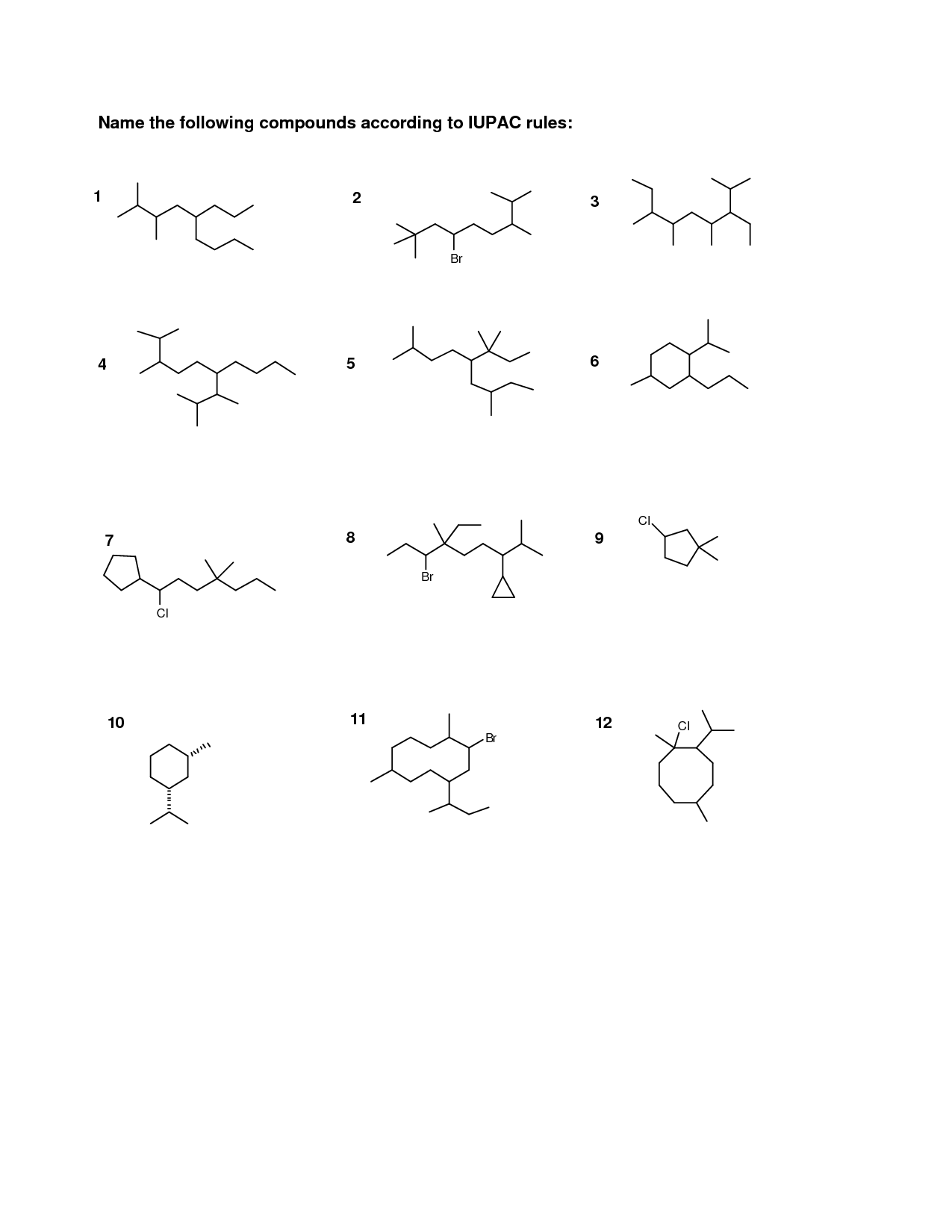
Organic Compounds Structure Worksheet
Are you a high school or college student studying organic chemistry? Do you find it challenging to grasp the intricate structure of organic compounds? If so, you've come to the right place! In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets as a valuable tool for understanding and mastering the complex world of organic compounds.
Table of Images 👆
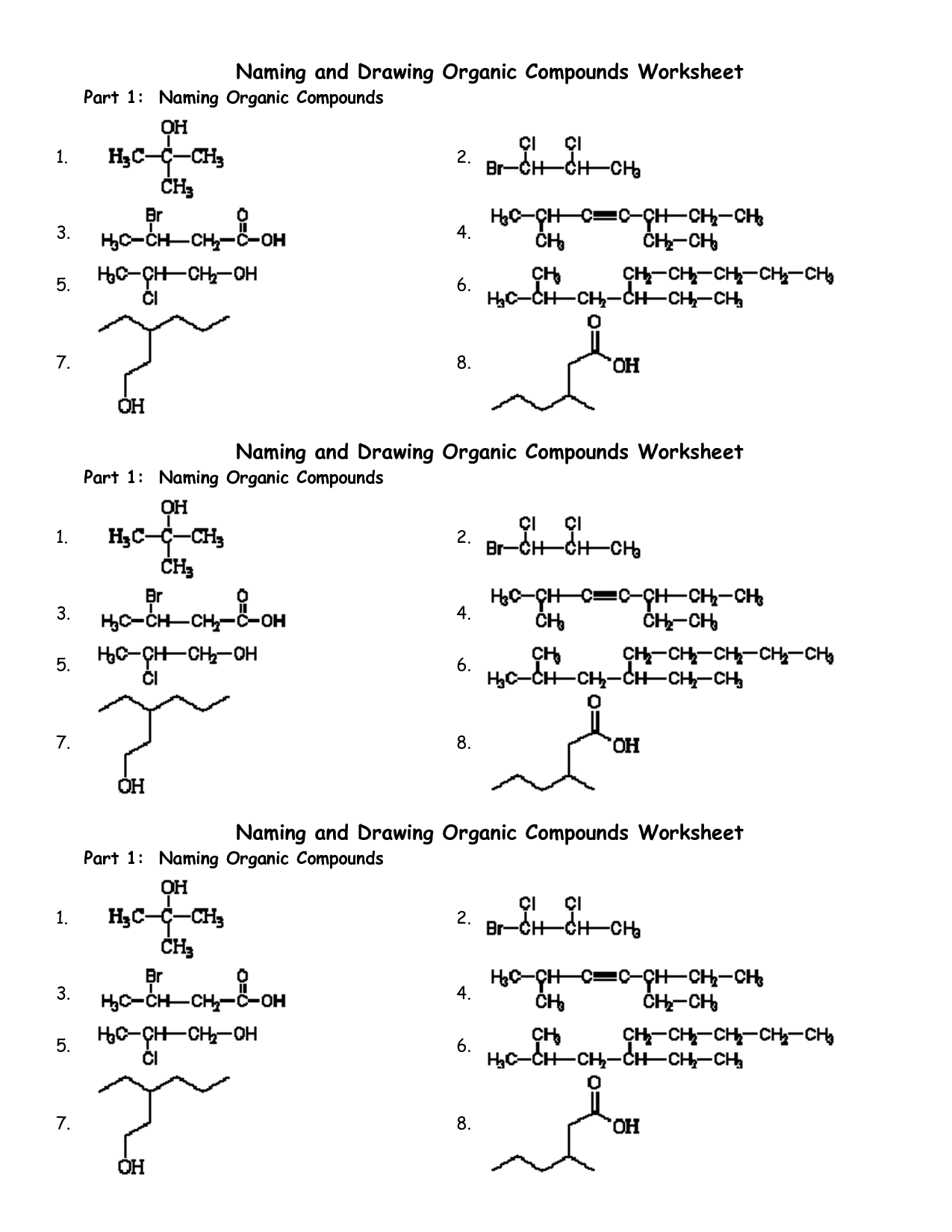
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Vocabulary Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Practice Worksheet
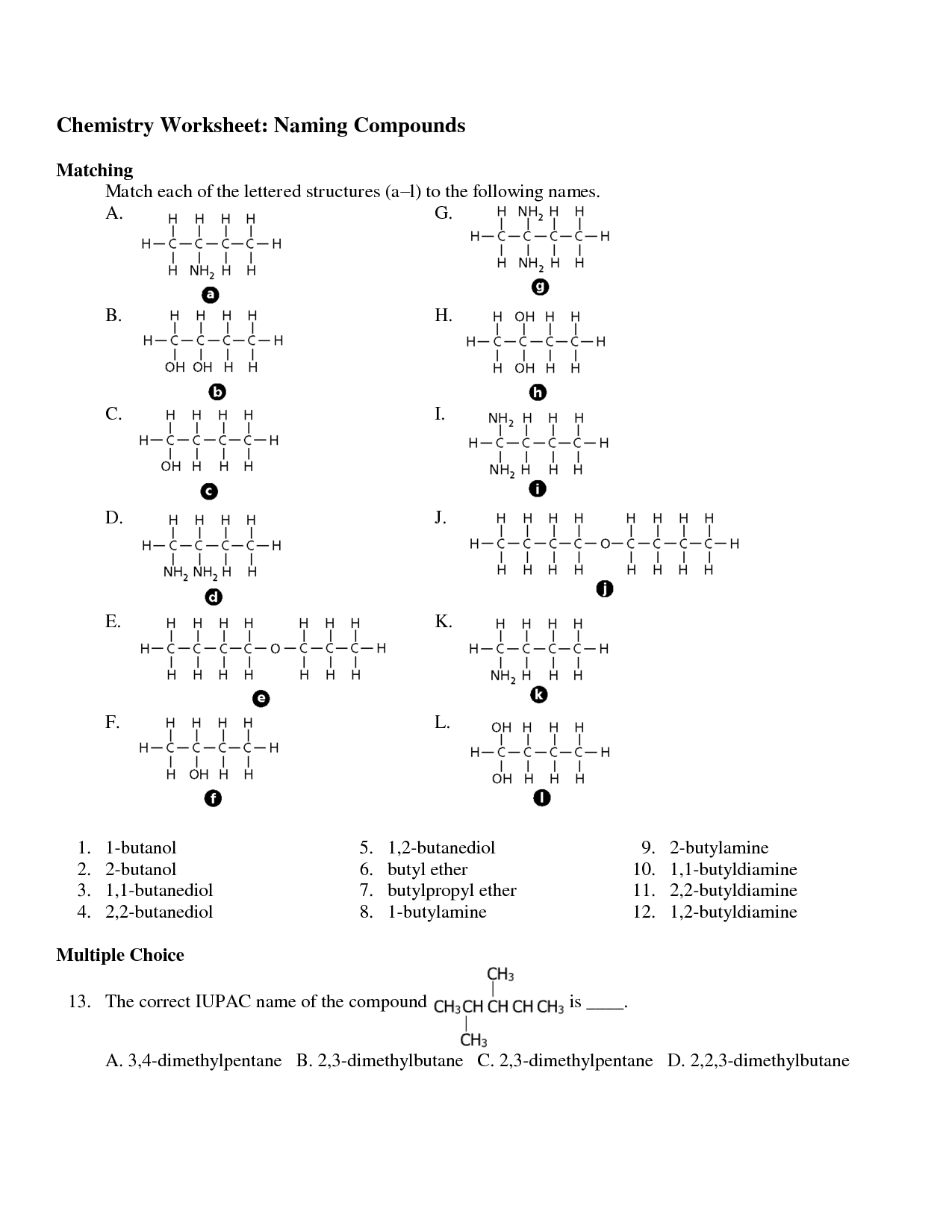
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
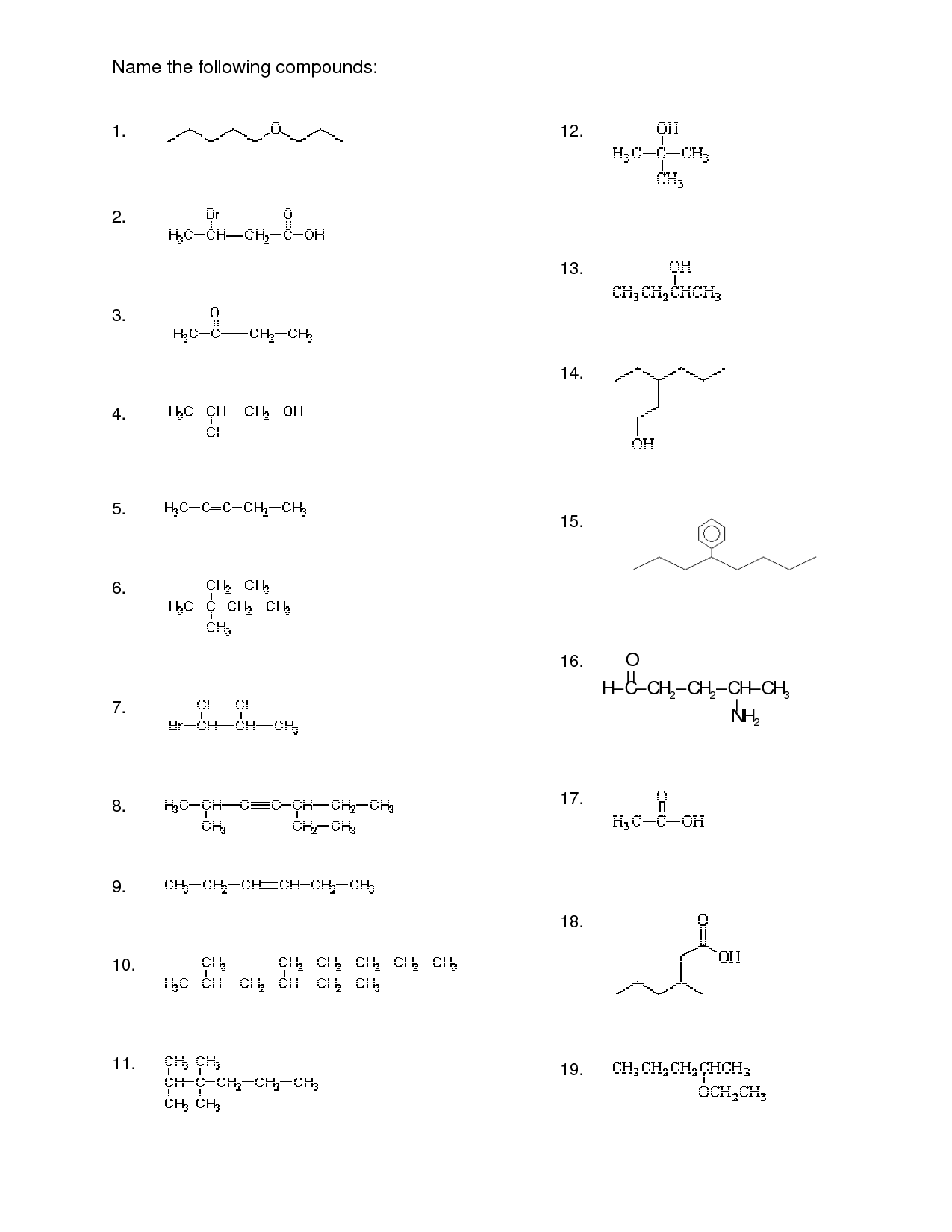
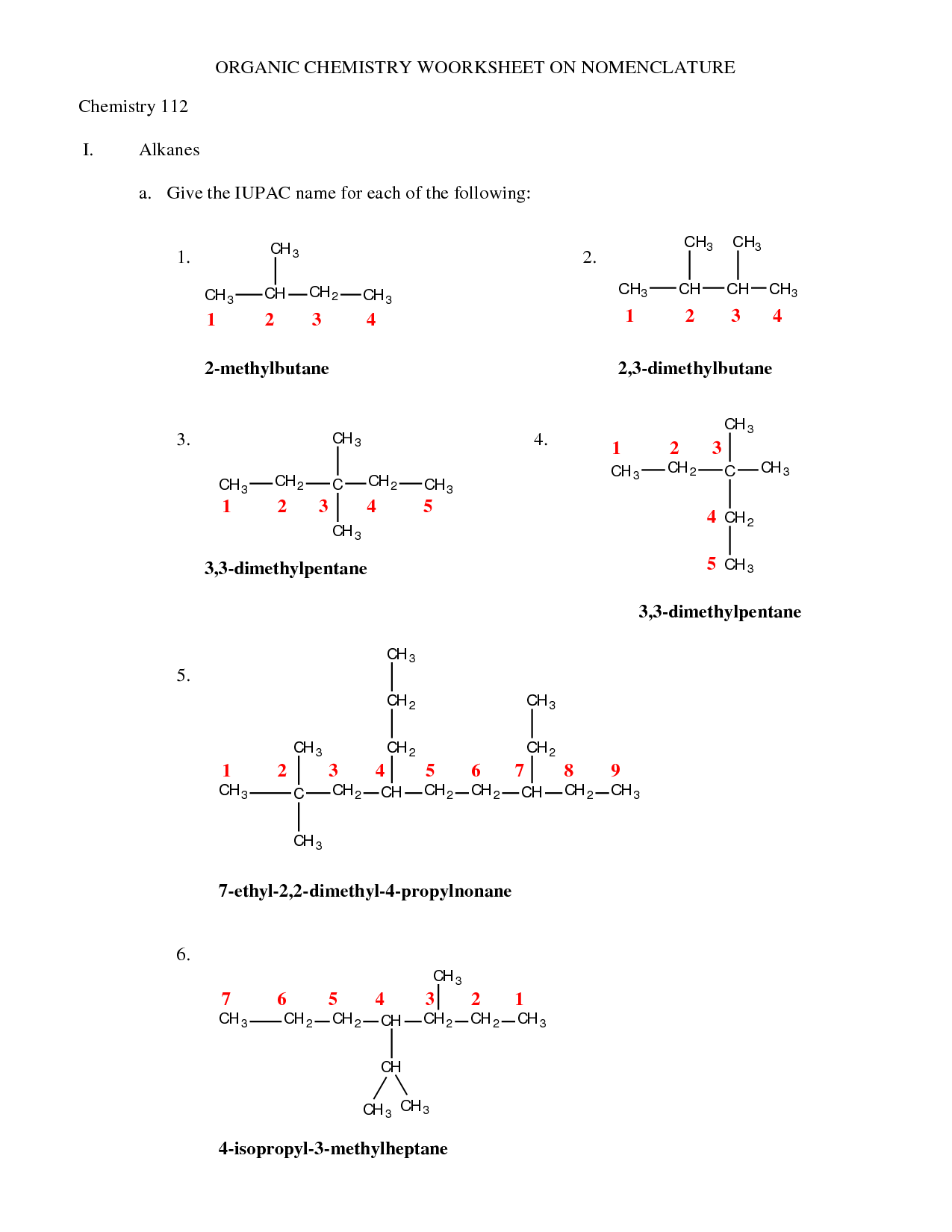
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
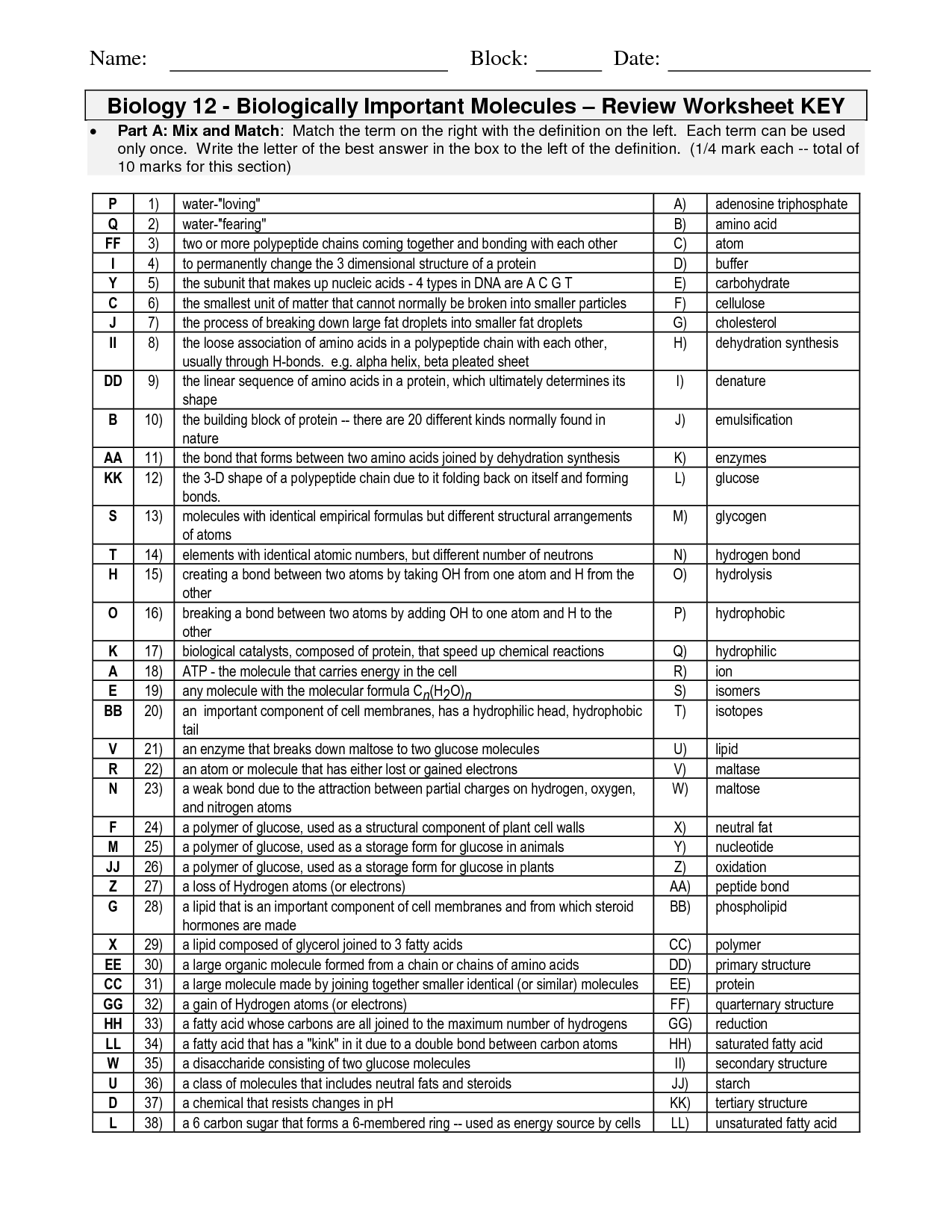
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Organic Compounds Worksheets
- Organic Chemistry Functional Groups
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheet
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheet
- Drawing Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
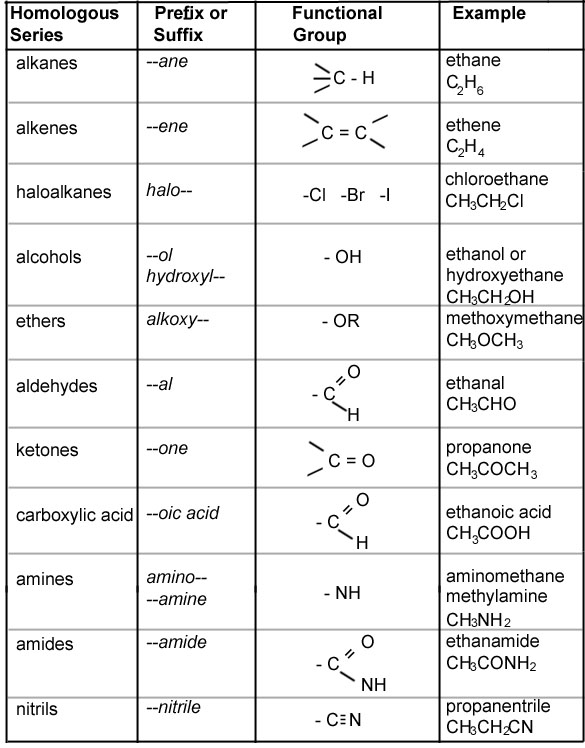
What are functional groups?
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions and properties of that molecule. These groups determine how a molecule will react with other molecules and participate in various biological and chemical processes. Examples of functional groups include hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), amino (-NH2), and carboxyl (-COOH).
How do you differentiate between alkanes and alkenes?
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds between carbon atoms, while alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between carbon atoms. This double bond in alkenes results in them being more reactive than alkanes. Additionally, alkenes have the general formula CnH2n, while alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
What is an aromatic compound? Provide an example.
An aromatic compound is a type of organic compound that contains a ring structure with alternating double bonds. One famous example of an aromatic compound is benzene, which consists of a hexagonal ring of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds.
Describe the structure of an aldehyde.
An aldehyde has a carbonyl group (C=O) which is bonded to a hydrogen atom (H) and an R group, where R represents any alkyl or aryl group. This functional group gives aldehydes their characteristic reactivity and chemical properties, such as being oxidized to form carboxylic acids. The general formula for an aldehyde is RCHO.
What are isomers? Provide an example.
Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, leading to different chemical properties. One example of isomers is butane and isobutane. Butane has a straight-chain structure with four carbon atoms in a row, while isobutane has a branched structure with three carbon atoms in a row and one carbon atom branching off the middle carbon atom.
Explain the concept of chirality in organic compounds.
Chirality in organic compounds refers to the property of a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. This asymmetry arises from having four different substituents attached to a central carbon atom, creating two non-superimposable mirror images known as enantiomers. Chiral molecules exhibit unique properties due to their handedness, affecting their interactions with other chiral molecules such as enzymes and receptors. These interactions have significant implications in fields like pharmacology, where the different enantiomers of a drug can exhibit varying effects in the body.
Describe the structure of a carboxylic acid.
A carboxylic acid has a structure consisting of a carboxyl group, which is a functional group composed of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the same carbon atom. The general formula for a carboxylic acid is RCOOH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group. The carboxyl group is typically located at the end of a carbon chain, making carboxylic acids organic compounds that are commonly found in nature and are important building blocks in chemistry.
What is the difference between an alcohol and a phenol? Provide an example of each.
The main difference between alcohols and phenols is the functional group they contain. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a carbon atom, while phenols have a hydroxyl group attached to a benzene ring. A common example of an alcohol is ethanol, which is found in alcoholic beverages, while an example of a phenol is phenol itself, which is used in various industrial applications such as disinfectants and pharmaceuticals.
Explain the structure and properties of an ester.
An ester is a compound formed by the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. It has a general structure RCOOR', where R and R' can be alkyl or aryl groups. Esters have a pleasant scent and are often used in flavorings and perfumes. They are also found in fats and oils and are essential in the formation of triglycerides. Esters have relatively low boiling points compared to other organic compounds, making them volatile and easily evaporated. Additionally, they are polar molecules, allowing them to mix with both polar and nonpolar solvents.
Describe the structure of an amine.
Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more carbon atoms. The general structure of an amine can be represented as R-NH2, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom. Amines can also have additional alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, leading to different types of amines such as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom makes amines basic in nature.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments