Population Genetics Worksheet
Are you a student studying population genetics? If so, you're likely no stranger to the complex concepts and calculations involved in understanding the genetic makeup of a population. With so many different variables to consider, having a reliable and comprehensive worksheet can be essential for organizing your thoughts and tackling the subject matter effectively. In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of worksheets in population genetics studies and highlight some key features that make them a valuable tool for students in this field.
Table of Images 👆
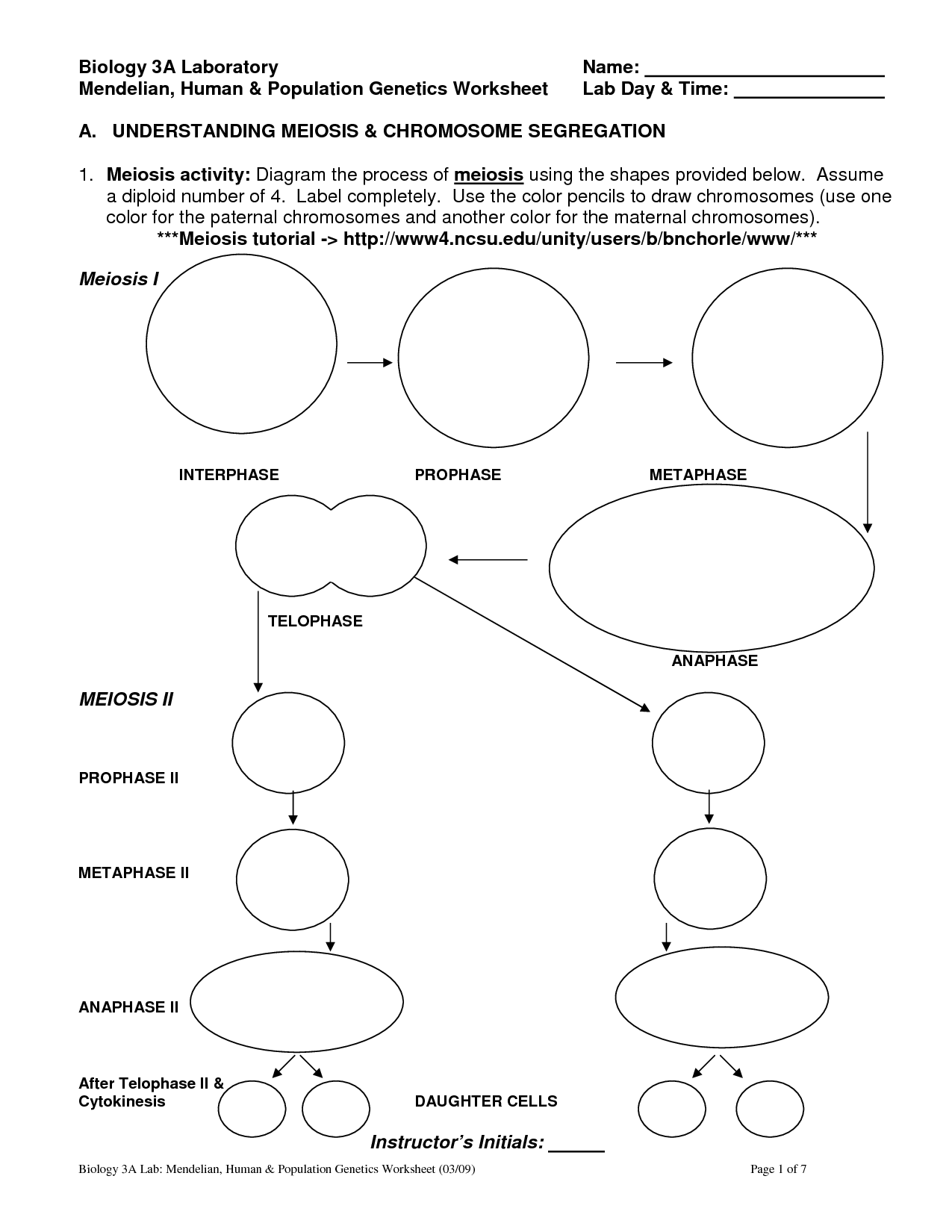
- Meiosis Coloring Worksheet
- Genetics and Heredity Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Variation Worksheet Answers
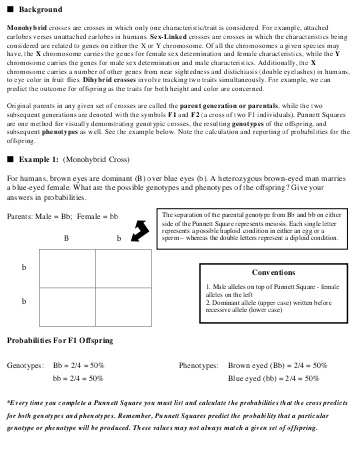
- Hardy-Weinberg Practice Problems Worksheet
- Genetic Drift Worksheet
- Population Genetics Lab Answers
- Ecosystem Population Worksheet
- Inherited Traits Worksheets
- Bikini Bottom Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Introduction to Genetics Worksheet
- Bacteria and Viruses Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics of Inheritance Patterns Worksheet
- Spelling Code Worksheet
- Answer Key Chapter 16 Evolution of Population
- Population Genetics Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is population genetics?
Population genetics is a branch of genetics that studies the genetic composition of populations and how genetic variation changes over time within a population. It explores how gene frequencies, traits, and genetic diversity evolve in a group of interbreeding individuals, incorporating principles from genetics, ecology, and evolution to understand patterns of genetic variation and the mechanisms driving them.
What are the sources of genetic variation in a population?
The sources of genetic variation in a population include mutations, which are random changes in DNA sequences; genetic recombination during meiosis, where maternal and paternal genetic material mix; and gene flow, which is the movement of genes between populations through migration. These processes contribute to the diversity of genes within a population, allowing for adaptation to changing environments and driving evolutionary change.
What is genetic drift and how does it impact population genetics?
Genetic drift is a random process in which allele frequencies within a population change due to chance events. It can have significant impacts on population genetics by leading to the loss of genetic diversity, especially in small populations, and influencing the evolution of a population through the fixation of certain alleles. Over time, genetic drift can lead to the divergence of populations and contribute to the genetic structure of species.
What is gene flow and how does it affect genetic diversity within a population?
Gene flow is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another through the movement of individuals or their gametes. This process can increase genetic diversity within a population by introducing new alleles from the outside gene pool. As gene flow continues, it can prevent populations from becoming genetically isolated and can promote the mixing of different genetic variations, reducing the chances of inbreeding and maintaining genetic variation within the population.
What are the different types of natural selection and how do they shape population genetics?
The different types of natural selection are directional selection, stabilizing selection, and disruptive selection. Directional selection favors individuals with traits at one extreme of the distribution, shifting the population towards that direction. Stabilizing selection favors individuals with intermediate traits, maintaining the status quo of the population. Disruptive selection favors individuals with extreme traits, leading to the diversification of the population into two or more distinct phenotypes. These types of natural selection shape population genetics by influencing the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population, driving evolutionary changes by selecting for advantageous traits that increase an individual's fitness in a given environment.
How does mutation contribute to genetic variation within a population?
Mutation contributes to genetic variation within a population by introducing new alleles or genetic traits into the gene pool. When a mutation occurs in the DNA sequence of an organism, it can lead to changes in the protein structure or gene expression, resulting in different characteristics or phenotypes. These variations can be inherited and passed down to offspring, contributing to the overall genetic diversity of the population. Over time, accumulation of mutations can drive evolutionary changes and adaptation to different environments.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle and what does it tell us about population genetics?
The Hardy-Weinberg principle is a fundamental concept in population genetics that describes the allele frequencies in a population that is not undergoing any evolutionary change. It states that in a large, randomly mating population with no selection, migration, or mutation, the genotype frequencies will remain constant from generation to generation. Deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can reveal factors such as selection, genetic drift, or gene flow that are affecting the genetic makeup of a population, providing insights into evolutionary processes and patterns.
What is founder effect and how does it influence genetic diversity in newly established populations?
The founder effect is a type of genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population isolated from the original population. Due to the limited genetic diversity of the founder population, the new population may display reduced genetic variation compared to the original population. This can lead to certain alleles becoming more common or being lost entirely in the new population, resulting in a less diverse gene pool overall. Over time, genetic diversity may evolve through mutation, genetic recombination, and natural selection, but the initial founder effect can have a lasting impact on the genetic makeup of newly established populations.
What is genetic bottleneck and how does it impact genetic variation within a population?
A genetic bottleneck is a significant reduction in the gene pool of a population due to a sharp decrease in population size, often caused by events like natural disasters or human activities. This reduction can lead to a loss of genetic diversity as certain alleles are lost, making the population more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes. It can also increase the prevalence of genetic disorders and reduce the overall adaptability of the population to evolving conditions, ultimately impacting its long-term survival and evolution.
How can population genetics be applied in understanding human evolution and disease susceptibility?
Population genetics can be applied in understanding human evolution and disease susceptibility by analyzing the genetic variation within and between populations. By studying the distribution of genetic polymorphisms, researchers can identify genetic changes that have occurred over time and understand how these changes have influenced human evolution. Additionally, population genetics can help identify genetic variants associated with increased susceptibility to certain diseases, as well as how these variants have spread or been selected for in different populations. This information is crucial for understanding the genetic basis of disease susceptibility and developing personalized medicine approaches to prevent and treat diseases.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments