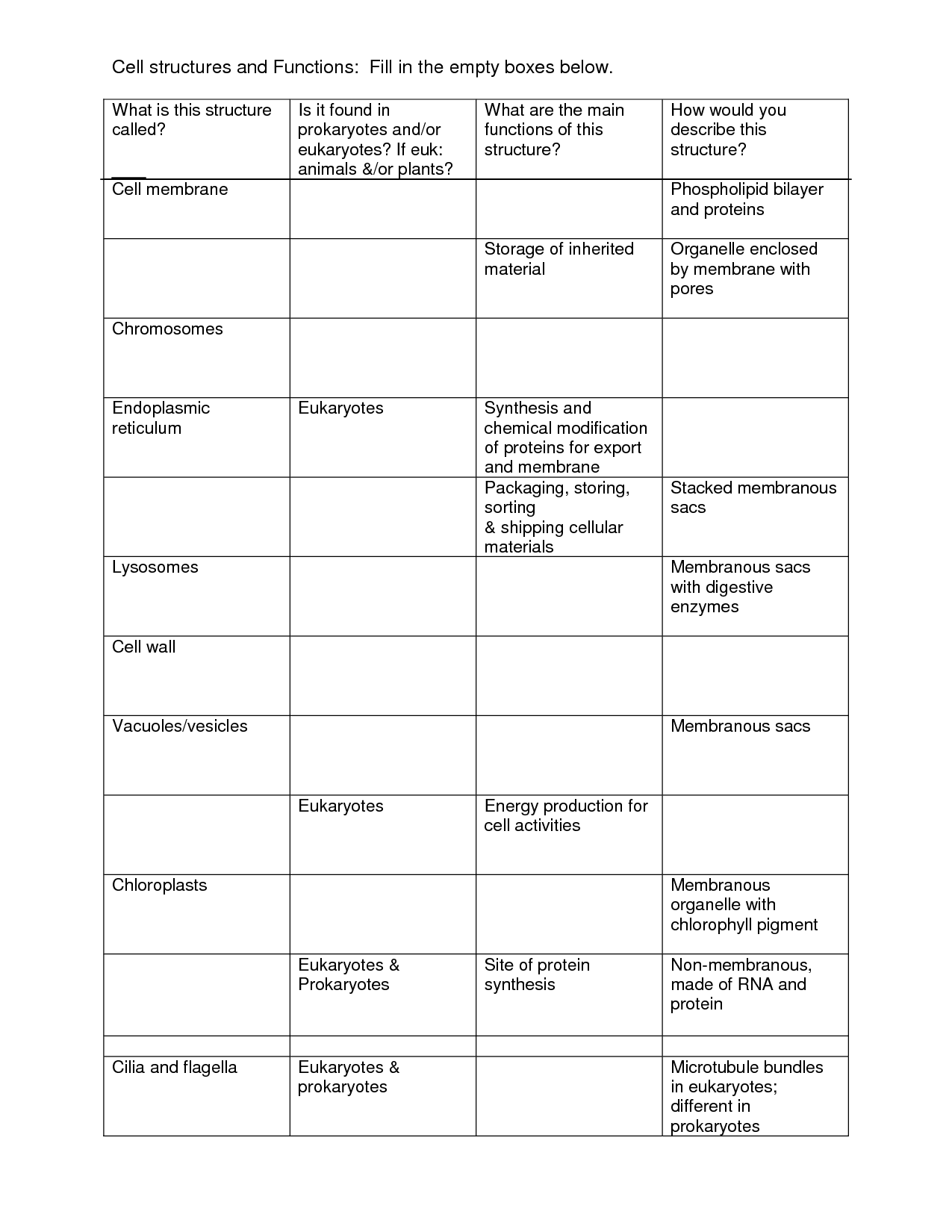
Parts of a Plant Cell Worksheet
Have you ever wondered about the different parts of a plant cell? If you're a student studying biology or simply curious about the inner workings of plants, this worksheet is perfect for you. By using this worksheet, you'll have the opportunity to learn and identify the various components that make up a plant cell in a clear and organized manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
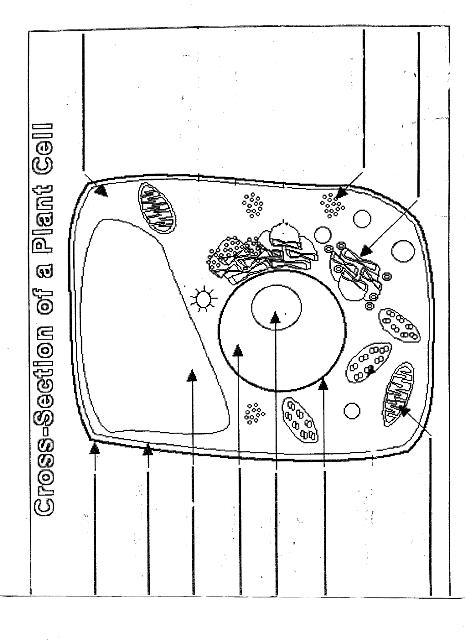
- Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet
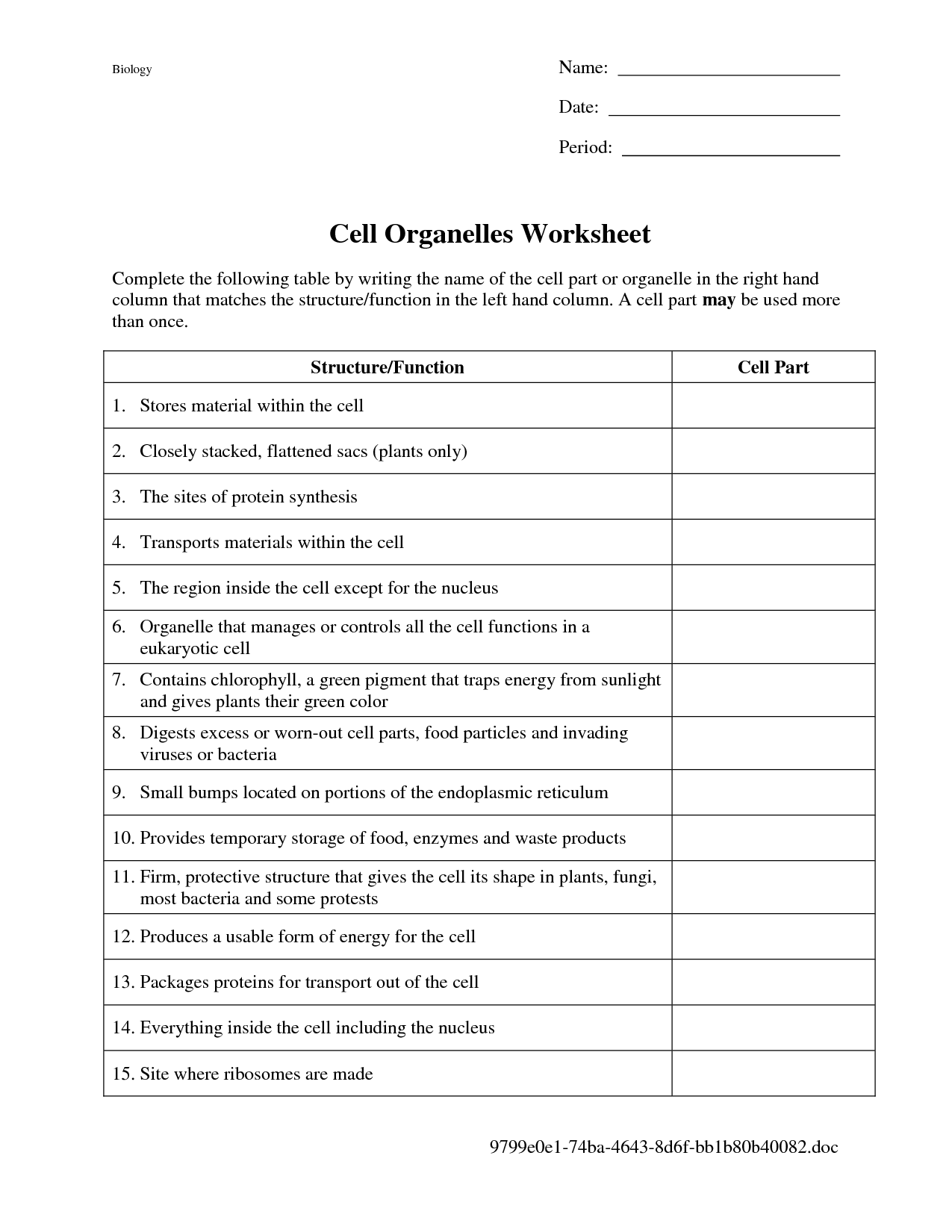
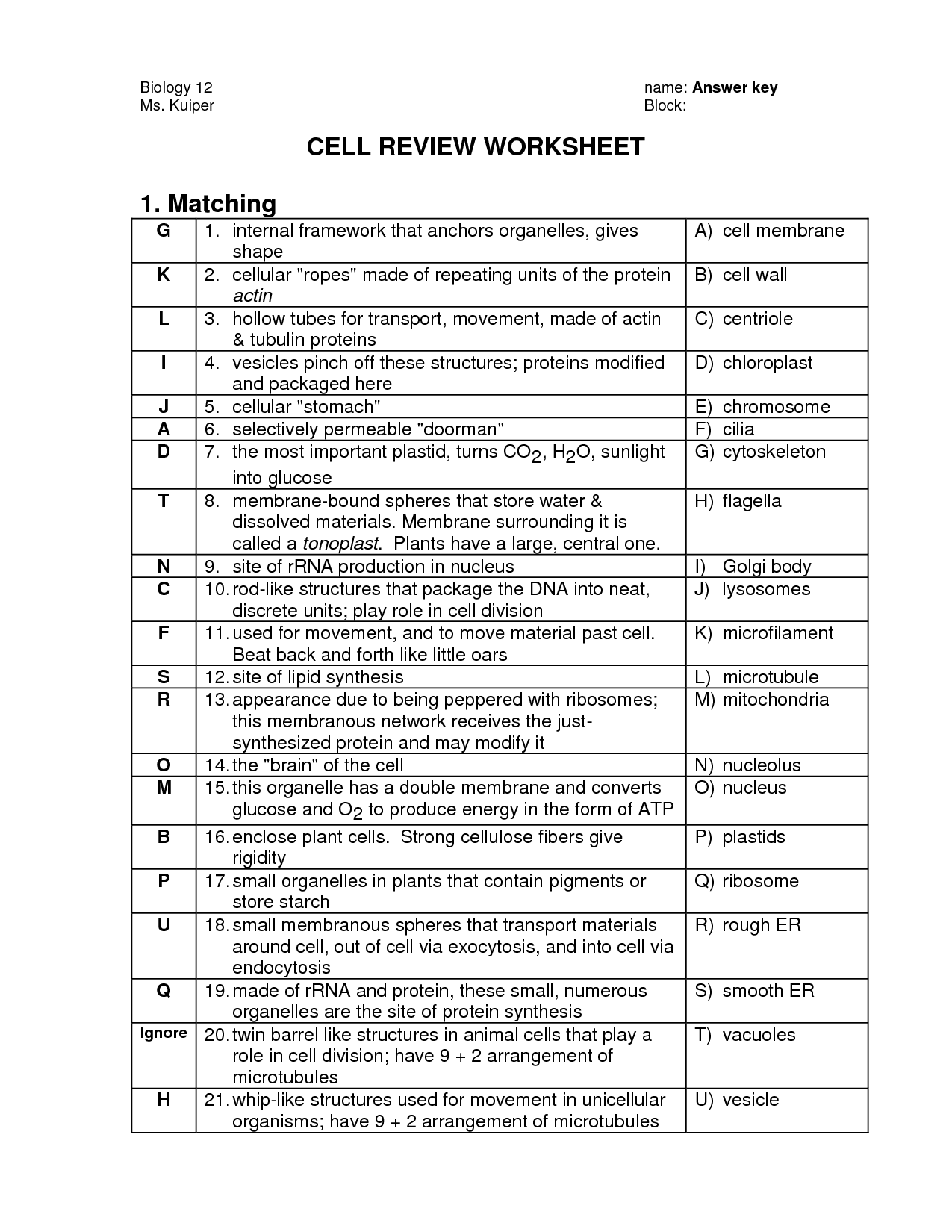
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets 7th Grade
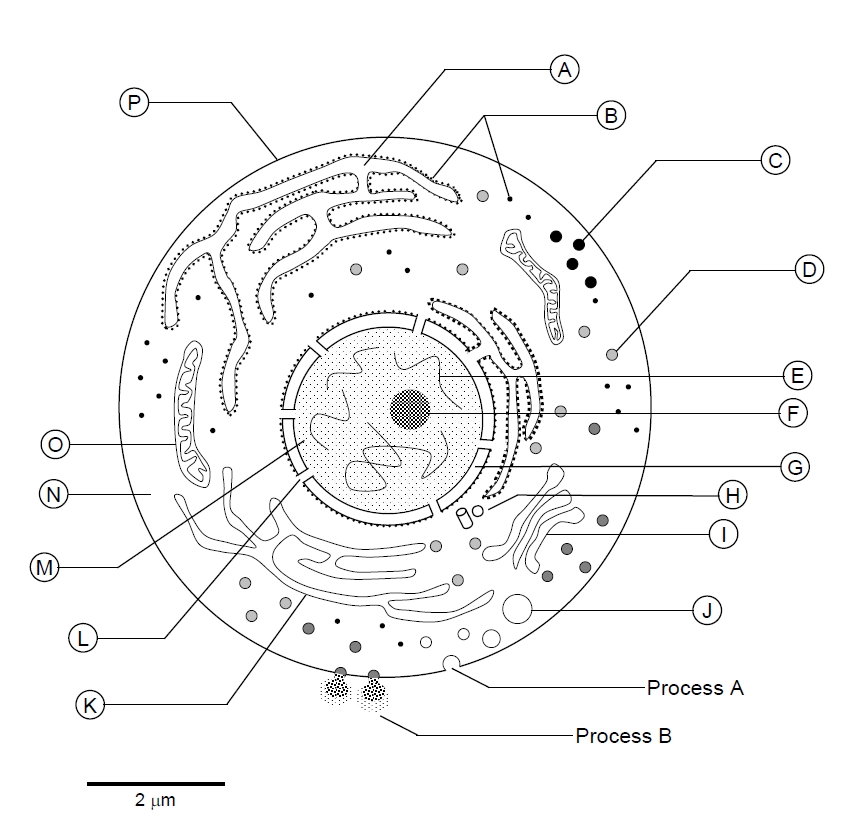
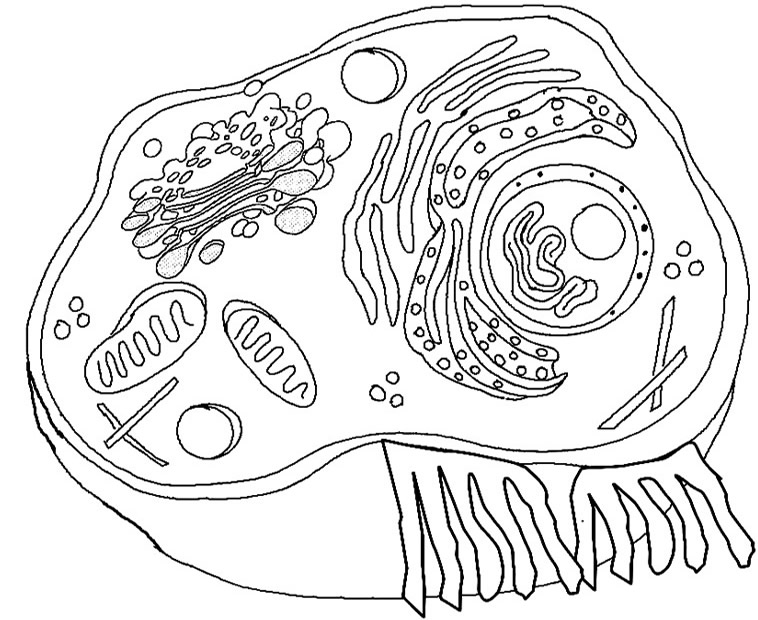
- Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Blank Animal and Plant Cell Diagram to Label
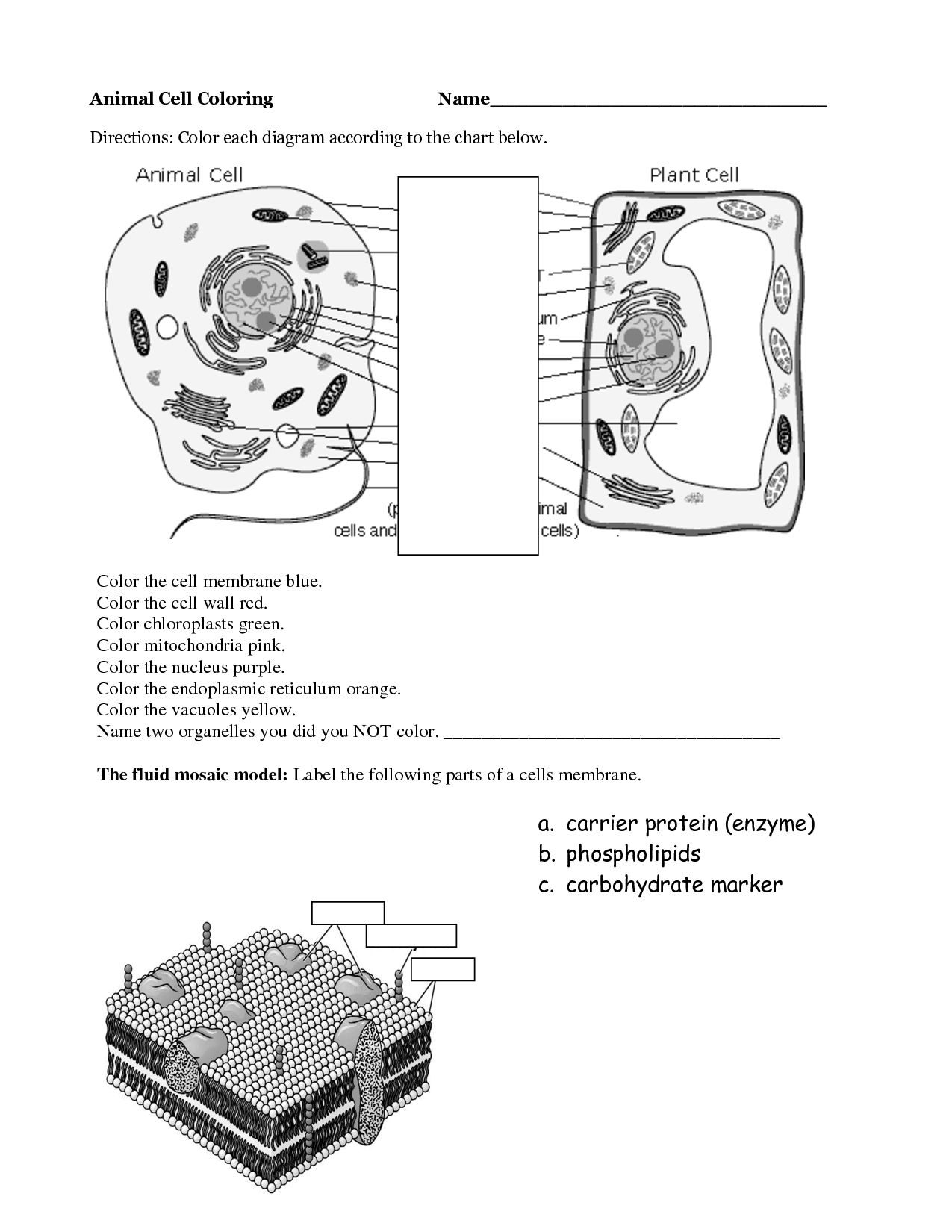
- Animal Cell Coloring Answers
- Plant and Animal Cell Coloring Worksheet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Animal Cell Parts and Definitions
- Cell Organelles and Their Functions Chart
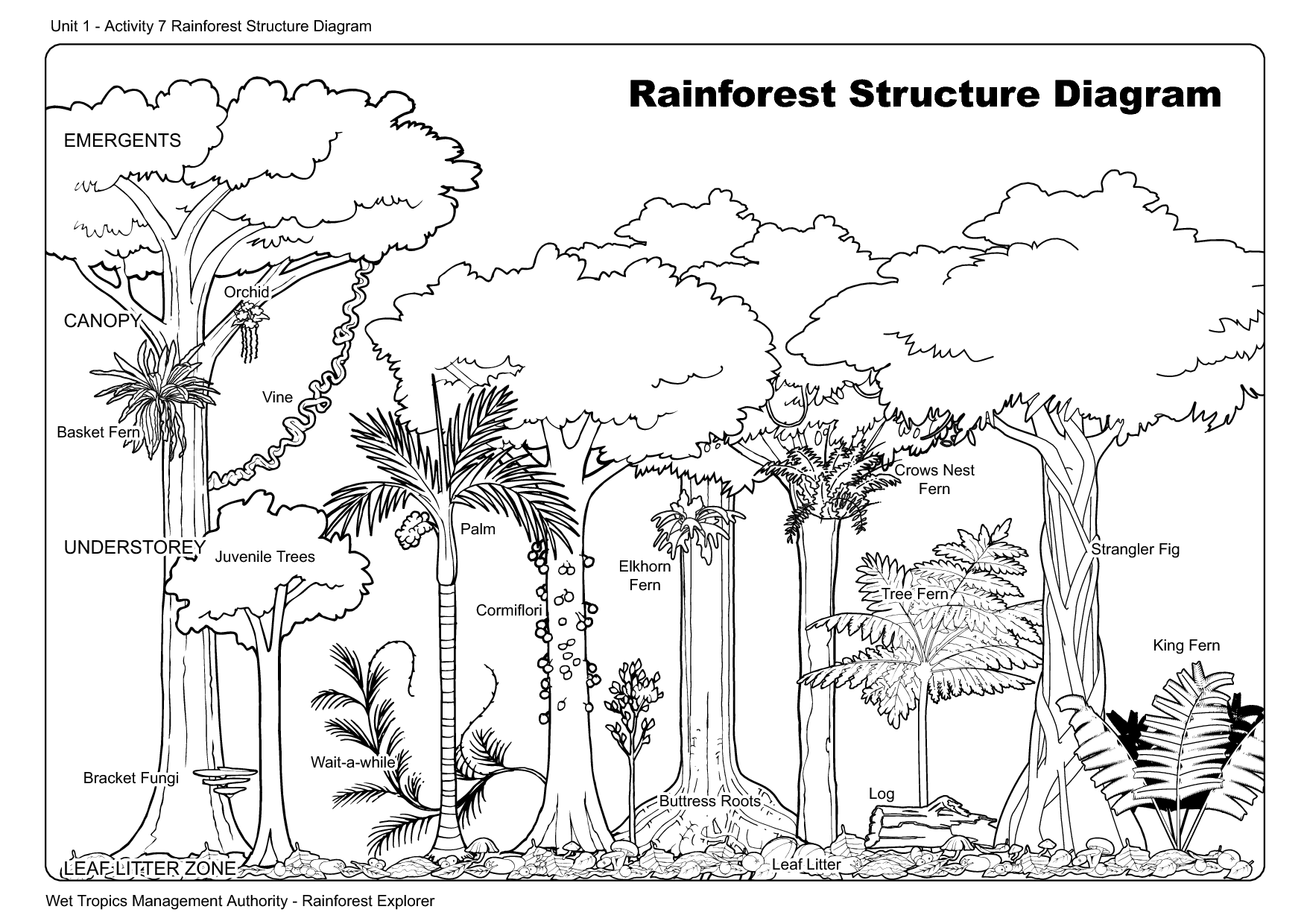
- Rainforest Structure Diagram
- Basic Plant Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the two main parts of a plant cell?
The two main parts of a plant cell are the cell wall and the cell membrane. The cell wall provides structure and support to the cell, while the cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a barrier that separates the inside of a cell from its external environment, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It also helps maintain the cell's shape and provides structural support, allowing the cell to interact with its surroundings and ensuring the internal environment is stable and suitable for cell functions. Additionally, the cell membrane is important for cell communication and recognition processes.
What is the role of the nucleus in a plant cell?
The nucleus in a plant cell plays a crucial role in storing and protecting the cell's genetic material, which is organized into chromosomes. It controls the cell's activities and gene expression by regulating the synthesis of proteins and RNA molecules. Additionally, the nucleus is involved in cell division processes such as mitosis and meiosis, which are essential for plant growth, development, and reproduction.
What is the function of the mitochondria in a plant cell?
The function of the mitochondria in a plant cell is to generate energy in the form of ATP through the process of cellular respiration. Mitochondria are responsible for breaking down nutrients such as sugars and fats to produce ATP, which is the primary energy source used by the plant cell to carry out its various metabolic processes and functions.
What is the purpose of the cytoplasm in a plant cell?
The cytoplasm in a plant cell serves as a medium for various cellular processes to occur, such as metabolic reactions, transportation of molecules, and support for organelles. It contains enzymes, ions, nutrients, and other molecules necessary for the cell's functioning. The cytoplasm also helps maintain the cell's shape and provides a scaffold for organelles to move and interact within the cell.
What is the function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
The cell wall in a plant cell provides structural support and protection, helping to maintain the shape of the cell and prevent it from bursting due to osmotic pressure. It also acts as a barrier to protect the cell from pathogens and environmental stresses. Additionally, the cell wall allows for cell-to-cell communication and provides rigidity to the plant, allowing it to stand upright and support its own weight.
What are chloroplasts and what is their function in a plant cell?
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis. Their main function is to capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide and water are transformed into glucose and oxygen. This energy is essential for the plant's growth and development, making chloroplasts crucial for the survival of plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in a plant cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum in a plant cell plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, storage, and transportation. It consists of rough endoplasmic reticulum that is involved in protein synthesis and smooth endoplasmic reticulum that is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification processes. Additionally, it plays a role in the proper folding and modification of proteins before they are transported to their final cellular destinations.
What is the function of the vacuole in a plant cell?
The vacuole in a plant cell serves multiple functions including storing nutrients, regulating turgor pressure to provide structural support, maintaining the pH balance within the cell, and storing waste products. Additionally, it can also help in plant growth by regulating cell elongation and aiding in processes such as decomposition and recycling of cellular components.
What is the purpose of the golgi apparatus in a plant cell?
The Golgi apparatus in a plant cell serves as a processing and packaging center for proteins and lipids. It modifies, sorts, and packages molecules produced in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) before transporting them to their final destination within the cell or for secretion outside the cell. Additionally, the Golgi apparatus is involved in the synthesis of cell wall components and the formation of lysosomes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments