Protein Function Worksheets
Protein function worksheets are valuable tools for biology students and researchers who want to delve deeper into the complex world of protein functionality. These worksheets serve as an efficient way to explore the diverse roles of proteins in living organisms, providing a structured and hands-on approach for studying this crucial biological entity. By engaging with these worksheets, students can gain a deeper understanding of protein functions and the various subjects related to protein research.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Vitamins and Minerals Worksheet
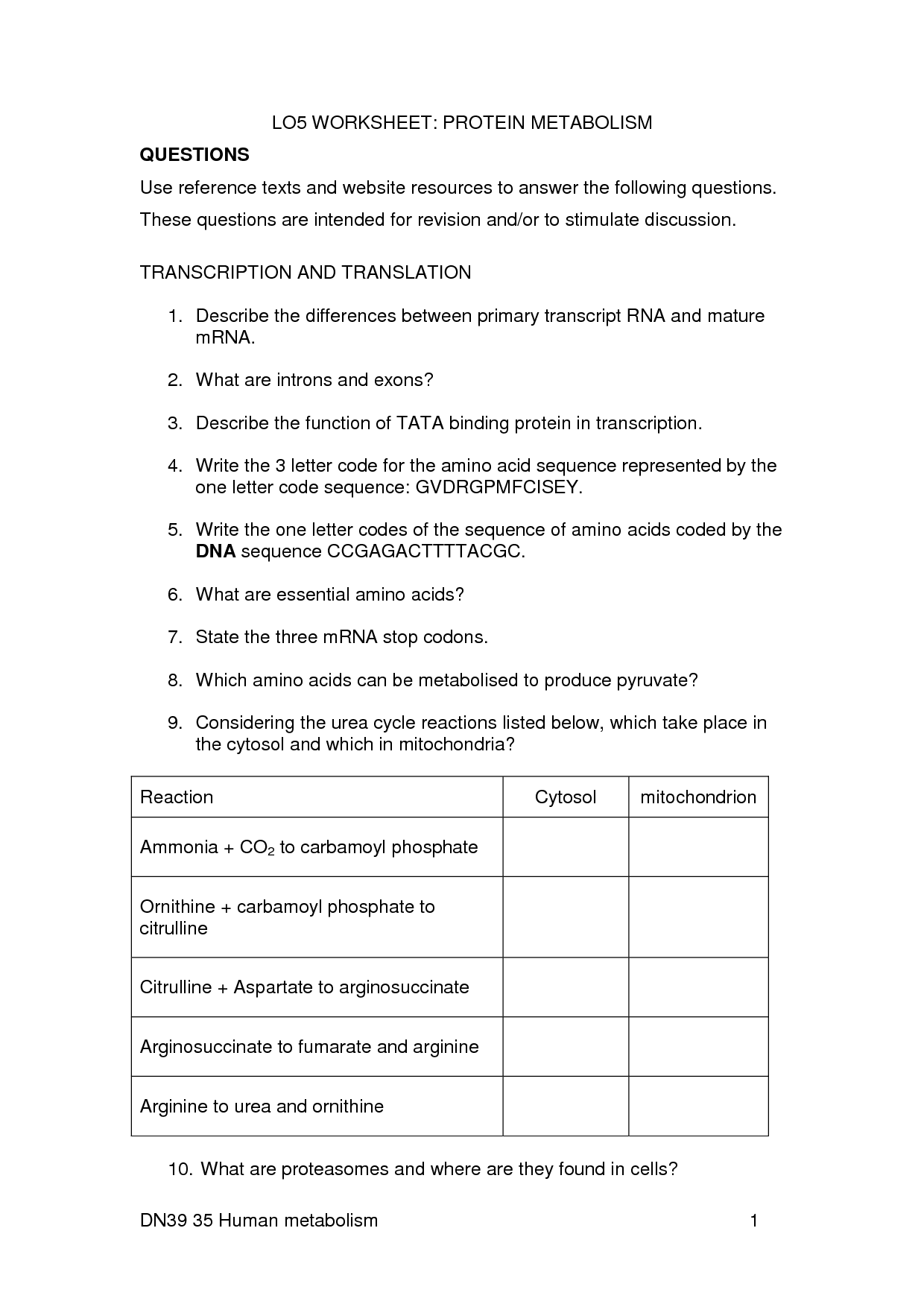
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Structure Worksheet Answers
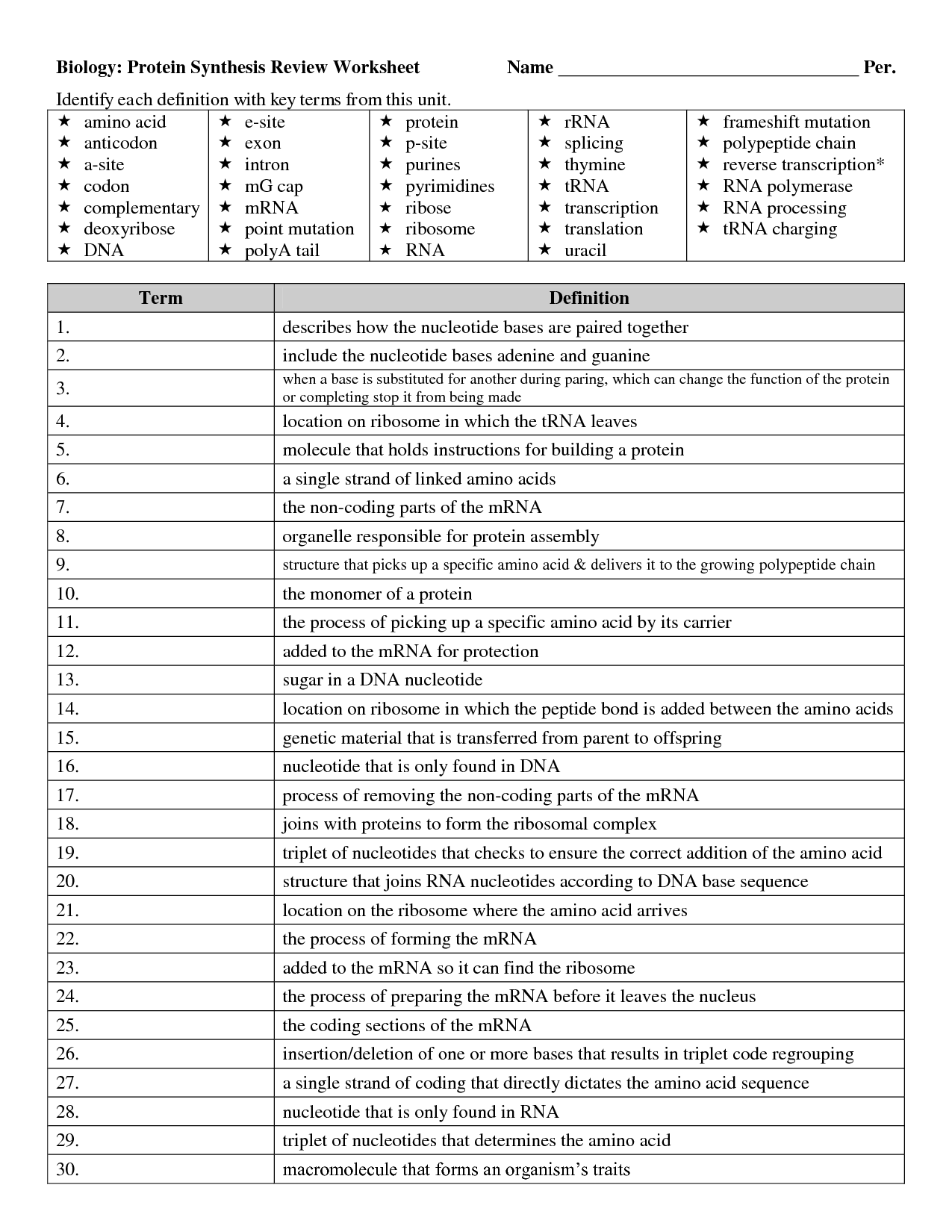
- Protein Synthesis Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Four Levels Protein Structure
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
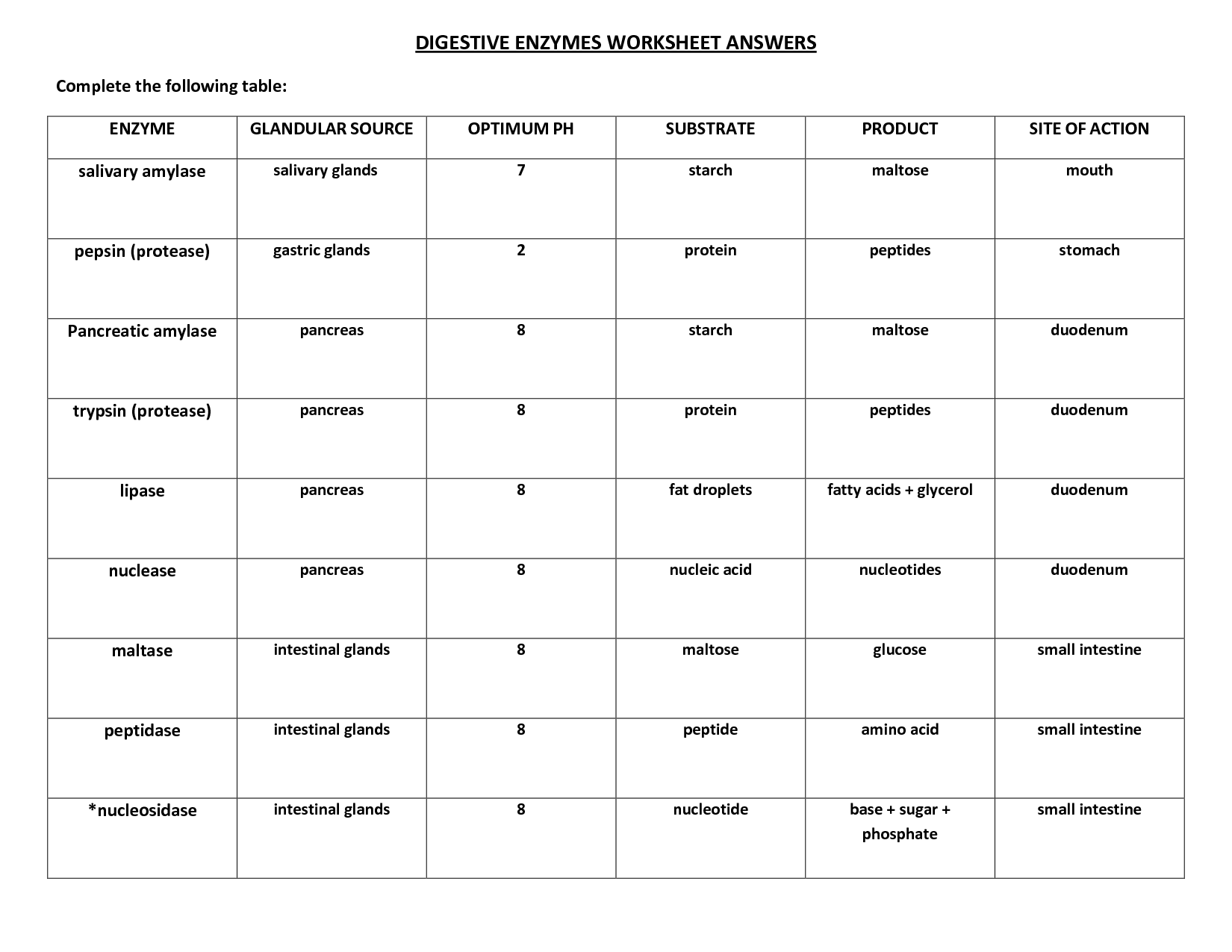
- Digestive Enzymes Worksheet
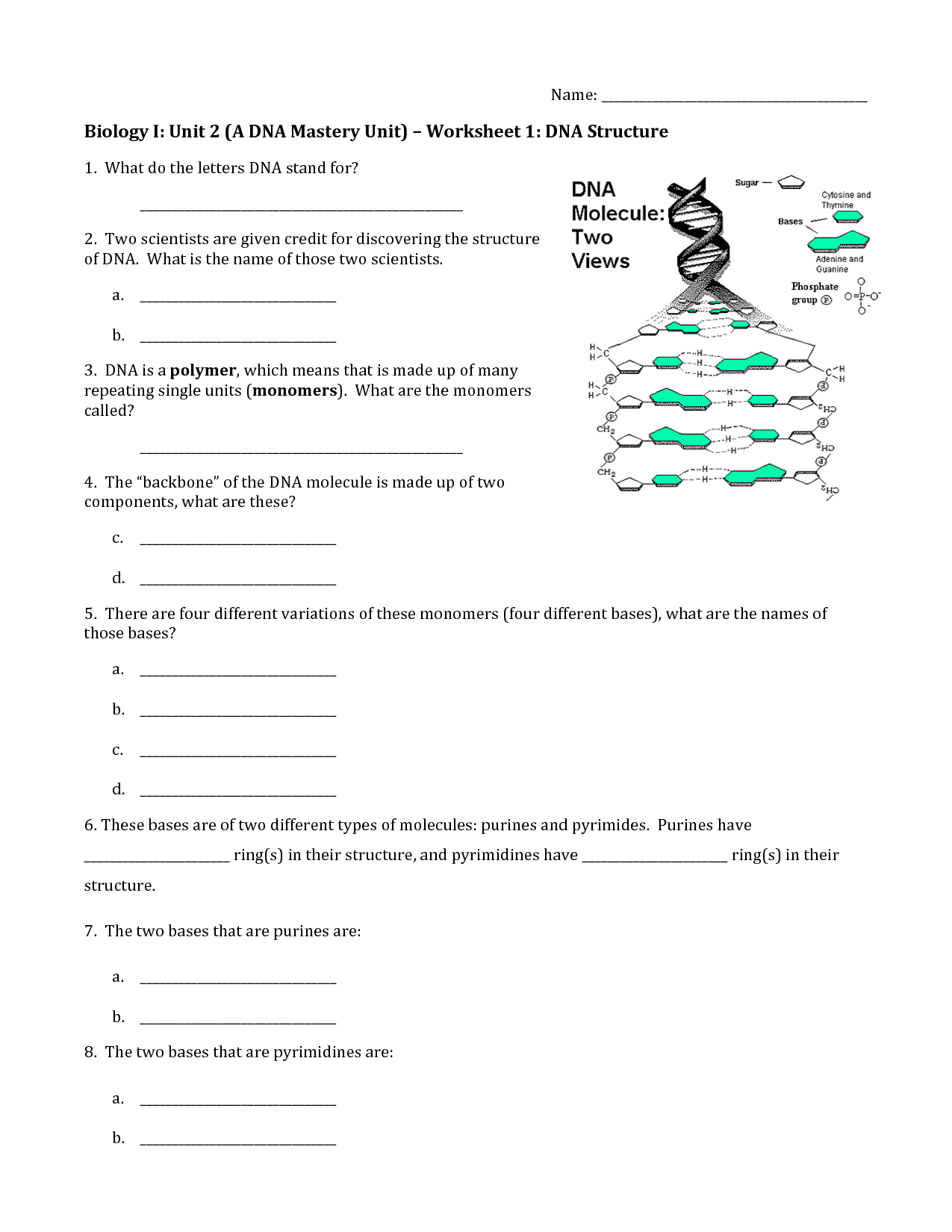
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
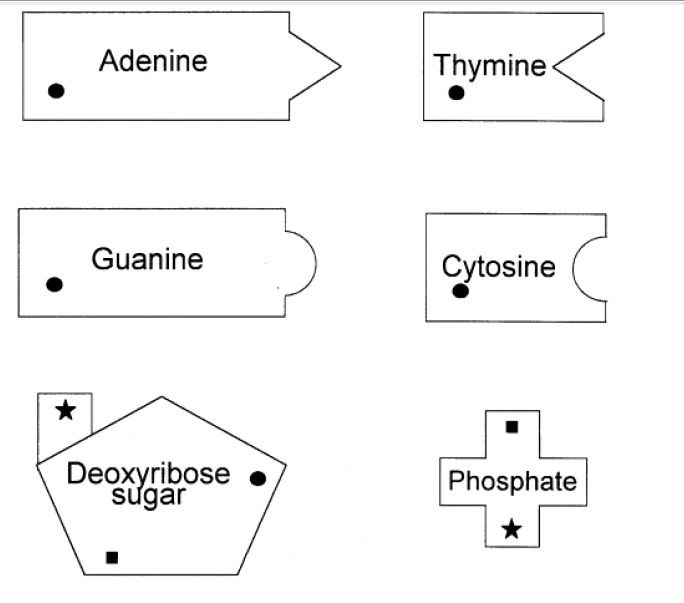
- DNA Model Cut Out Worksheets
- Blood Cells and Functions Worksheets
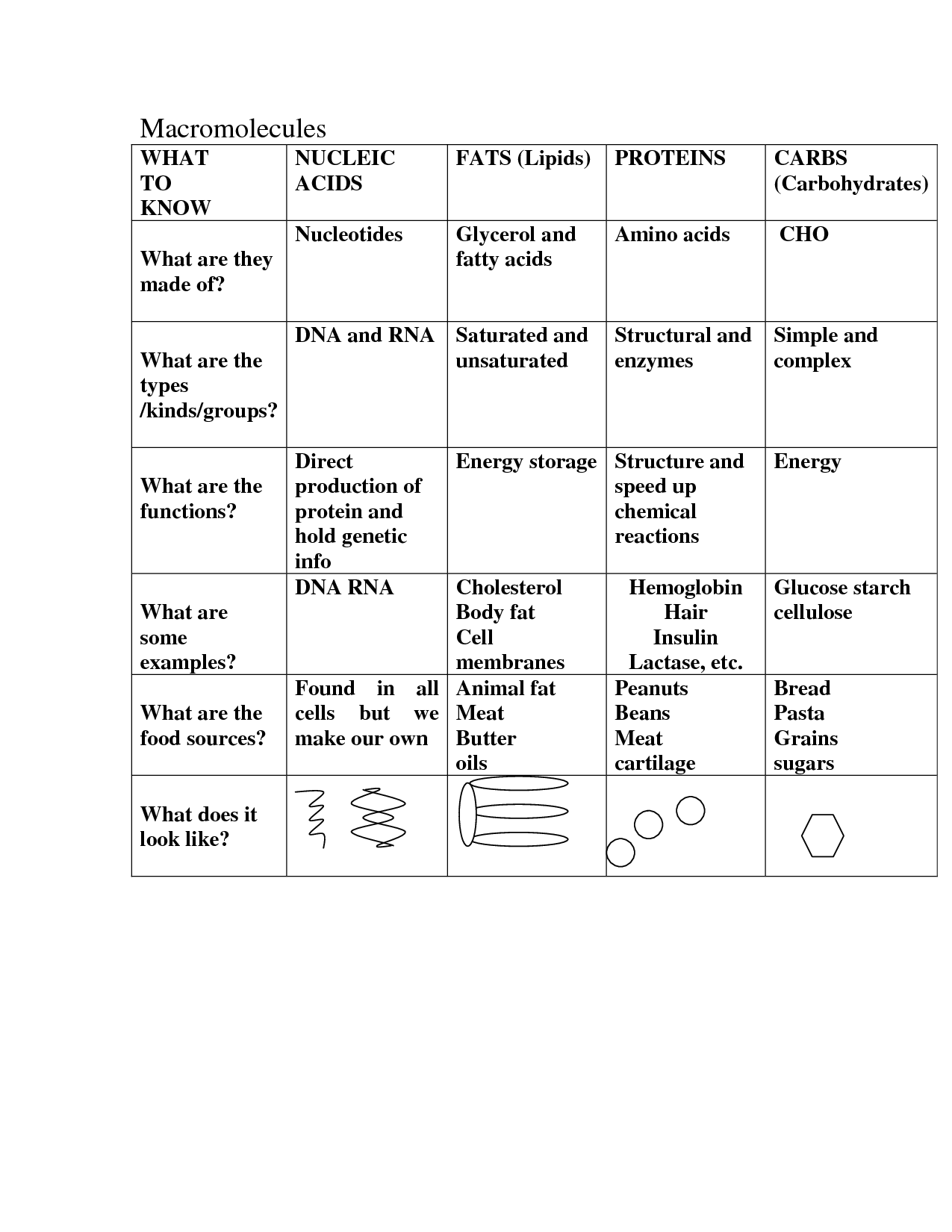
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
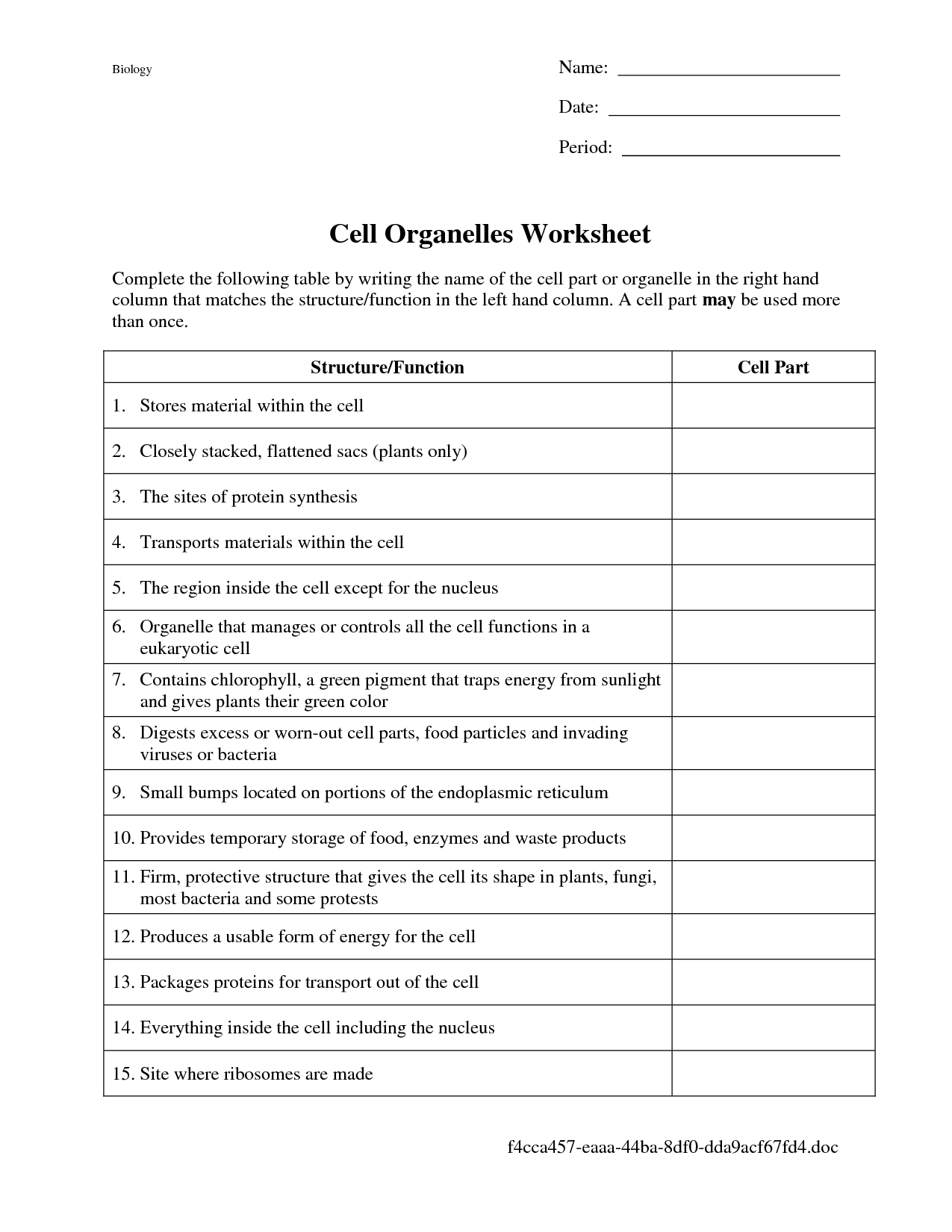
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
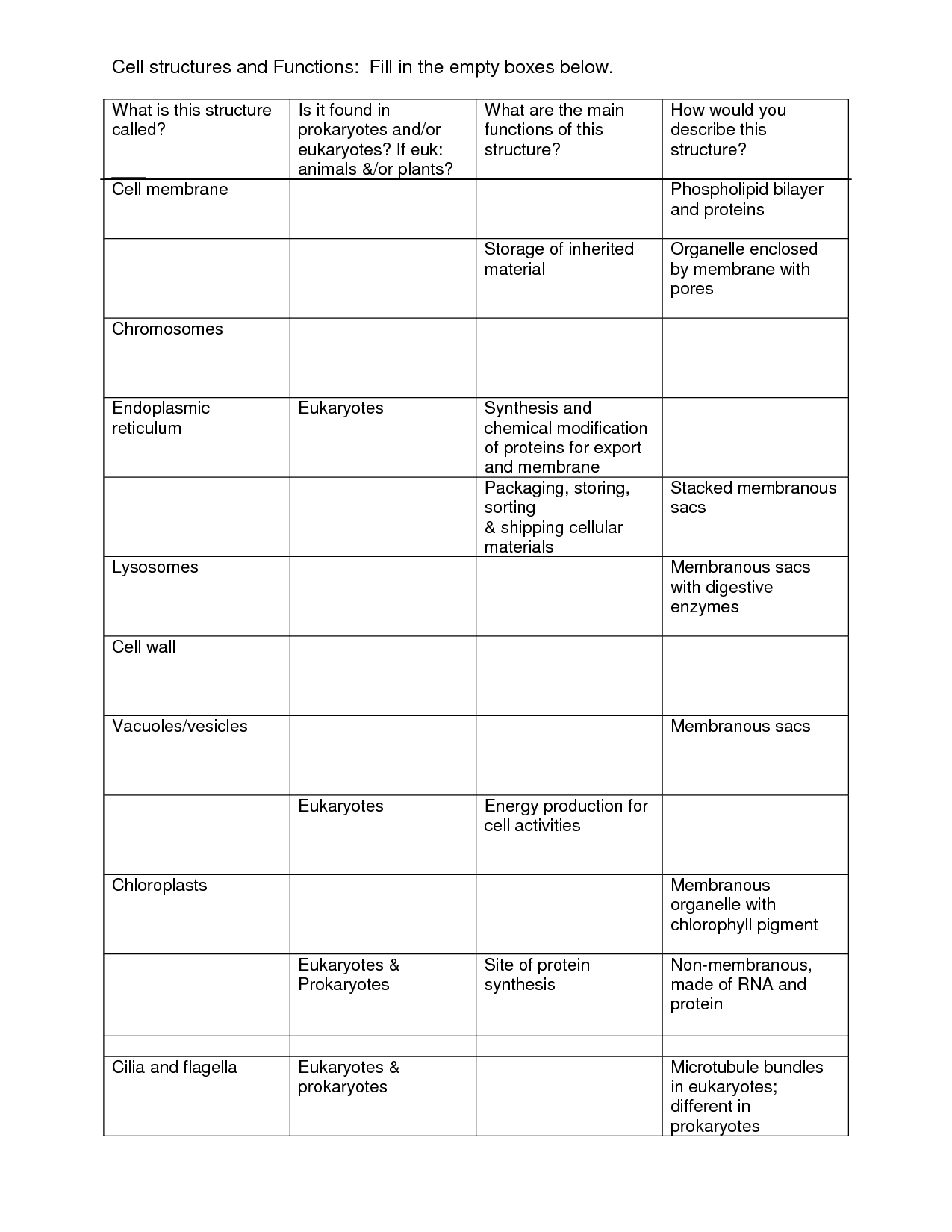
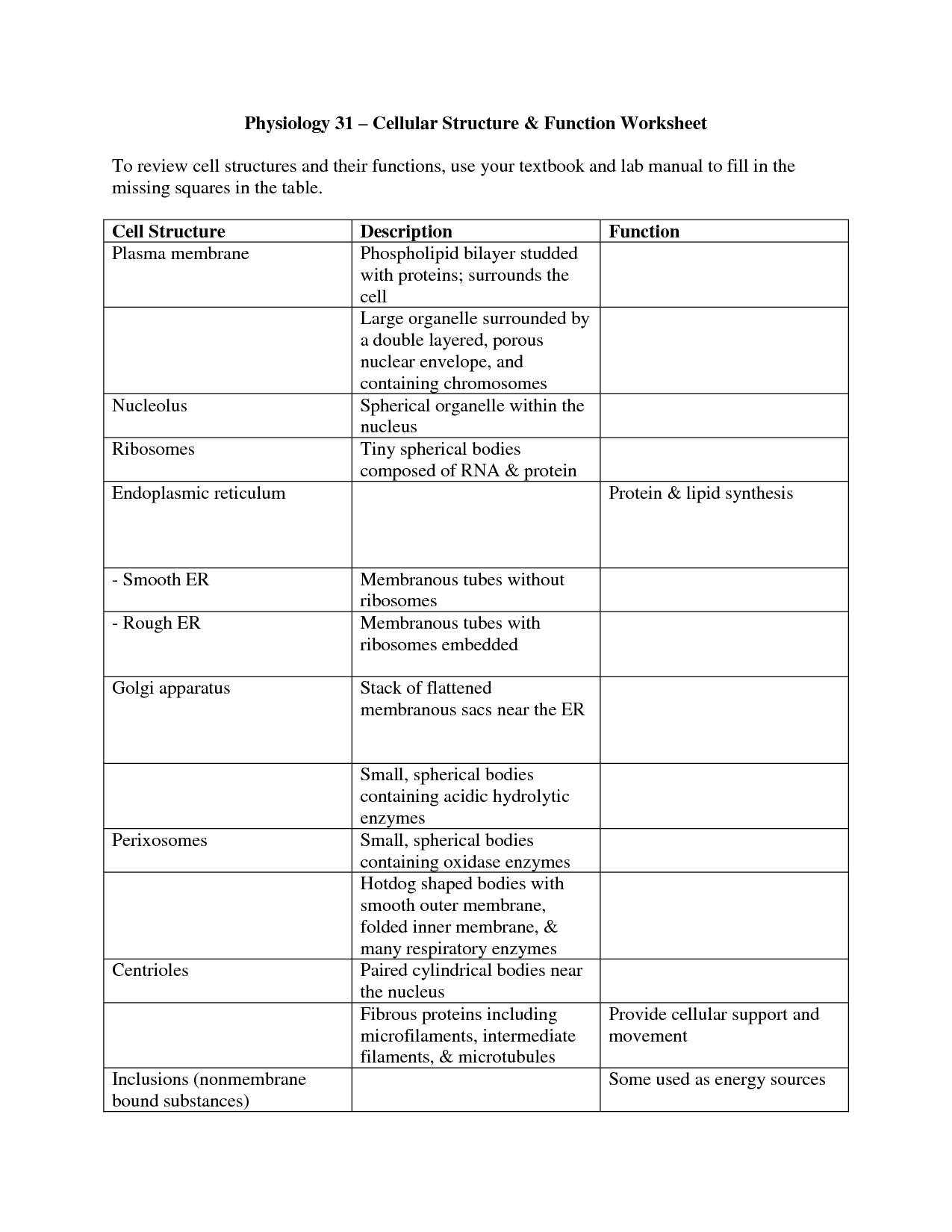
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
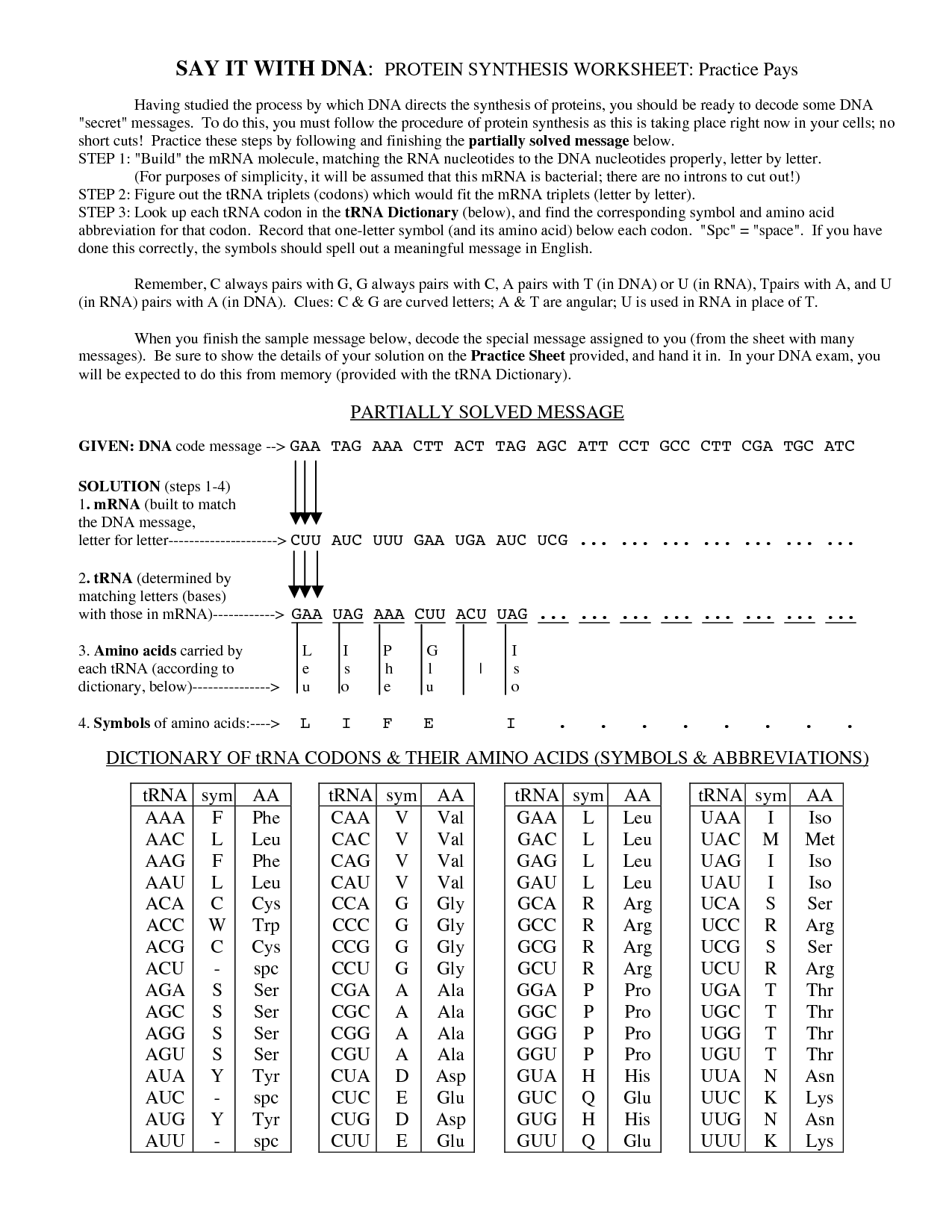
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the primary function of proteins in living organisms?
The primary function of proteins in living organisms is to perform a wide range of important roles, including serving as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, providing structural support to cells and tissues, facilitating transport of molecules across cell membranes, regulating gene expression, and serving as antibodies to defend against pathogens. Proteins are essential for the proper functioning of the body and are involved in nearly every biological process.
How do proteins contribute to the structure of cells and tissues?
Proteins play a crucial role in the structure of cells and tissues by acting as building blocks and providing structural support. Proteins like collagen, actin, and keratin form the framework of cells and tissues, contributing to their strength, elasticity, and shape. They also help in cell adhesion, signaling, and transport, maintaining the integrity and functionality of the cellular structure. Overall, proteins are essential components for the organization and maintenance of cells and tissues in the body.
What role do proteins play in enzyme catalysis?
Proteins play a crucial role in enzyme catalysis by providing a three-dimensional structure that allows them to bind to specific substrate molecules and carry out chemical reactions. This structure, known as the active site, provides a precise environment for the reaction to occur and facilitates the formation of enzyme-substrate complexes that lower the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. Additionally, proteins can undergo conformational changes upon binding to substrates, further enhancing the catalytic efficiency of enzymes in facilitating biochemical reactions.
How do proteins aid in the transport of molecules across cell membranes?
Proteins aid in the transport of molecules across cell membranes by acting as carriers or channels that can facilitate the movement of specific substances. Transport proteins, such as channel proteins and carrier proteins, provide pathways for molecules to pass through the cell membrane, ensuring that essential molecules can enter the cell while unwanted substances are kept out. These proteins can also actively pump molecules against their concentration gradients through processes like active transport. Overall, proteins play a crucial role in regulating the trafficking of molecules across cell membranes to maintain proper cellular function and homeostasis.
What is the function of proteins in the immune system?
Proteins in the immune system play a crucial role in defending the body against pathogens by recognizing, capturing, and destroying them. These proteins include antibodies, cytokines, and enzymes that work together to identify foreign invaders and trigger an immune response to eliminate them. Proteins also help regulate the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and maintain a balanced immune system.
How do proteins participate in cell signaling and communication?
Proteins participate in cell signaling and communication by acting as messengers, receptors, enzymes, and structural components. Signaling proteins transmit information by binding to specific receptors on the cell surface and triggering a cascade of events within the cell. These proteins can also relay signals to other cells or tissues by acting as hormones or growth factors. Enzymes, such as kinases and phosphatases, regulate the activation or inactivation of signaling pathways. Additionally, structural proteins help organize signaling complexes and provide physical support for signaling processes within the cell. Overall, proteins play essential roles in coordinating cellular responses to various external stimuli and ensuring proper communication within and between cells.
What role do proteins play in muscle contraction and movement?
Proteins play a crucial role in muscle contraction and movement by acting as the main structural components of muscle fibers as well as by participating in the process of muscle contraction. The two main proteins involved in muscle contraction are actin and myosin, which work together to generate the force necessary for muscle movement. Actin and myosin interact to create the sliding filament mechanism, where myosin molecules pull on actin filaments to shorten the muscle fiber and produce movement. Additionally, other proteins such as troponin and tropomyosin regulate the interaction between actin and myosin, playing a key role in controlling muscle contraction.
How do proteins function as hormones in regulating various physiological processes?
Proteins function as hormones by binding to specific receptor molecules on target cells, triggering a cascade of cellular responses that regulate various physiological processes. After binding to the receptor, the hormone-protein complex can activate or inhibit specific signaling pathways within the cell, ultimately influencing gene expression, metabolism, growth, and other functions. This process allows proteins to act as chemical messengers in the body, coordinating and fine-tuning a wide range of physiological activities.
What is the function of proteins in DNA replication and gene expression?
Proteins play essential roles in both DNA replication and gene expression. In DNA replication, proteins such as DNA polymerases help in the synthesis of new DNA strands. Meanwhile, in gene expression, various proteins like transcription factors regulate the transcription of genes into messenger RNA. Additionally, other proteins like RNA polymerases and ribosomes are involved in the translation of mRNA into functional proteins. Overall, proteins are vital in ensuring accurate DNA replication and proper gene expression in cells.
How do proteins contribute to the storage and transport of essential molecules, such as oxygen in blood?
Proteins play a crucial role in the storage and transport of essential molecules like oxygen in blood. For example, hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen in the lungs and carries it to tissues throughout the body. Additionally, proteins like albumin help transport essential molecules such as hormones, nutrients, and waste products in the bloodstream. Overall, the specific structures and functions of proteins enable them to efficiently store and transport essential molecules in the body, ensuring optimal physiological functioning.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments