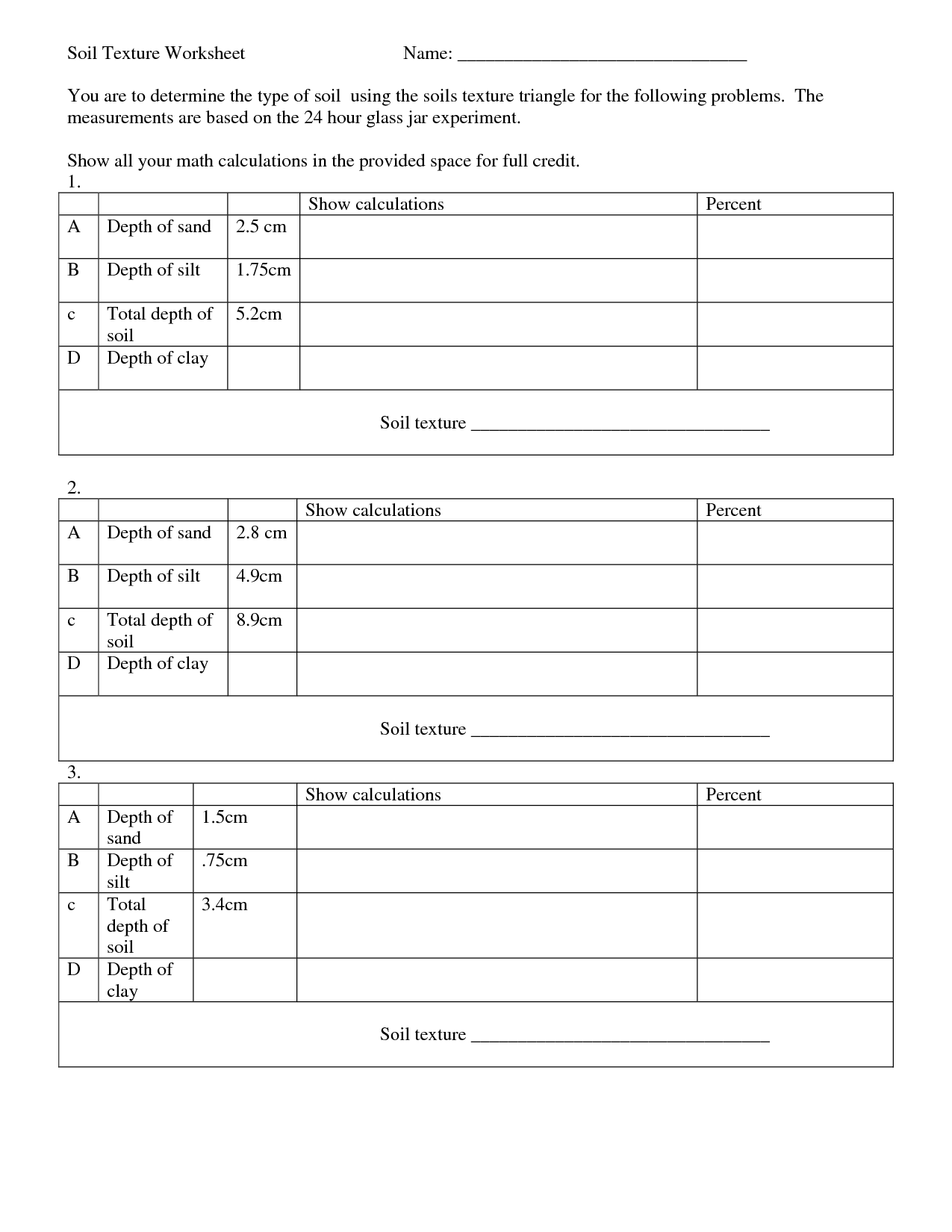
Soil Texture Worksheet
Understanding soil texture is essential for any gardener or farmer. It helps determine the suitability of the soil for different types of plants and crops, and it guides decisions on irrigation, drainage, and nutrient management. For anyone seeking a reliable tool to assess and record soil texture, a soil texture worksheet can be invaluable. This simple yet effective entity allows gardeners, farmers, and land managers to accurately identify and classify the particles in their soil, enabling them to make informed decisions for the success of their crops and gardens.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is soil texture?
Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in a soil. These particles determine the texture categories of soil, which can range from sandy (larger particles) to silty (medium particles) to clayey (small particles). Soil texture influences water retention, drainage, aeration, and nutrient availability, all of which play a crucial role in determining soil fertility and suitability for different types of plant growth.
How is soil texture determined?
Soil texture is determined by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles present in a soil sample. This is typically done using the soil texture triangle, which involves analyzing the soil sample, feeling its texture, and observing how it behaves when moistened. Different combinations of sand, silt, and clay give soil distinct textures such as sandy, loamy, or clayey.
What are the different soil texture classes?
The different soil texture classes are sand, silt, and clay. These classes are based on the size of the particles that make up the soil. Sand particles are the largest, followed by silt, and then clay particles are the smallest. Soils can also be classified as loam, which is a combination of sand, silt, and clay in balanced proportions.
Describe sandy soil texture.
Sandy soil has a gritty texture and is made up of larger particles than other soil types. It feels loose and drains easily, making it prone to dryness and poor nutrient retention. Despite these challenges, sandy soil is great for plants that need good drainage and don't like to sit in water for too long. It warms up quickly in the spring and is easy to work with due to its light and airy composition.
Describe silt soil texture.
Silt soil texture is characterized by particles that are smaller than sand but larger than clay, ranging from 0.002 to 0.05 mm in size. It has a smooth, flour-like texture that feels soft and powdery when dry, and sticky and slippery when wet. Silt soil retains moisture well and has good fertility due to its ability to hold nutrients, making it ideal for growing a variety of crops. However, it can be easily compacted and may have poor drainage if not properly managed.
Describe clay soil texture.
Clay soil texture is characterized by its fine particles that are tightly packed together, providing high water retention and excellent nutrient holding capacity. It is smooth to the touch and forms a sticky, heavy ball when wet, but hard and difficult to work with when dry. Clay soil tends to compact easily and can become waterlogged, leading to poor drainage and potential for root rot in plants. However, its ability to hold onto moisture and nutrients can be beneficial for certain plants if managed properly.
What are the properties of sandy soil?
Sandy soil is characterized by its large particles that allow for good drainage and aeration, making it well-suited for plants that prefer drier conditions. However, sandy soil has poor water and nutrient retention due to its high permeability, requiring frequent watering and fertilization. It warms up quickly in the spring and is easy to work with, but can also be prone to erosion and nutrient leaching. Overall, sandy soil is ideal for certain plant species and landscaping situations, but may require additional care and amendments to maintain fertility and moisture levels.
What are the properties of silt soil?
Silt soil is a fertile soil that is made up of fine particles, smaller than sand but larger than clay. It has good moisture retention and drainage properties, making it ideal for growing crops. Silt soil is also easy to work with and has good porosity, allowing for air circulation and root development. However, because of its fine texture, silt soil can become compacted easily, reducing its drainage and aeration capabilities. It is important to add organic matter and practice proper soil management to maintain the fertility and structure of silt soil.
What are the properties of clay soil?
Clay soil is characterized by its fine texture, high nutrient content, excellent water retention capacity, and tendency to compact easily. It has a high cation exchange capacity, making it fertile for plant growth. However, its poor drainage can lead to waterlogging and root rot in plants. Clay soil also tends to harden when dry, making it difficult to work with and prone to forming cracks.
How does soil texture affect water and nutrient retention?
Soil texture directly influences water and nutrient retention as it determines the pore space available for water and nutrient storage. Fine-textured soils like clay have smaller pores which can hold onto water and nutrients more effectively but may lead to poor drainage, while coarse-textured soils like sand have larger pores which drain water quickly but have low nutrient retention capability. Soil texture affects the movement, availability, and retention of water and nutrients in the soil, ultimately impacting plant growth and ecosystem health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments