Protein Synthesis Graphic Organizer Worksheet
This blog post introduces a Protein Synthesis Graphic Organizer Worksheet, designed to assist high school and college students in understanding the complex process of protein synthesis. This worksheet provides an organized visual representation of the entities involved in protein synthesis and helps students grasp the subject matter with clarity and comprehension.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Model Cut Out Worksheets
- Main Idea Graphic Organizer
- Science Graphic Organizers
- Story Structure Graphic Organizers
- Superhero Story Template
- Compare and Contrast Story Graphic Organizer Kindergarten
- Draw the Structure of a Glucose Molecule
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Printable KWL Chart Graphic Organizer
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of the Protein Synthesis Graphic Organizer Worksheet?
The purpose of the Protein Synthesis Graphic Organizer Worksheet is to visually represent and explain the process of protein synthesis which involves the creation of proteins in a cell. This worksheet helps students to understand the stages of protein synthesis, including transcription and translation, and how these processes work together to create specific proteins based on the genetic code stored in DNA. It allows students to organize and connect key concepts, helping them to grasp the complex process of protein synthesis more effectively.
What are the main steps involved in protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, DNA is used as a template to produce messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. mRNA then moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. In translation, mRNA is read by ribosomes, which use transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to bring amino acids to the ribosome in the correct sequence to assemble a polypeptide chain. The ribosome reads the mRNA codons and matches them with the corresponding tRNA anticodons, building the protein one amino acid at a time. Finally, the protein is folded into its proper shape and often undergoes post-translational modifications to become functional.
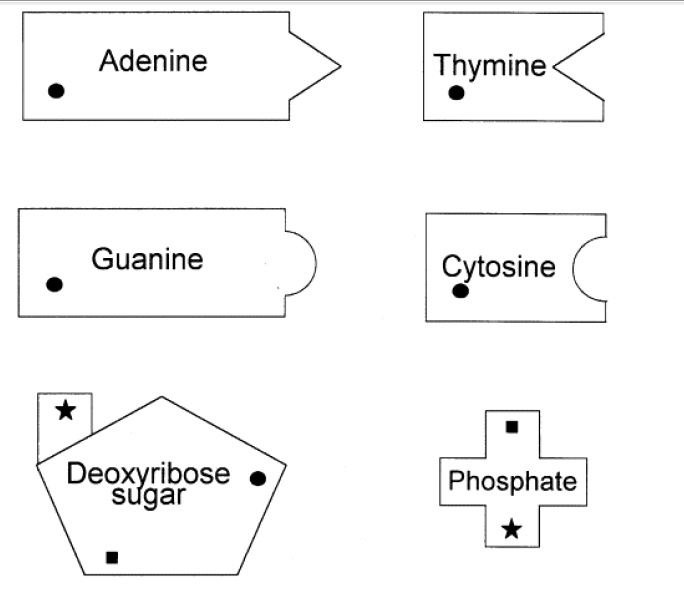
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA provides the instructions for protein synthesis by serving as a template for the formation of messenger RNA (mRNA) in a process called transcription. mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis takes place. The sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein. Therefore, DNA plays a crucial role in determining the structure and function of proteins in the cell.
Describe the process of transcription in protein synthesis.
Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis where DNA is used as a template to create a complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at the start site of a gene, unwinds the DNA double helix, and reads the DNA sequence. As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, it adds complementary RNA nucleotides to the growing mRNA strand. This process continues until RNA polymerase reaches a stop signal on the DNA. The newly formed mRNA molecule then carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where it will be used as a template for protein synthesis during translation.
Explain the role of mRNA in protein synthesis.
mRNA, or messenger RNA, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis as it carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The ribosomes read the mRNA molecule and use it as a template to assemble the corresponding amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. In this way, mRNA serves as the intermediary messenger that translates the genetic code into the sequence of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
What happens during translation in protein synthesis?
During translation in protein synthesis, the mRNA molecule is read by ribosomes, which then use transfer RNA (tRNA) to assemble amino acids in the correct sequence to form a polypeptide chain. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, tRNA molecules bring their amino acids to the ribosome, where they are joined together to form a growing polypeptide chain. This process continues until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA, signaling the end of translation and the release of the newly synthesized protein.
Describe the function of tRNA in protein synthesis.
tRNA, or transfer RNA, plays a key role in protein synthesis by bringing amino acids to the ribosome during translation of the mRNA code. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid on one end and has an anticodon region on the other end that can base pair with the complementary mRNA codon. This allows the tRNA to accurately deliver the right amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain according to the genetic code, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the protein being synthesized.
What is a codon and how does it relate to protein synthesis?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in DNA or mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid or signals the start or stop of protein synthesis. During protein synthesis, ribosomes read the sequence of codons in mRNA and use it as a template to assemble a chain of amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, ensuring that the correct sequence of amino acids is translated from the mRNA to produce the desired protein.
Explain the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis.
Ribosomes play a crucial role in protein synthesis by serving as the site where the translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins occurs. They consist of two subunits, each containing ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. The ribosomes read the genetic information carried by the mRNA and use transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a polypeptide chain, which ultimately folds into a functional protein. This process occurs in the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm or on the rough endoplasmic reticulum in prokaryotic cells.
How does protein synthesis contribute to the overall functioning of cells and living organisms?
Protein synthesis is essential for the overall functioning of cells and living organisms as proteins perform a wide variety of functions within cells and throughout the body. Proteins are involved in enzymatic reactions, cell structure, communication between cells, transportation of molecules, and immunity. Without proper protein synthesis, cells would not be able to carry out vital processes required for growth, maintenance, repair, and reproduction, ultimately impacting the overall health and functioning of living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments