Physical Science Energy Worksheet
Are you a physical science student or educator in search of a comprehensive energy worksheet? Look no further! This blog post is perfect for you. We understand the importance of having a well-structured and informative resource to enhance your understanding of energy concepts in physical science. In this post, we will introduce you to a high-quality energy worksheet that covers various topics related to energy, ensuring a solid foundation in this critical subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Science Worksheets Energy Transformation
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet
- Work and Simple Machines Worksheets
- Science Worksheets Heat Energy
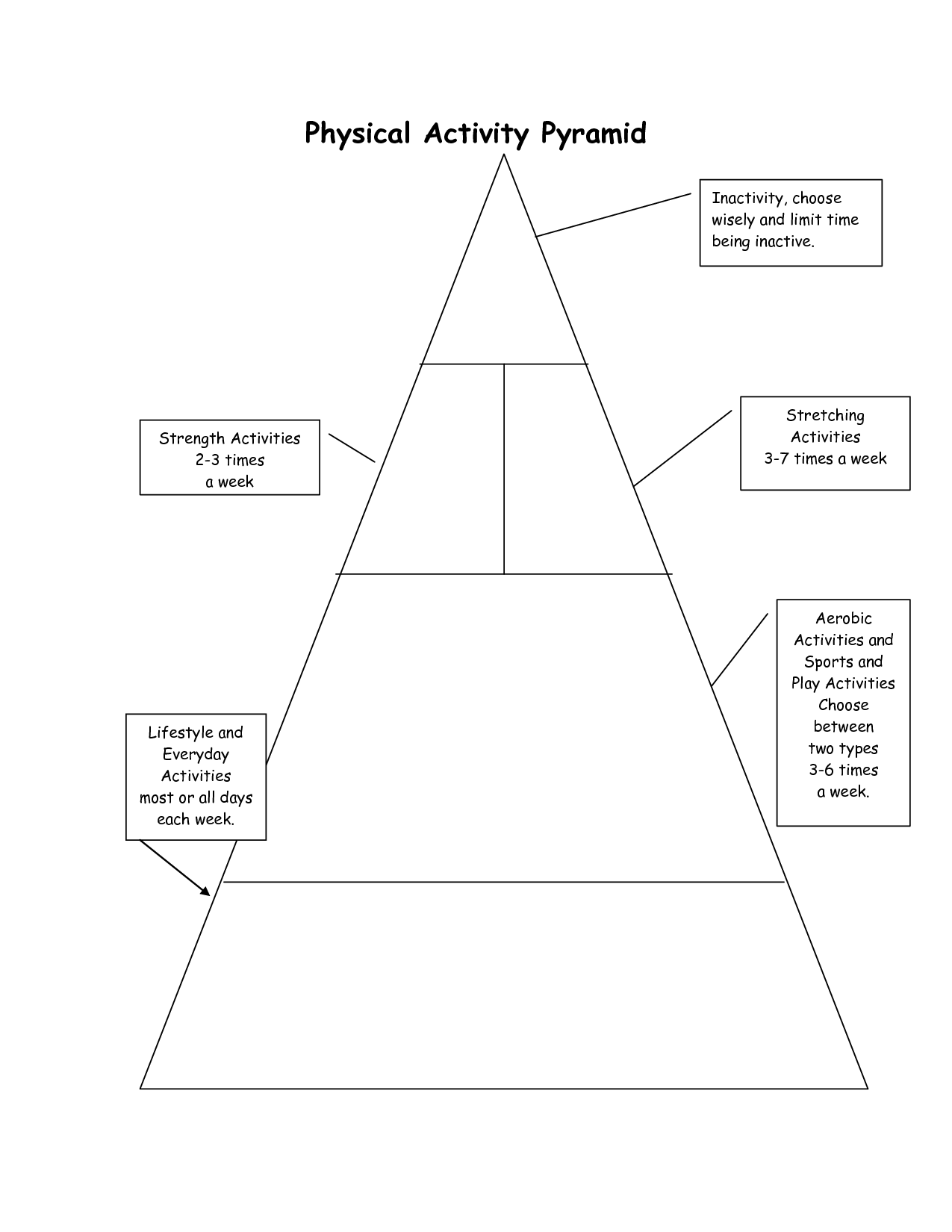
- Physical Activity Pyramid Worksheet
- Glencoe Chemistry Chapter Assessment Answers
- Science States of Matter Worksheets
- Science Properties of Matter Worksheets
- Physical and Chemical Property of Matter Worksheet
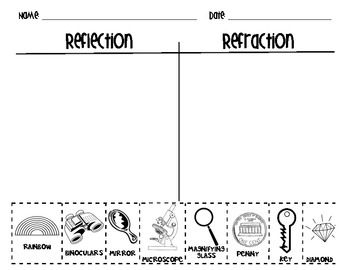
- Light Reflection and Refraction Worksheet
- Somerset Sheet Music Trumpet
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is energy?
Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. It exists in various forms, such as thermal, kinetic, potential, and electrical energy, and is necessary for all physical processes to occur in the universe. Energy is constantly transferred or converted from one form to another, but it is never created or destroyed, in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
What are the different forms of energy?
The different forms of energy include thermal energy (heat), mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy, radiant energy (light), and sound energy. These forms of energy can be categorized based on their source and how they are produced or transformed.
Define potential energy.
Potential energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position or state. It is a form of stored energy that can be transformed into kinetic energy when the object moves or changes position. Potential energy can exist in different forms, such as gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy, depending on the forces and interactions involved.
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is calculated as one-half the product of the object's mass and the square of its velocity. The higher the mass and velocity of the object, the greater its kinetic energy.
Explain the law of conservation of energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system; it can only change forms. This means that the total energy within a closed system remains constant over time, and energy can only be transformed from one form to another. Energy can be converted from potential to kinetic, mechanical to thermal, or between other forms, but the total amount of energy within the system will always remain the same.
How does thermal energy transfer occur?
Thermal energy transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. In conduction, heat is transferred through direct contact between particles in a material. Convection involves the movement of hot fluids or gases that carry thermal energy from one place to another. Lastly, radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, that do not require a medium to travel through. These three mechanisms work together to transfer thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one.
Describe the process of conduction.
Conduction is the process of heat transfer through a material by direct contact between particles. When one part of a material is heated, the particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate more, colliding with neighboring particles and transferring heat. This process continues throughout the material until thermal equilibrium is reached and the temperature is the same throughout. Conduction is more effective in solids as particles are closely packed and can easily pass on kinetic energy through collisions.
What is convection and how does it work?
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluid, such as air or water. In this process, the fluid near a heat source becomes warm and less dense, causing it to rise. As it rises, cooler fluid descends to take its place and gets heated, creating a continuous flow. This cycle of rising and falling fluid transfers heat energy from one area to another, making convection an important mechanism for distributing heat in fluids and gases.
Explain how radiation transfers energy.
Radiation transfers energy through electromagnetic waves, such as light, microwaves, and x-rays, that carry energy as they propagate through space. These waves have varying wavelengths and frequencies, with higher energy waves able to transfer more energy. When radiation encounters matter, it can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted, leading to the transfer of its energy to the material. This process is the basis for various applications in technology, such as in heating, communication, and medical imaging.
What are some examples of energy transformation in everyday life?
Energy transformation can be seen in a variety of everyday activities, such as when electrical energy powers a toaster to turn into thermal energy to make toast, or when mechanical energy from pedaling a bicycle is transformed into kinetic energy for movement. Another example is in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. Additionally, the conversion of food into mechanical energy for physical tasks and the transformation of gasoline into mechanical energy in a car engine are further examples of energy transformation in daily life.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments