Reconstruction After the Civil War Worksheets
Reconstruction after the Civil War was an immensely significant period in American history, and understanding its complexities is crucial for students seeking to gain a deeper insight into this transformative era. In order to aid in the comprehensive understanding of this subject, the use of Reconstruction After the Civil War Worksheets can prove to be an invaluable resource for educators and students alike. These worksheets focus on various aspects of Reconstruction, including the major policies, the impact on different groups of people, and the challenges faced during this time.
Table of Images 👆
- Civil War and Reconstruction Worksheets
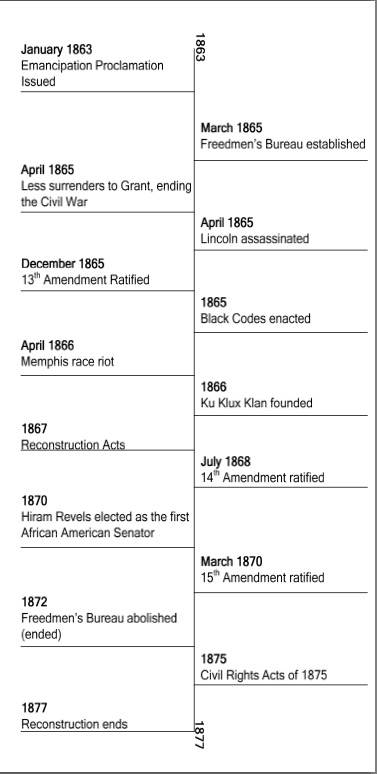
- Civil War Reconstruction Timeline
- Civil War and Reconstruction Worksheets
- Civil War and Reconstruction Worksheets
- Civil War and Reconstruction Worksheets
- Printable Civil War Worksheet High School History
- Civil War Reconstruction Timeline
- Civil War Reconstruction Political Cartoons
- Economic Reconstruction After Civil War
- The South Reconstruction After the Civil War
- KWL Chart
- Civil War Worksheets 5th Grade
- Civil War Reconstruction Era
- Civil Rights Movement Essay Paper
- The South Reconstruction After the Civil War
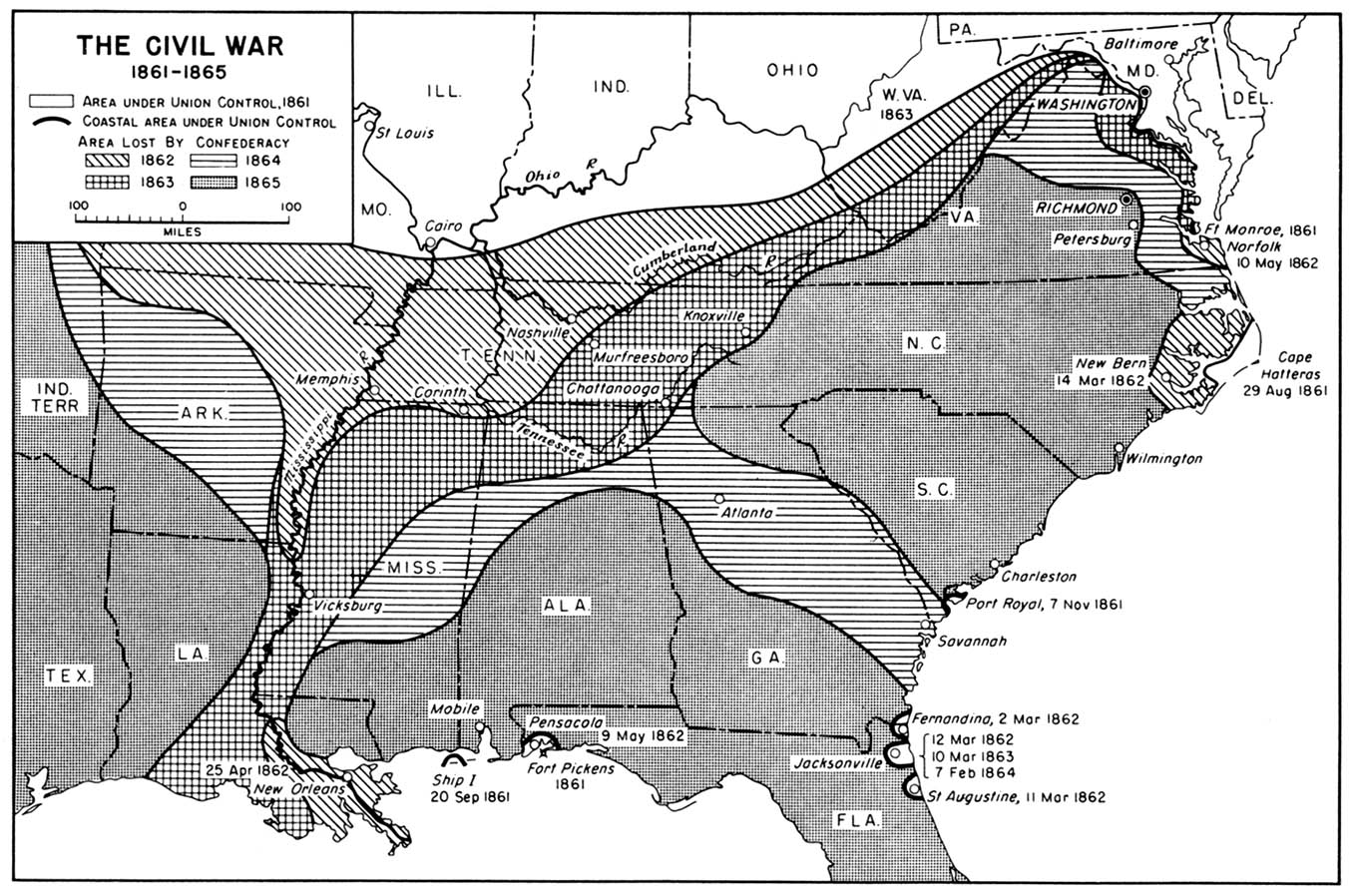
- Civil War Map 1861
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What was the purpose of Reconstruction after the Civil War?
The purpose of Reconstruction after the Civil War was to rebuild the Union and reintegrate the Southern states that had seceded back into the United States, as well as to address the social, political, and economic issues stemming from slavery and the war. Reconstruction aimed to provide civil rights, citizenship, and voting rights to newly freed African Americans, establish new political systems in the South, and ensure the nation's unity and healing after the devastating conflict.
What were the three major amendments that were passed during Reconstruction?
The three major amendments that were passed during Reconstruction were the 13th Amendment which abolished slavery, the 14th Amendment which granted citizenship and equal protection under the law to all persons born or naturalized in the United States, and the 15th Amendment which prohibited the denial of voting rights based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude.
Who were the Radical Republicans and what was their role in Reconstruction?
The Radical Republicans were a faction of the Republican Party during Reconstruction in the United States. They advocated for a more aggressive approach towards rebuilding the South and ensuring civil rights for freed slaves. Their role in Reconstruction included passing legislation such as the Civil Rights Act of 1866 and the Fourteenth Amendment, which aimed to protect the rights of African Americans. They also pushed for the impeachment of President Andrew Johnson, who they believed was too lenient towards the former Confederate states. Overall, the Radical Republicans played a significant role in shaping the political landscape during the Reconstruction era.
How did Reconstruction policies affect the rights and lives of African Americans?
Reconstruction policies aimed to grant rights and improve the lives of African Americans by providing them with citizenship, voting rights, and access to education. However, the policies were met with resistance from white supremacist groups, leading to violence, discrimination, and the emergence of discriminatory laws such as Jim Crow laws. Despite advancements in civil rights, African Americans continued to face systemic racism and inequality, which shaped their experiences and limited their opportunities for generations to come.
What were the goals of the Freedmen's Bureau during Reconstruction?
The Freedmen's Bureau was established during Reconstruction with the goals of providing assistance to newly emancipated slaves and impoverished whites by offering education, healthcare, housing, and employment opportunities, as well as ensuring their civil rights and helping them transition to freedom and citizenship.
What were some of the challenges and obstacles faced during the Reconstruction era?
Some of the challenges and obstacles faced during the Reconstruction era included resistance from white Southerners to the rights and freedoms of newly freed African Americans, violence and intimidation tactics from groups like the Ku Klux Klan, political strife over the direction of Reconstruction between President Andrew Johnson and the Radical Republicans in Congress, economic struggles for both freedmen and white Southerners, and the inability of the federal government to fully enforce new laws protecting the rights of African Americans in the South.
What were the differences between Presidential and Congressional Reconstruction?
Presidential Reconstruction, led by President Andrew Johnson after the Civil War, aimed to bring the Southern states back into the Union swiftly with limited federal interference, allowing for more lenient treatment of former Confederate leaders. In contrast, Congressional Reconstruction, initiated by Congress through the passage of the Reconstruction Acts, sought to implement more stringent conditions for readmission, including the establishment of military districts in the South, voting rights for freedmen, and the disqualification of former Confederates from holding office. Congressional Reconstruction also led to the passage of the 14th and 15th Amendments, granting equal protection under the law and voting rights to African Americans, signaling a more radical approach to rebuilding the post-war South.
How did the Southern states respond to and resist Reconstruction?
The Southern states responded to and resisted Reconstruction by enacting "Black Codes" that restricted the rights and freedoms of freed slaves, forming white supremacist groups like the Ku Klux Klan to intimidate and terrorize African Americans, implementing literacy tests and poll taxes to disenfranchise black voters, and engaging in violent uprisings and acts of defiance against federal authority. These actions were aimed at maintaining white supremacy and power in the South, despite the efforts of the federal government to grant rights and protections to newly freed African Americans during Reconstruction.
What role did violence and intimidation play during Reconstruction?
Violence and intimidation played a significant role during Reconstruction as white supremacist groups like the Ku Klux Klan used terror tactics to intimidate newly freed African Americans and undermine their political and civil rights. This violence was aimed at maintaining white supremacy and control over the newly reconstructed South, often leading to widespread fear, disenfranchisement, and loss of life among black communities. The fear and intimidation caused by these acts of violence made it difficult for African Americans to fully exercise their rights and actively participate in the political process during this tumultuous period in American history.
Why did Reconstruction ultimately fail to fully achieve its goals?
Reconstruction ultimately failed to fully achieve its goals due to various factors including widespread resistance from Southern white supremacists who sought to regain power and maintain racial hierarchy, the lack of sufficient federal enforcement of civil rights laws, the withdrawal of federal troops from the South, and the shift in national priorities towards economic growth and westward expansion. Additionally, the assassination of key leaders such as Abraham Lincoln and the lack of sustained political will to address systemic racial inequality further hindered the success of Reconstruction efforts.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments