soil is essential for plant growth as it provides a medium for plants to anchor their roots, obtain nutrients, water, and oxygen. It serves as a reservoir for nutrients and water, regulates temperature and pH levels, and supports beneficial microorganisms that aid in nutrient cycling. Healthy soil is vital for supplying plants with the necessary resources for growth and development, making it a crucial component for sustaining plant life.
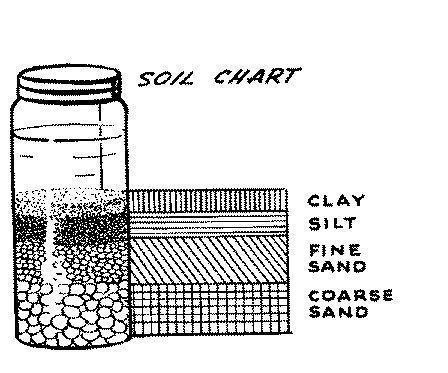
How does the texture of soil influence its water-holding capacity?
The texture of soil influences its water-holding capacity as finer-textured soils like clay have smaller pore spaces that can hold more water and retain it longer compared to coarser-textured soils like sand, which have larger pore spaces that drain water more quickly. Silt, being intermediate in texture, has a moderate water retention ability. Therefore, soil with a higher clay content tends to have a higher water-holding capacity compared to soil with a higher sand content.
What are the main components of soil?
The main components of soil include mineral particles (sand, silt, and clay), organic matter (decaying plant and animal material), water, air, and living organisms (such as bacteria, fungi, earthworms, and insects). These components work together in a complex system to support plant growth and provide nutrients for the ecosystem.
How does soil pH affect plant growth?
Soil pH plays a crucial role in plant growth as it influences nutrient availability. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH range for optimal nutrient uptake. When soil pH is too high or too low, certain nutrients may become chemically bound and unavailable for plants to absorb, leading to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth. Additionally, extreme pH levels can also affect soil microbial activity, further impacting plant health and growth.
What factors can degrade the quality of soil?
Several factors can degrade the quality of soil, including erosion, excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, deforestation, urbanization, overgrazing, industrial activities, and pollution. These factors can lead to soil erosion, nutrient depletion, compaction, salinization, and contamination, which can negatively impact soil fertility, water retention, biodiversity, and overall ecosystem health. Sustainable land management practices and conservation efforts are essential to prevent further degradation and restore soil health.
How can soil erosion be prevented?
Soil erosion can be prevented by implementing various conservation practices such as planting cover crops, building terraces, creating stone barriers, planting trees along hillsides, practicing crop rotation, reducing tillage, and implementing erosion control structures like silt fences and grassed waterways. Additionally, proper land management practices such as reducing deforestation and overgrazing can help stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
How can soil be improved for better crop yields?
Soil can be improved for better crop yields by implementing practices such as crop rotation, adding organic matter through compost or manure, minimizing tillage to preserve soil structure, using cover crops to reduce erosion and improve soil health, applying appropriate fertilizers based on soil test results, and managing water efficiently through irrigation or drainage systems. These practices contribute to soil fertility, structure, and overall health, resulting in increased crop yields.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments