Protein Biology Worksheet
Protein biology worksheets provide a valuable resource for students and researchers interested in studying the intricate world of proteins. These worksheets effectively break down complex topics and concepts into manageable sections, allowing users to grasp the entity and subject matter with ease. Designed to help suitable target audiences comprehend protein structure, function, and interactions, these worksheets serve as a useful tool for academic and scientific endeavors.
Table of Images 👆
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Model Cut Out Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets with Answer Key
- Macromolecules Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Worksheets
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
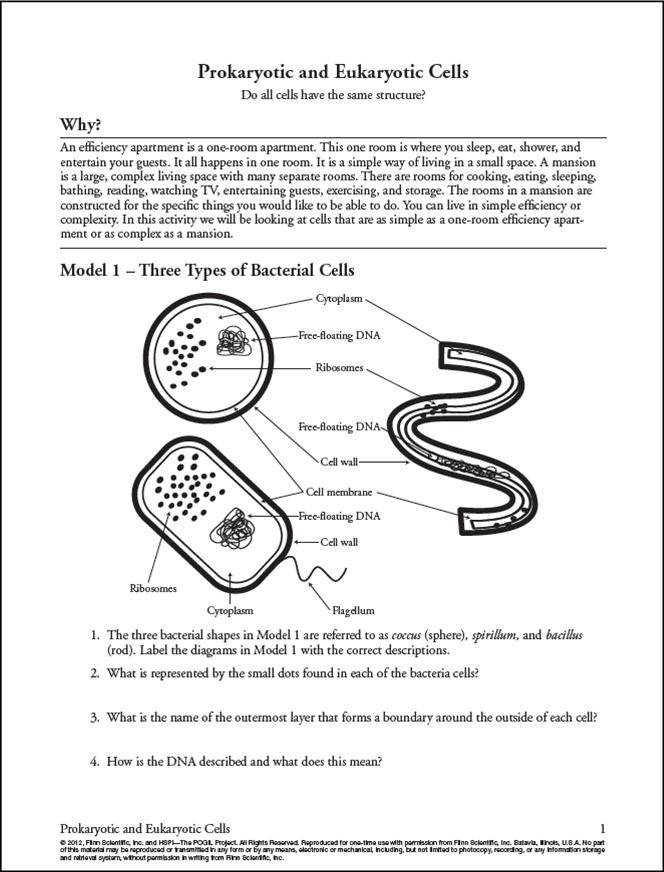
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Answer Key POGIL
- The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
- DNA and RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
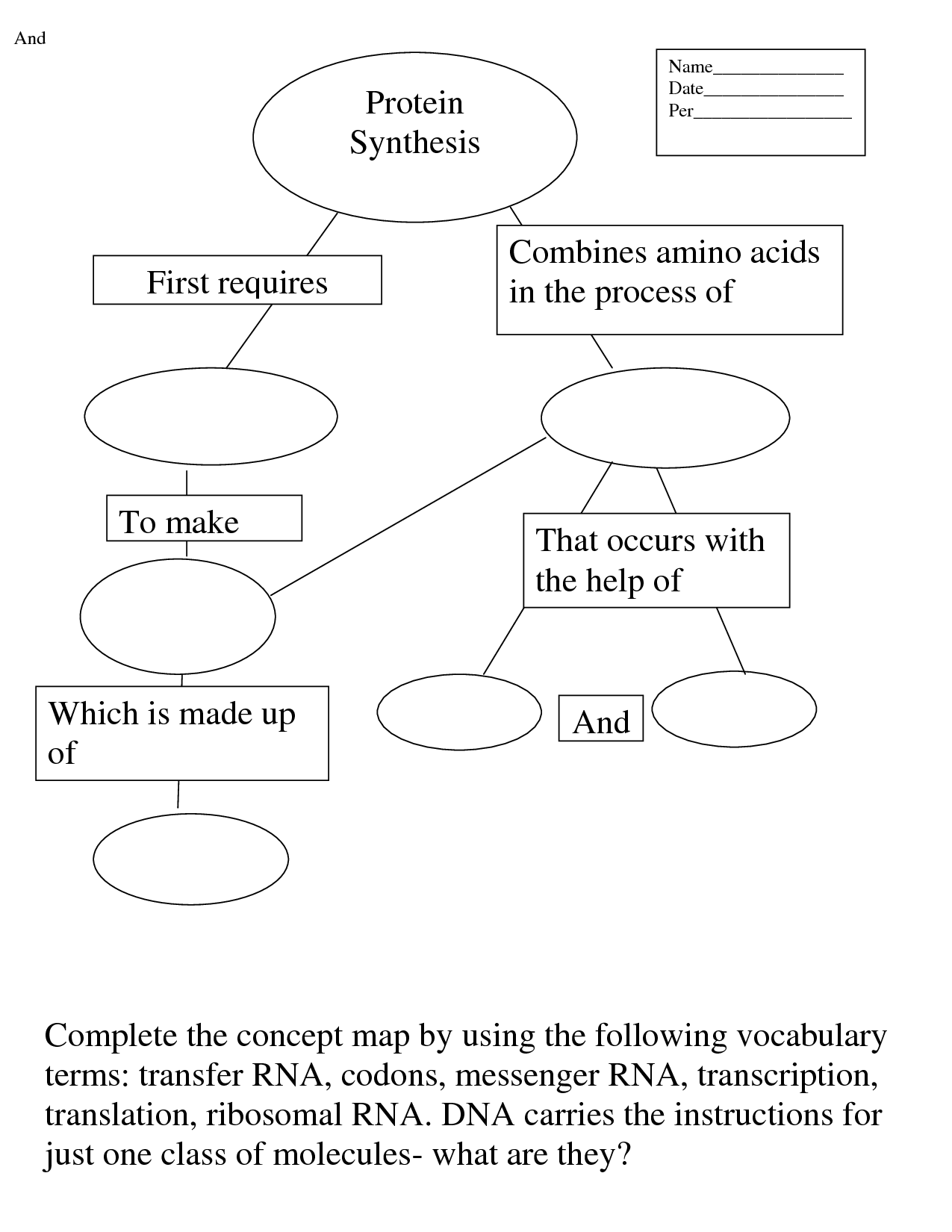
- Protein Synthesis Concept Map
- Protein Synthesis Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. It is the linear chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. This primary structure is fundamental to a protein's overall three-dimensional structure and ultimately determines its function in biological processes.
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
The secondary structure of a protein refers to the local folded structures within a polypeptide chain, specifically the alpha helices and beta sheets. These structures are formed through hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the protein sequence, leading to the coiling of the chain (alpha helix) or the folding of the chain into a pleated sheet (beta sheet). The secondary structure plays a crucial role in determining the overall three-dimensional shape and function of the protein.
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The tertiary structure of a protein is the three-dimensional arrangement of all the atoms in the protein, including the folding of the secondary structures (alpha helices and beta sheets) into a unique overall shape. This structure is critical for the protein's function as it determines its specific active sites, binding sites, and overall conformation, which allow it to interact with other molecules or perform specific biological functions in the cell.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The quaternary structure of a protein refers to the arrangement of multiple individual protein subunits (polypeptide chains) and any associated molecules in a complex, functional protein assembly. This higher level of protein structure involves the interaction and binding of multiple protein subunits to form a larger, biologically active protein complex. The quaternary structure affects the overall function and stability of the protein, allowing it to perform its specific role within the cell or organism.
How is protein folding governed?
Protein folding is governed by various factors including the amino acid sequence, physicochemical properties of the amino acids, environmental conditions such as temperature and pH, as well as the presence of chaperone proteins. These factors influence the folding process by determining the interactions between different parts of the protein chain, leading to the formation of the final three-dimensional structure that is crucial for the protein's function.
What is denaturation of a protein?
Denaturation of a protein is the disruption of its native structure, leading to loss of its biological activity. This can be caused by factors such as heat, pH changes, or exposure to certain chemicals, which break the bonds necessary for the protein to maintain its three-dimensional shape and function. Denaturation can result in irreversible changes to the protein, rendering it non-functional.
What are the functions of proteins in the body?
Proteins have various important functions in the body, including building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, acting as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, transporting molecules like oxygen in the blood, and serving as hormones to regulate cell processes. Proteins also play a role in cell signaling, maintaining fluid balance, and providing structure and support to cells and tissues. Overall, proteins are essential for the proper functioning of the human body.
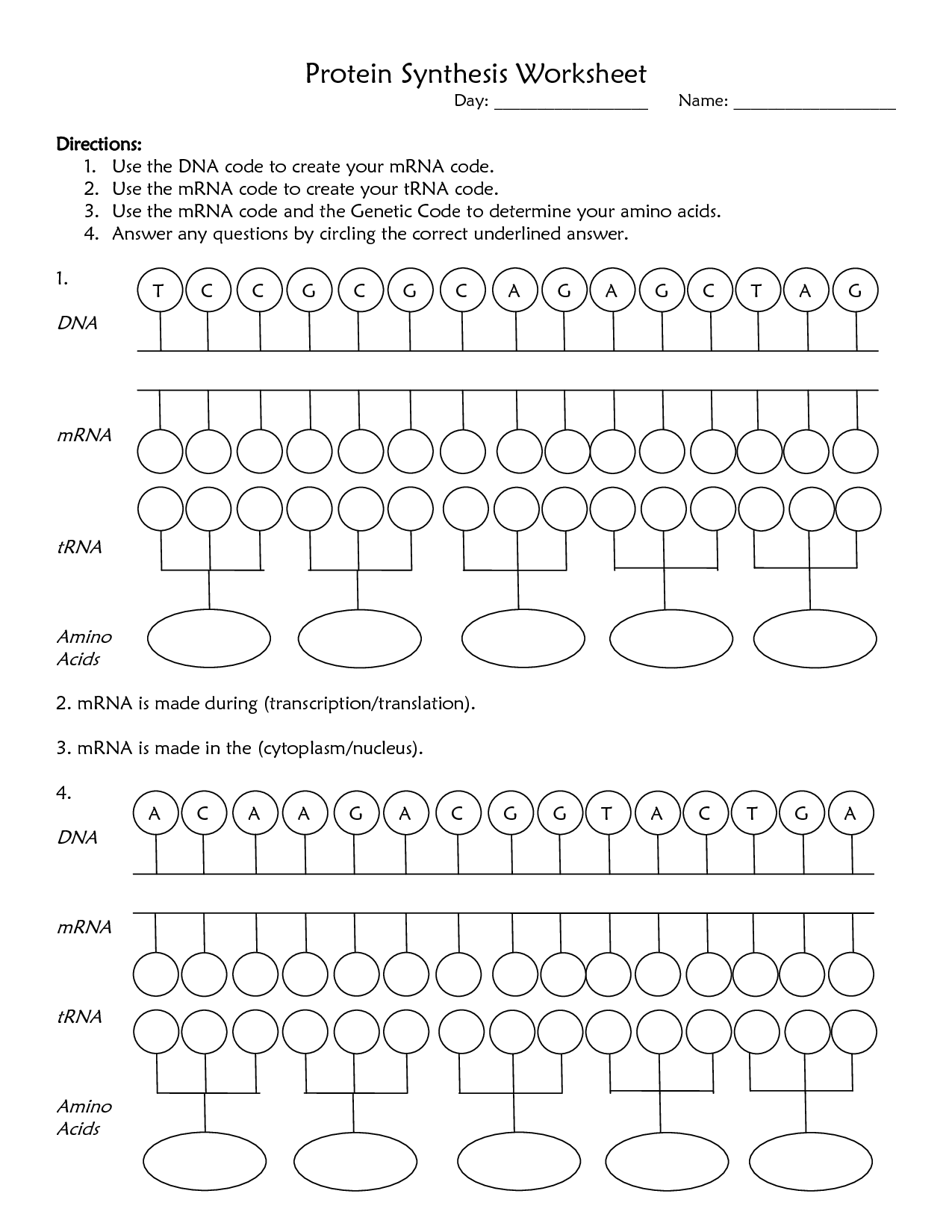
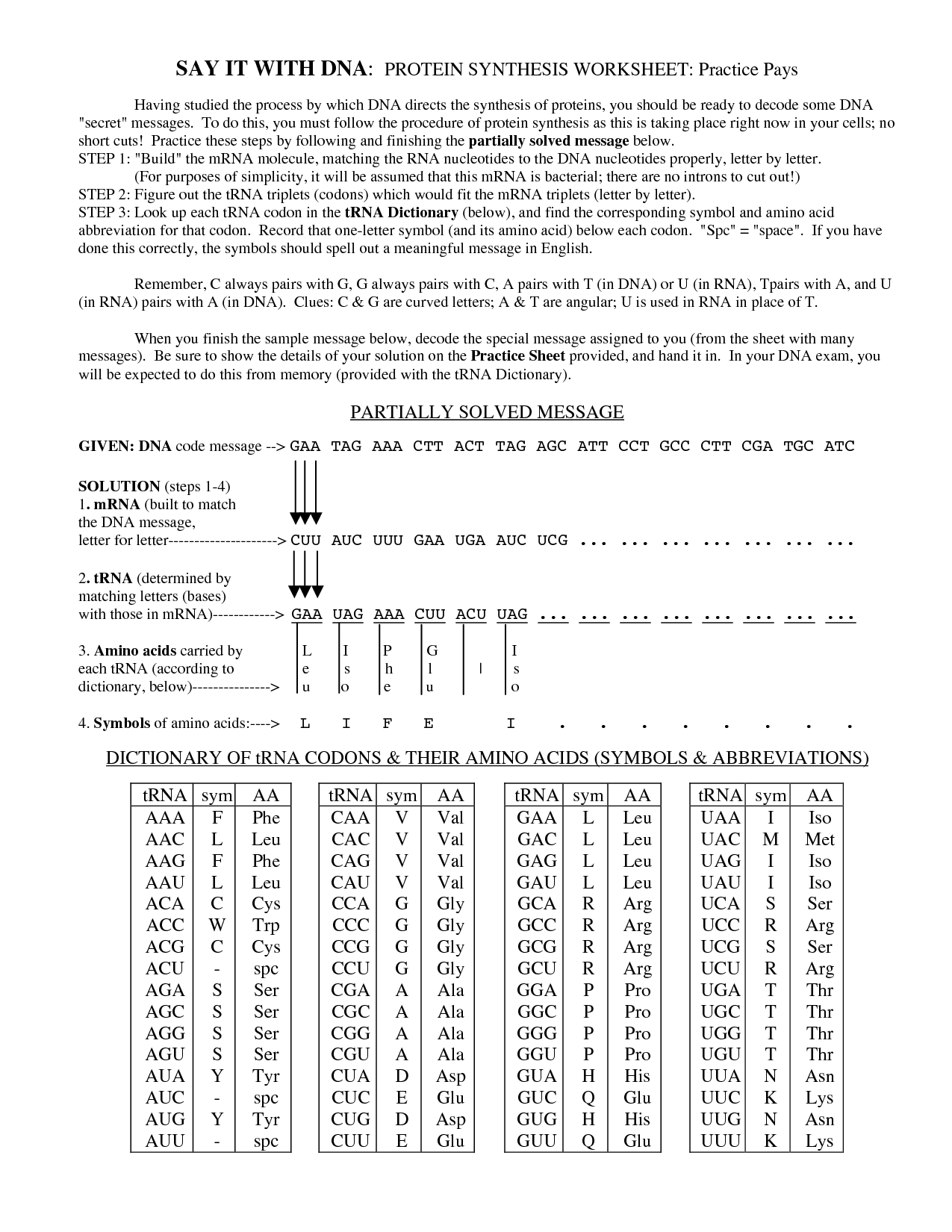
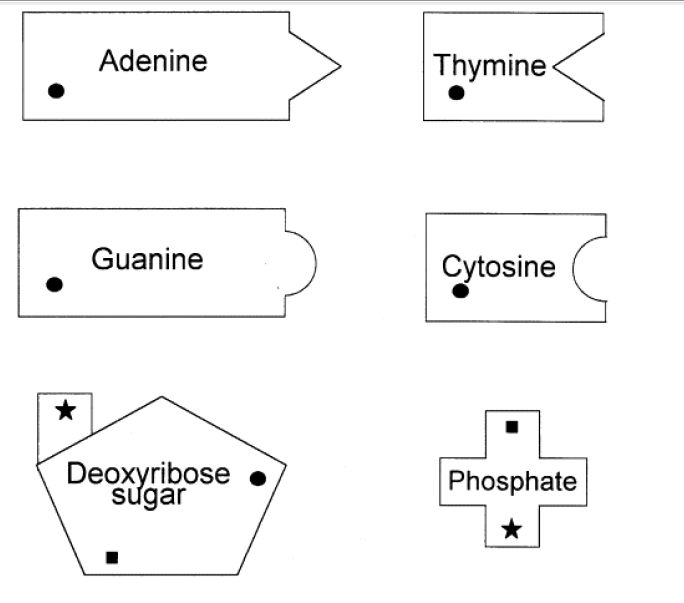
What is protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells make proteins, using the information encoded in DNA. It involves two main steps: transcription, where a copy of the gene is made in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA), and translation, where the mRNA is read by ribosomes to build a specific sequence of amino acids that make up a protein molecule. This process is essential for cell growth, repair, and overall functioning in living organisms.
How do proteins interact with other molecules?
Proteins can interact with other molecules through various mechanisms such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions, and electrostatic interactions. These interactions can influence the structure, stability, and function of proteins. Proteins can bind to other molecules specifically through sites on their surfaces, which allows for the recognition of substrates, ligands, or other protein partners. The nature of the interaction between a protein and another molecule is dependent on the composition of their respective chemical groups and the environmental conditions in which the interaction occurs.
What are some common techniques used to study proteins?
Some common techniques used to study proteins include x-ray crystallography for determining the 3D structure of proteins, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for analyzing protein dynamics and interactions, mass spectrometry for identifying and quantifying proteins, Western blotting for detecting specific proteins in a sample, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for measuring protein concentrations, and chromatography techniques such as size-exclusion and affinity chromatography for separating and purifying proteins.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments