Printable Worksheets Muscle Anatomy
Printable worksheets on muscle anatomy are a helpful resource for students studying biology or anyone wanting to expand their knowledge of human anatomy. These worksheets provide a clear and concise way to learn about the different muscles in the body and their functions. Whether you are a student looking to reinforce your understanding or an educator searching for teaching materials, printable muscle anatomy worksheets offer a convenient and comprehensive tool.
Table of Images 👆
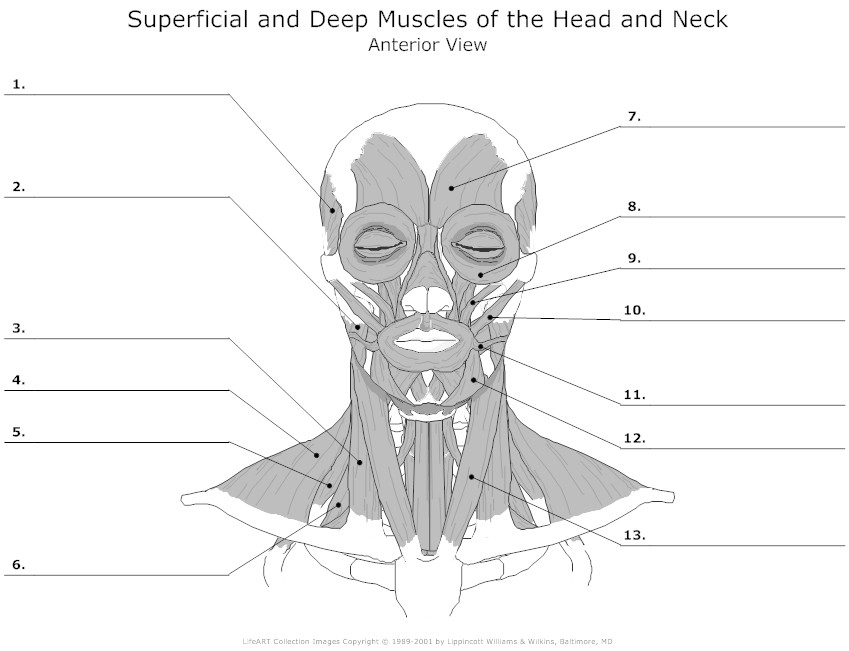
- Blank Head and Neck Muscles Diagram
- Anatomy Coloring Book Pages
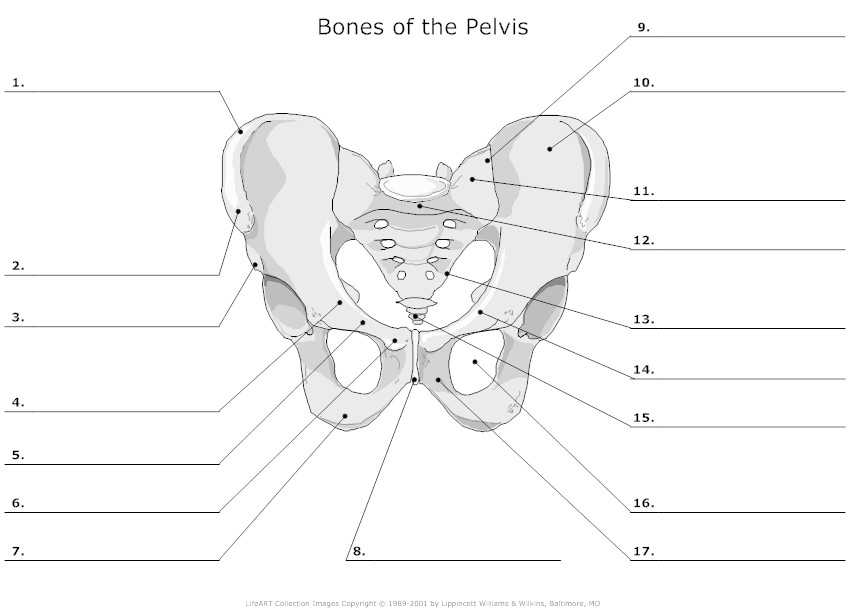
- Unlabeled Pelvis Bone Anatomy
- Anatomy Muscle Worksheets Printable
- The Human Skeleton System Labeled Bones
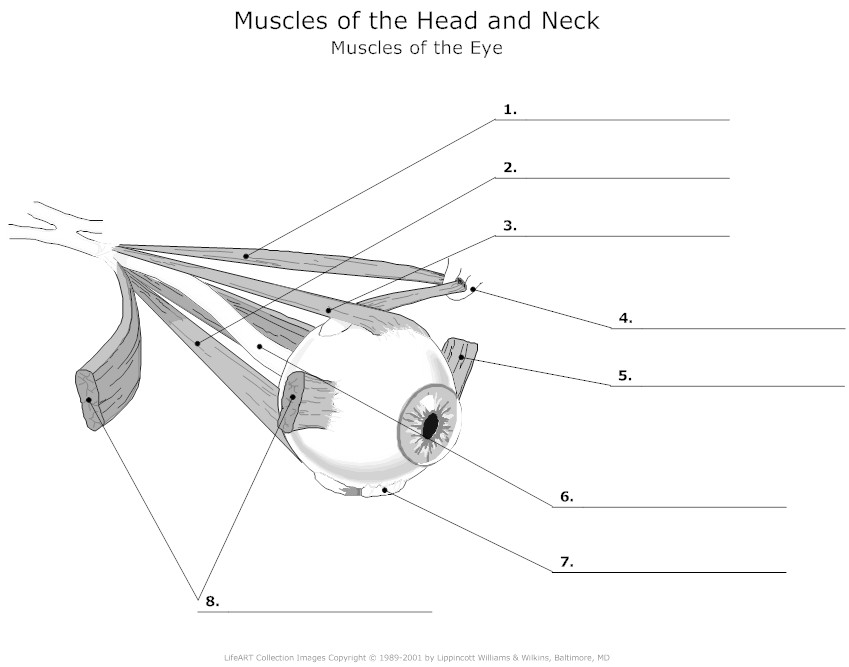
- Eye Muscles Diagram Unlabeled
- Human Body Organs Worksheets
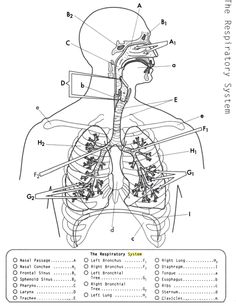
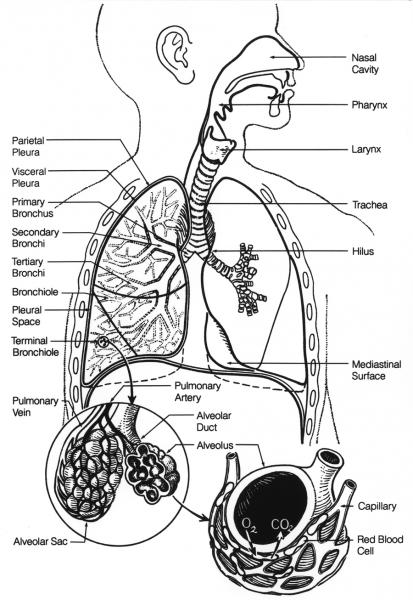
- Respiratory System Diagram Worksheets
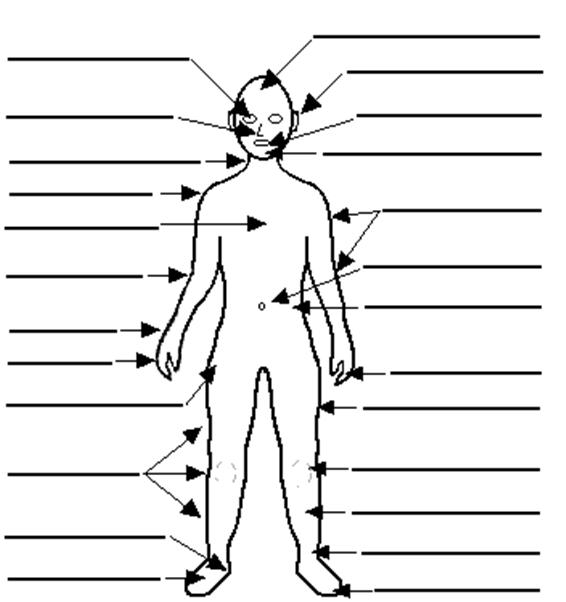
- Body Pressure Points
- Lung Respiratory System Diagram
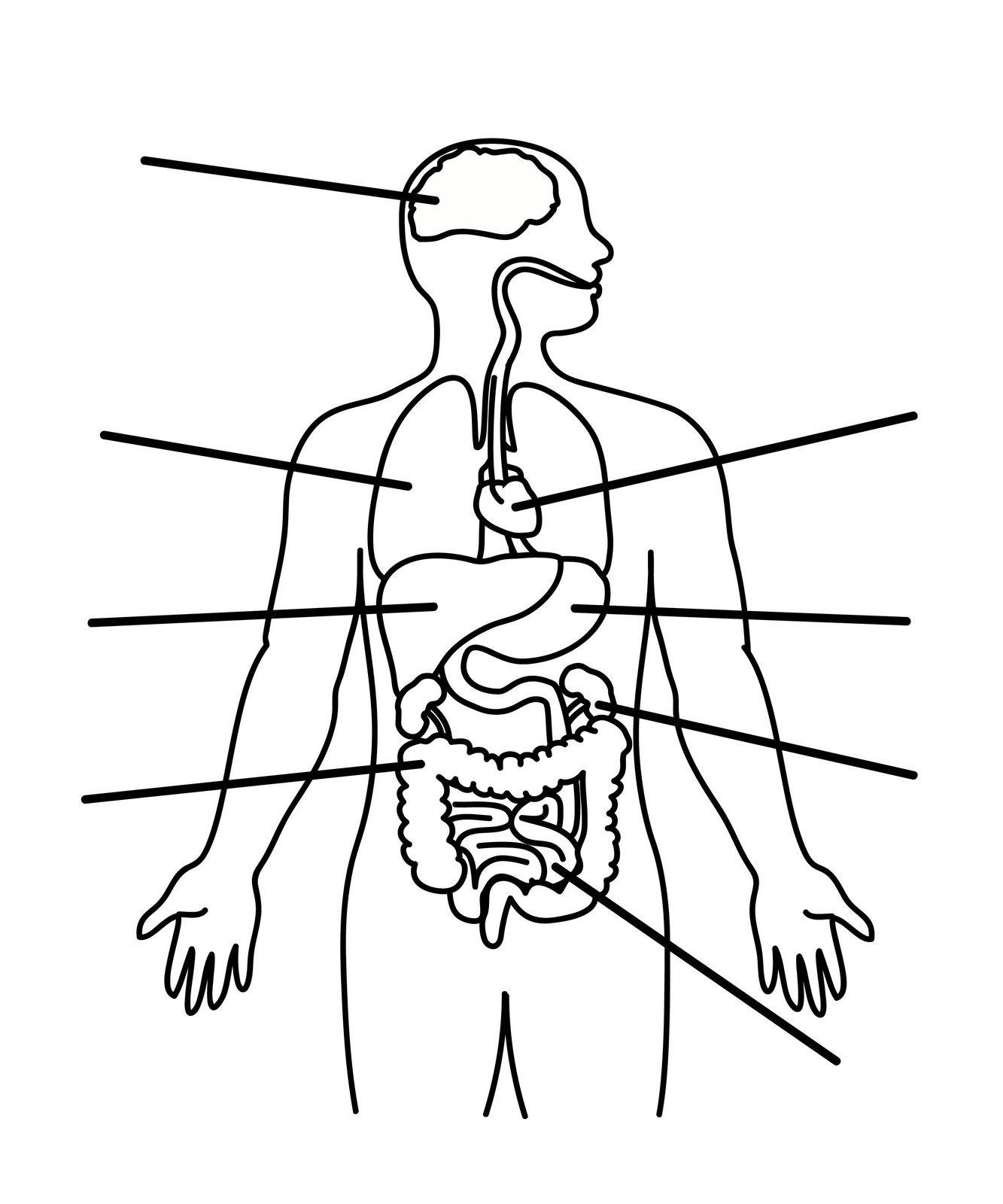
- Blank Human Body Parts Diagram
- Freely Movable Joints Functional Classification
- Names Horse Face Markings
- Names Horse Face Markings
- Names Horse Face Markings
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What does the term "muscle anatomy" refer to?
The term "muscle anatomy" refers to the study of the structure, function, and relationships of muscles in the human body. It involves understanding the different types of muscles, their attachments, blood supply, and innervation, as well as how they work together to produce movement and stability.
How are muscles classified in terms of their structure?
Muscles are classified into three main types based on their structure: skeletal muscles, which are attached to bones and facilitate movement; smooth muscles, found in organs and blood vessels and responsible for involuntary movements like digestion; and cardiac muscles, exclusive to the heart, enabling it to pump blood. Each type of muscle has specific characteristics and functions based on its structure and location in the body.
What is the role of tendons in muscle anatomy?
Tendons are strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that attach muscles to bones, playing a crucial role in muscle anatomy by transferring the force generated by muscles to the bones they are attached to. They provide stability and transmit muscle contractions to produce movement, allowing for coordinated and efficient musculoskeletal functions. Additionally, tendons also help in maintaining joint integrity and providing support during physical activities.
What are the main types of muscle tissue found in the human body?
The main types of muscle tissue found in the human body are skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for voluntary movements. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of organs and blood vessels, and is responsible for involuntary movements such as peristalsis.
How do muscles work together to produce movement?
Muscles work together to produce movement through a process called muscle coordination. This coordination involves the activation of different groups of muscles to work in sync, ensuring smooth and efficient movement. When a movement is initiated, the brain sends signals to the specific muscles involved, causing them to contract and produce force. Synergistic muscles work together to create the desired movement, while antagonist muscles work in opposition to control and stabilize the motion. This cooperative effort allows for precise and coordinated movements to be executed.
What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles?
Voluntary muscles are under conscious control, such as skeletal muscles that allow us to move our limbs, while involuntary muscles are not under conscious control, such as cardiac muscle in the heart or smooth muscle in the digestive system that work automatically without us having to consciously think about them.
How are muscles named based on their location or function?
Muscles are named based on their location or function to provide a clear indication of their anatomy or purpose. Location-based names often refer to the specific body part the muscle is near, such as the biceps brachii in the arm. Function-based names describe what the muscle does, like the flexor muscles that bend a joint. These naming conventions help healthcare professionals and anatomists easily identify and understand the muscles and their roles in the body.
What are the different levels of organization in muscle anatomy, from largest to smallest?
The different levels of organization in muscle anatomy, from largest to smallest, are muscle, fascicle, muscle fiber (myofiber), myofibril, sarcomere, and myofilaments (actin and myosin).
What are the major muscle groups in the human body and their functions?
The major muscle groups in the human body include the deltoids, biceps, triceps, pectorals, latissimus dorsi, abdominals, obliques, quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteals, and calves. These muscles serve various functions such as movement, stability, support, flexibility, and overall posture. They work together to allow us to perform tasks like walking, running, lifting, pushing, pulling, and maintaining balance. Strengthening and conditioning these muscle groups through exercise is important for overall health and well-being.
How can understanding muscle anatomy be beneficial in sports, fitness, and rehabilitation?
Understanding muscle anatomy is beneficial in sports, fitness, and rehabilitation as it helps individuals optimize their training, performance, and recovery. By knowing the specific muscles being targeted in exercises, athletes can tailor their workouts to strengthen weak areas, improve muscle function, and prevent injuries. In rehabilitation, knowledge of muscle anatomy aids in creating effective rehabilitation programs, targeting specific muscle groups to regain strength and mobility after an injury. Overall, understanding muscle anatomy allows individuals to train more effectively, enhance their performance, and promote overall physical well-being in sports, fitness, and rehabilitation settings.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments