Present Perfect Past Simple Worksheets
Looking for worksheets to practice present perfect and past simple? Look no further! We have a wide range of engaging and comprehensive worksheets designed to help learners of English master these grammatical concepts. Whether you are a student wanting to practice on your own, a teacher looking for materials to supplement your lessons, or a parent supporting your child's language learning journey, our worksheets are just what you need.
Table of Images 👆
- Past Perfect Tense Exercises
- Present Perfect Past Simple Test
- Simple Past Tense Exercises
- Present Simple Structure
- Present Perfect Past Simple
- Simple Past vs Present Perfect Continuous Exercises PDF
- Present Continuous Exercises
- Present Continuous Exercises
- Spanish Present Perfect Worksheet
- Present Perfect Tense Test Coz
- Past Tense Verb Worksheet
- All About Me Graphic Organizer Timeline
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
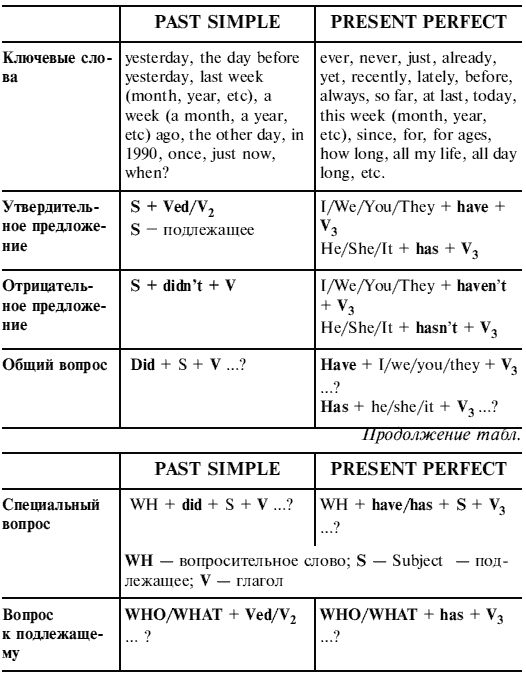
What is the main difference between present perfect and past simple tense?
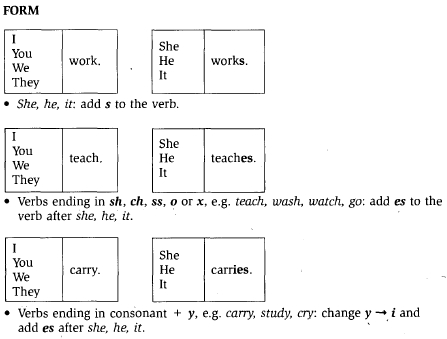
The main difference between present perfect and past simple tense is that present perfect is used to connect the past with the present, indicating a relevance to the present moment, while past simple is used to talk about specific actions or events that happened at a definite time in the past. Additionally, present perfect is formed with the auxiliary verb "have" (or "has" for third person singular) followed by the past participle of the main verb, whereas past simple is formed by using the past form of the verb.
How do we form the present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb "have" (or "has" for the third person singular) followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example, "I have seen", "She has eaten", "They have studied". This tense is used to indicate actions that were completed in the past but have relevance to the present, or actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
When do we use the past simple tense?
The past simple tense, also known as the simple past tense, is used to describe actions that were completed at a specific point in the past. We use this tense to talk about actions that happened at a definite time in the past or actions that were completed in the past and are not continuing into the present. It is also used to narrate a series of events that occurred in the past.
Can present perfect and past simple be used to talk about finished actions?
Yes, both present perfect and past simple can be used to talk about finished actions. The past simple is typically used to talk about actions that happened at a specific time in the past, while the present perfect is used to show a connection between past actions and the present or to talk about actions that have just been completed.
What is the significance of time expressions when using present perfect and past simple?
Time expressions play a crucial role in distinguishing between the present perfect and past simple tenses in English. Present perfect is used to talk about past actions or experiences that have a connection to the present moment, often indicated by time expressions such as "just," "already," "ever," and "never." On the other hand, past simple is used for actions or events that are completed in the past and not relevant to the present, typically with time expressions like "yesterday," "last week," and "in 1999." Therefore, selecting the appropriate time expression helps convey the intended meaning and timeframe of the action being described in a sentence.
What type of verbs are commonly used with present perfect tense?
Common types of verbs used with present perfect tense are action verbs, state verbs, and stative verbs. These verbs are used to describe actions or states that have occurred at an unspecified time in the past, emphasizing more on the result of the action rather than the time it took place. Examples include "have seen," "has lived," "have been," "has worked," and "have known.
Can present perfect and past simple be used to talk about past experiences?
Yes, both present perfect and past simple can be used to talk about past experiences. Present perfect is typically used when the exact time of the experience is not specified or is considered to be relevant to the present moment. On the other hand, past simple is used when the exact time of the experience is specified or the focus is on a specific point in the past. Both tenses are valid options to convey past experiences, depending on the context and emphasis you want to place on the timeline of events.
How do we form negative sentences in present perfect and past simple?
To form negative sentences in present perfect, you typically use "have not" or "has not" followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example: "I have not seen the movie." In the past simple tense, you use "did not" followed by the base form of the main verb. For example: "She did not finish her homework.
Can we use specific time expressions with present perfect tense?
Yes, it is common to use specific time expressions with the present perfect tense. This tense is often used to talk about actions or events that have happened at an unspecified time in the past but are connected to the present moment. Specific time expressions such as "today," "this week," "recently," or "in the past few years" can be used to give more context and detail to when the action took place.
Which tense is commonly used when talking about recent events or actions?
The present perfect tense is commonly used when talking about recent events or actions that have a connection to the present moment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments