Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is a fundamental concept in biology. This worksheet provides a thorough exploration of the key features and functions of these two types of cells, making it an ideal learning resource for students or anyone seeking a comprehensive review of cell structures and characteristics.
Table of Images 👆
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Worksheet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure Worksheet
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function
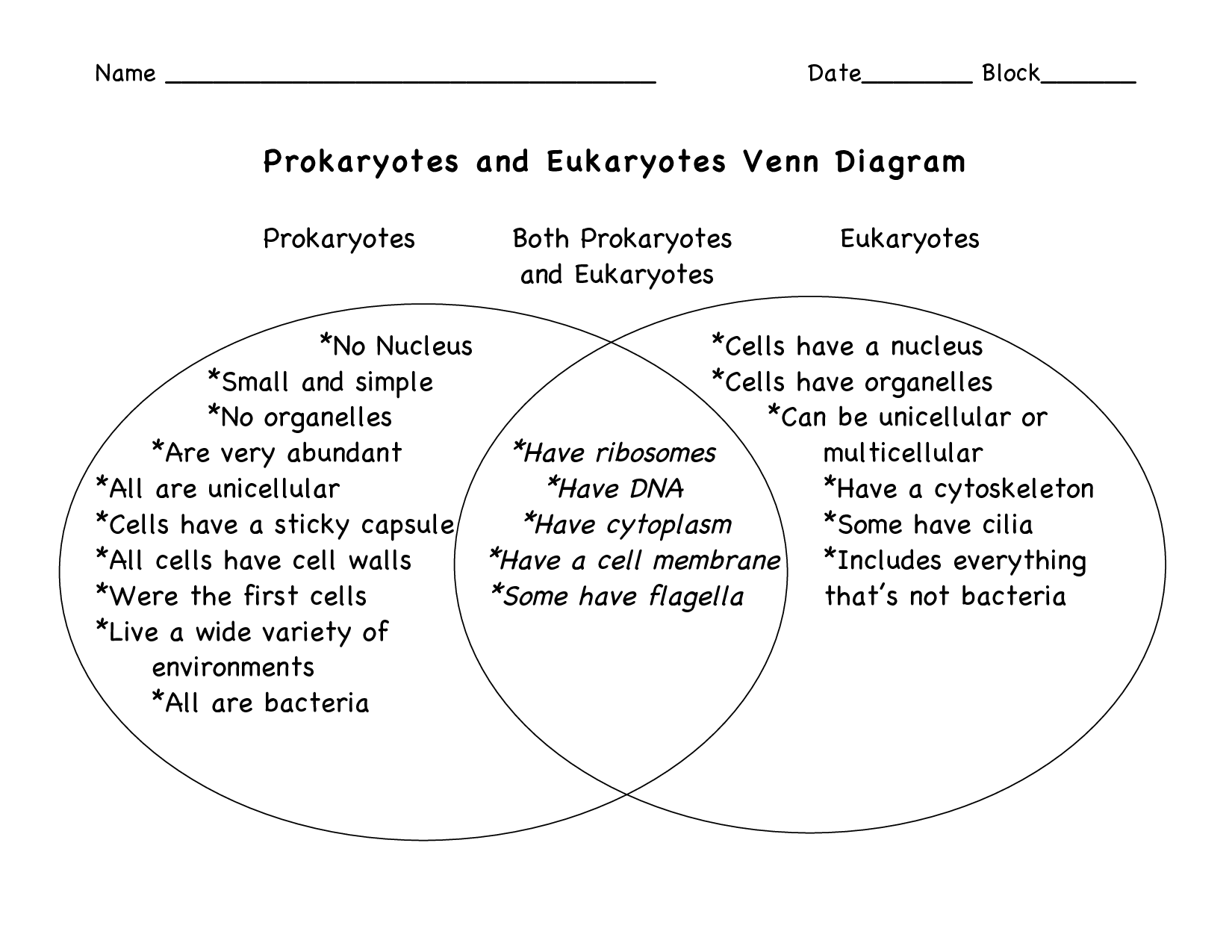
- Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Venn Diagram
- Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Venn Diagram
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Venn Diagram
- Prokaryotic Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- Eukaryotic Cell Coloring
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell Diagrams
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
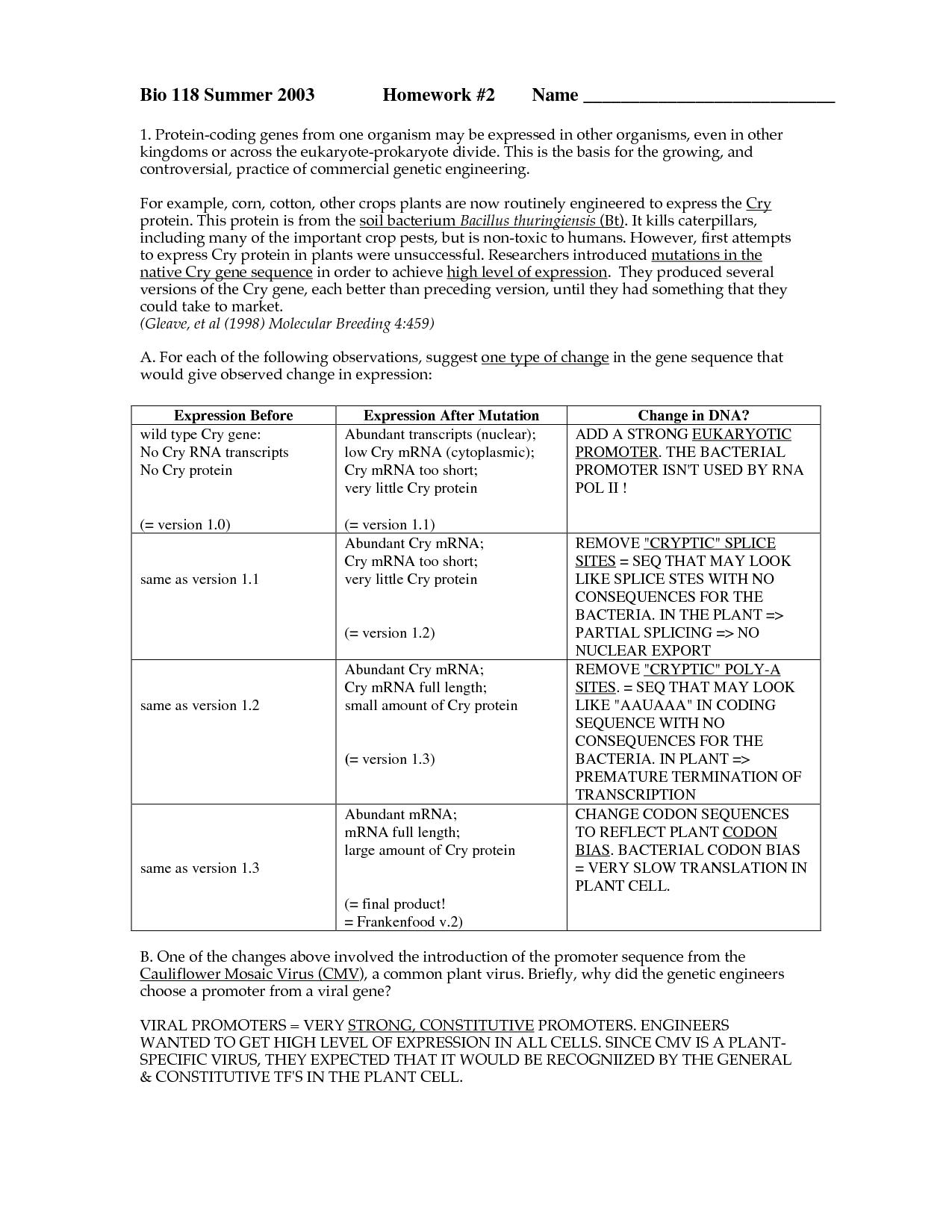
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
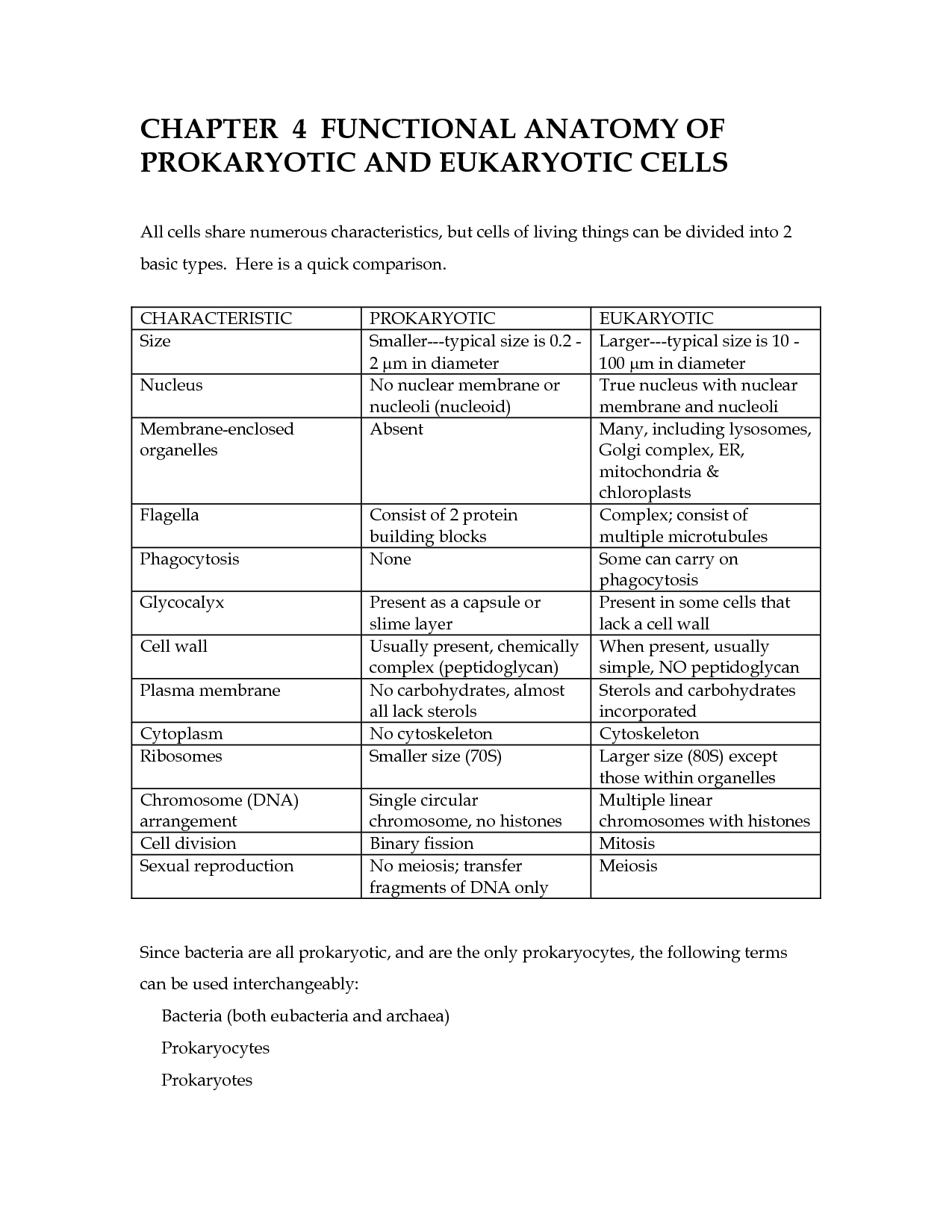
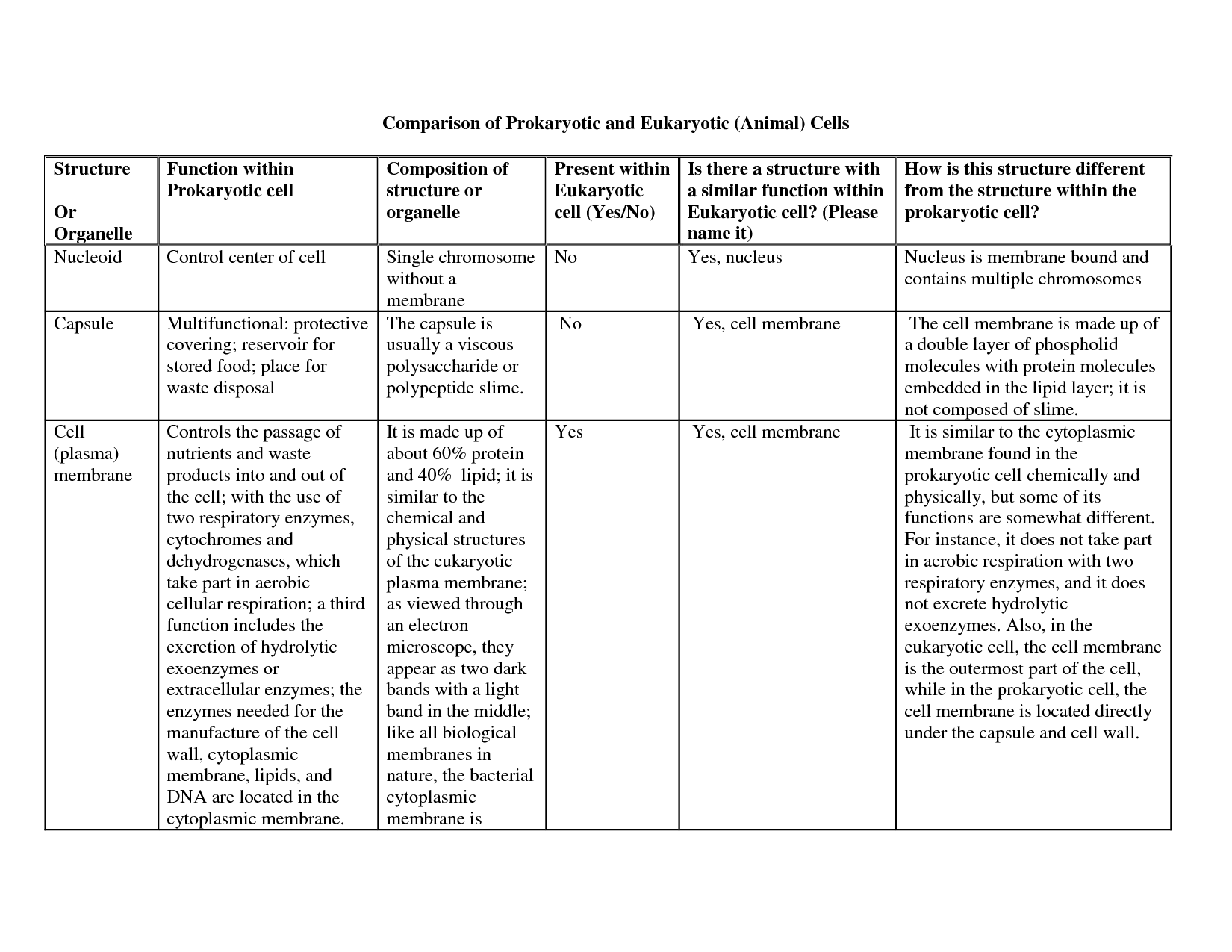
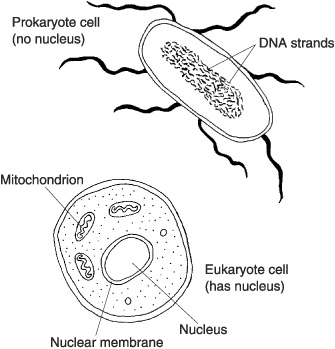
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a true nucleus: eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus that houses their genetic material, while prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and their genetic material is located in the nucleoid region of the cell. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are typically larger and more complex, with membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, while prokaryotic cells lack these organelles and are generally smaller and simpler in structure.
Describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell.
A prokaryotic cell is a single-celled organism without a distinct nucleus. Its genetic material is located in a region called the nucleoid, which is not enclosed within a membrane. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum, but may have ribosomes, flagella, and a cell wall. They are typically smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of the cell wall in prokaryotes?
The cell wall in prokaryotes provides structural support and protection to the cell, maintaining its shape and preventing it from bursting due to changes in osmotic pressure. It also helps in preventing harmful substances from entering the cell and provides a barrier against hostile environments.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce through a process called binary fission, where a single prokaryotic cell divides into two identical daughter cells. During binary fission, the prokaryotic cell copies its genetic material, then divides into two cells, each containing one copy of the genetic material. This results in two genetically identical offspring cells being produced from the parent cell.
What organelles are present in eukaryotic cells but absent in prokaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes, which are absent in prokaryotic cells. These membrane-bound organelles compartmentalize different cellular functions, providing eukaryotic cells with increased complexity and efficiency in carrying out various biological processes.
Explain the role of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that houses the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It serves as the control center of the cell, regulating gene expression, DNA replication, and cell division. The nucleus also plays a crucial role in coordinating various cellular activities by transmitting genetic information to ribosomes in the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. Ultimately, the nucleus is essential for the cell's overall function and survival.
Describe the basic structure of a eukaryotic cell.
A eukaryotic cell has a true nucleus that houses the cell's genetic material, enclosed within a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The cell also contains various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts in plant cells. The cytoplasm, which fills the cell and surrounds the organelles, contains the cytoskeleton that provides structure and shape to the cell. Eukaryotic cells also have a plasma membrane that encloses the entire cell and regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cell.
How do eukaryotic cells obtain energy for cellular processes?
Eukaryotic cells obtain energy for cellular processes primarily through the process of cellular respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, the cell's main energy currency. This process occurs in the mitochondria, where a series of complex reactions take place to convert glucose into usable energy in the form of ATP. Additionally, eukaryotic cells can also generate energy through processes such as fermentation in the absence of oxygen, but this is less efficient compared to cellular respiration.
What is the advantage of having membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells?
Having membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells allows for compartmentalization of different cellular functions. This segregation enables specialized environments for various processes to occur simultaneously within the cell, enhancing efficiency and organization. Additionally, the membranes help protect the cell's internal structures and contents, regulate the exchange of materials, and facilitate communication and coordination between different organelles, ultimately promoting cellular complexity and functionality.
Compare and contrast the size of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller in size compared to eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells typically have a diameter of 1-10 micrometers, while eukaryotic cells are larger, ranging from 10-100 micrometers in diameter. Additionally, eukaryotic cells often have more complex structures and organelles, which contribute to their larger size and increased complexity compared to the simpler prokaryotic cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments