Organic Compound Worksheet Answers Biology
Are you in search of organic compound worksheet answers for your biology class? Look no further! This blog post is designed to provide you with a helpful resource to assist you in understanding and practicing organic compound concepts. Whether you are a high school or college student, this worksheet will help reinforce your knowledge and improve your understanding of this essential subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Biology Organic Molecules Worksheet Review
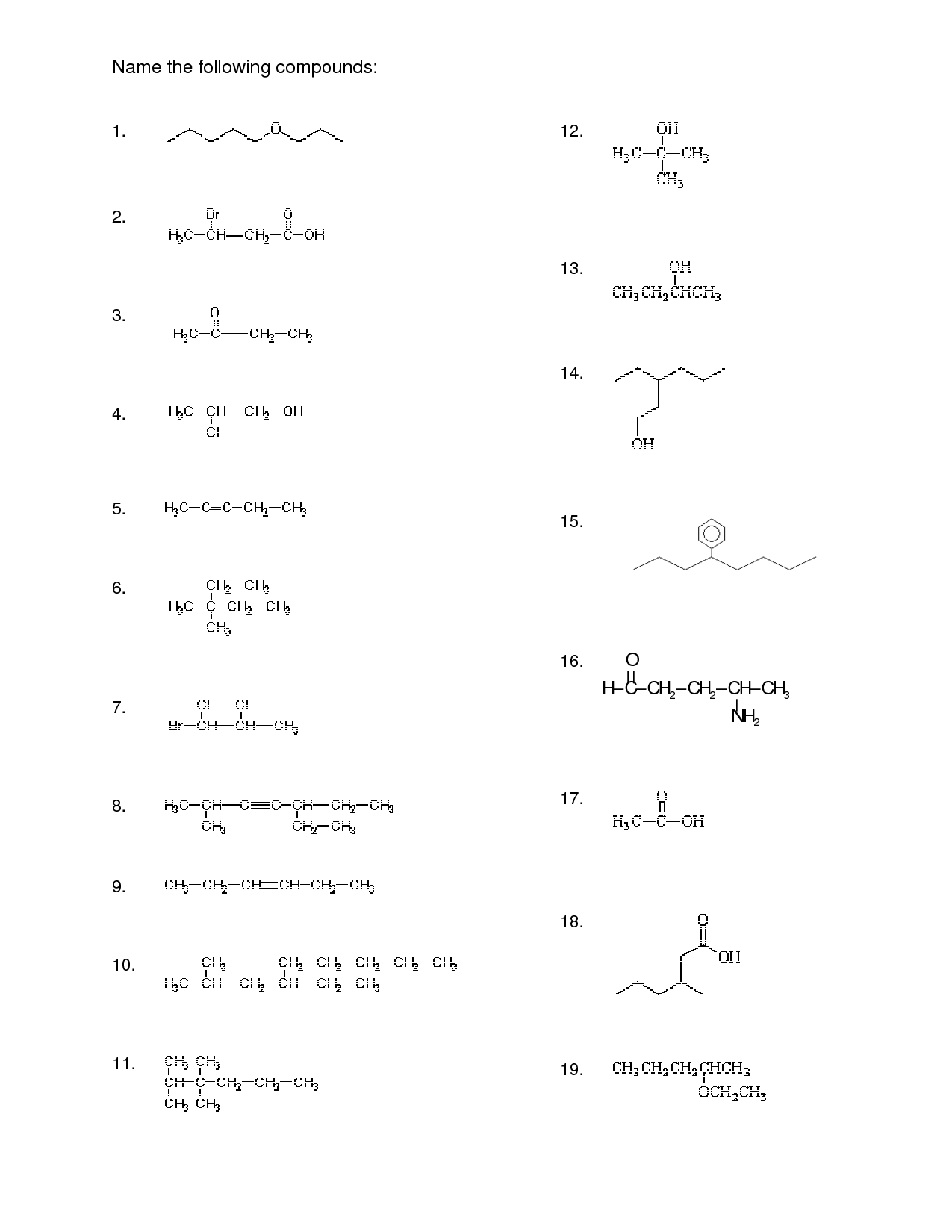
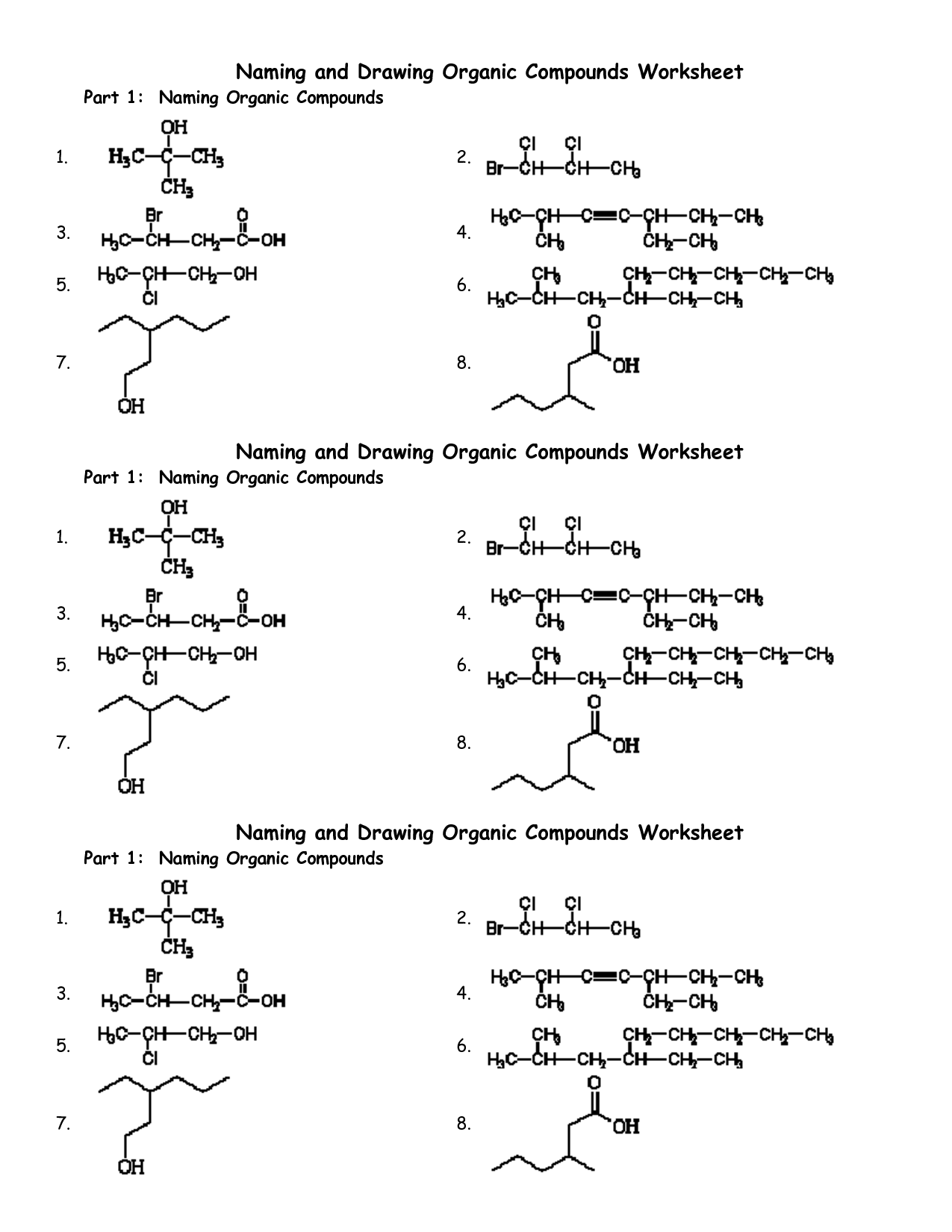
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Organic Chemistry Worksheets
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic Compounds Worksheet
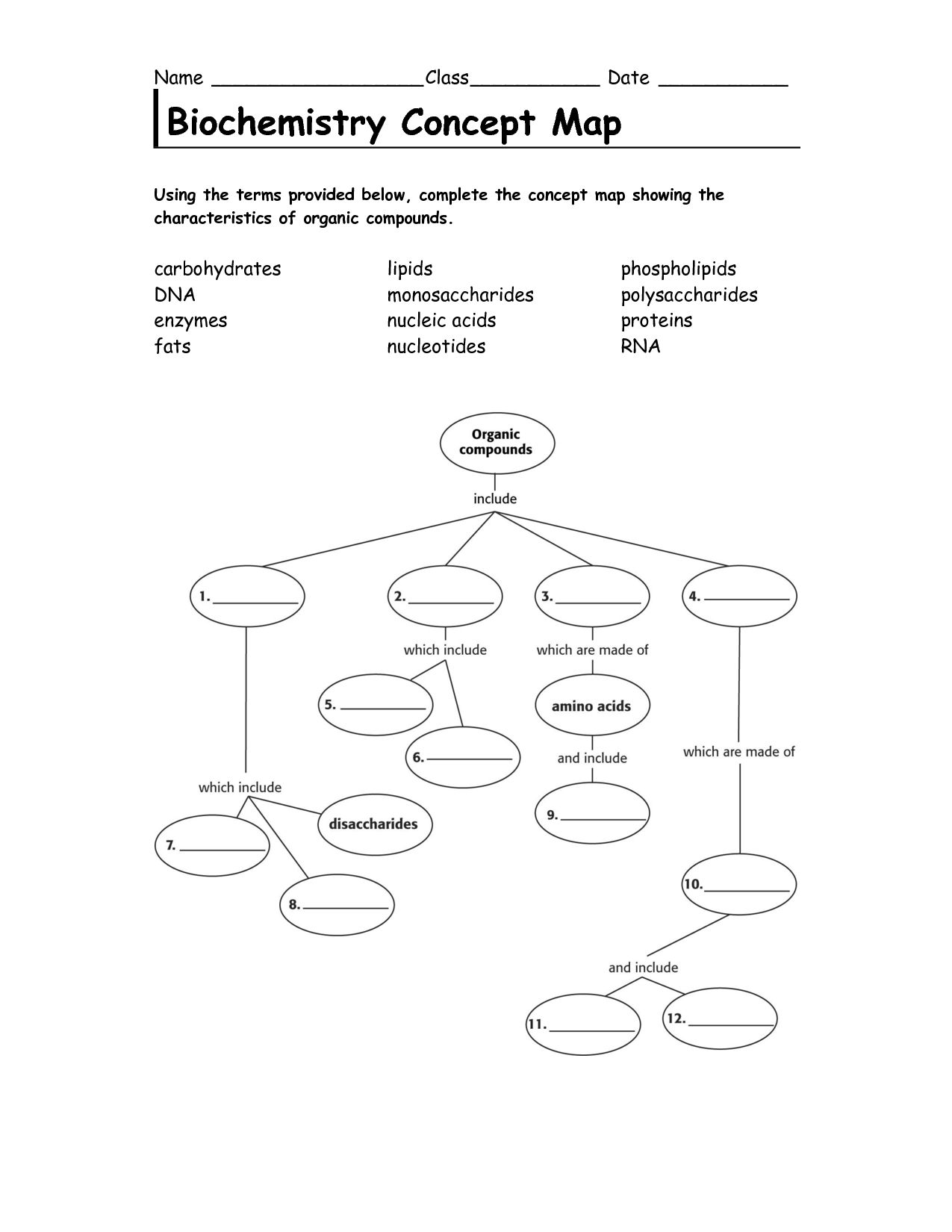
- Biochemistry Concept Map Organic Compounds Answers
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Vocabulary Worksheet
- Transition Metal Naming Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Unit 5 Worksheet 2 Answer Key
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is the definition of an organic compound?
An organic compound is a chemical compound that contains carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, along with other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These compounds are the basis of life and are typically found in living organisms, as well as in petroleum and other fossil fuels.
Name three common examples of organic compounds.
Three common examples of organic compounds are glucose (sugar), ethanol (alcohol), and methane (natural gas).
What elements make up organic compounds?
Organic compounds are primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Additionally, they may contain elements such as nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and halogens like fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. These elements form the diverse and complex structures found in organic molecules, allowing for the vast array of compounds and functions they can exhibit in biological processes and everyday substances.
Define functional groups in organic compounds.
Functional groups in organic compounds are specific groups of atoms that determine the chemical reactivity and properties of the molecule. These groups confer unique characteristics to the compound, influencing its behavior and functionality in reactions. Examples of functional groups include hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), amino (-NH2), and carboxyl (-COOH), among others, each contributing distinct chemical properties to the organic compound they are a part of.
How do organic compounds differ from inorganic compounds?
Organic compounds contain carbon bonded to other atoms, typically hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus, and are often associated with living organisms. In contrast, inorganic compounds do not contain carbon bonded to hydrogen and are not typically associated with living organisms. Additionally, organic compounds tend to have complex structures and are commonly found in nature, while inorganic compounds can have simpler structures and include minerals, salts, and metals.
What is the role of carbon in organic compounds?
Carbon is essential in organic compounds as it is the primary element that forms the backbone of organic molecules. Carbon atoms can form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms and with various other elements, allowing for a vast diversity of structures and functions in organic molecules. This versatility of carbon enables it to form the complex structures found in living organisms and other organic materials.
Explain why organic compounds are often associated with living organisms.
Organic compounds are often associated with living organisms because they are primarily composed of carbon atoms bonded with other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Carbon has a unique ability to form diverse and complex molecules through covalent bonding, which allows for the vast array of structures found in living organisms, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids essential for life processes. Additionally, organic compounds play crucial roles in biological functions such as energy storage, cell structure, and signaling pathways, making them integral components of living systems.
How are organic compounds classified?
Organic compounds are classified mainly based on their functional groups, which are specific arrangements of atoms responsible for the compounds' reactivity and properties. Common functional groups include alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and amines. Additionally, organic compounds can also be classified based on the number of carbon atoms they contain, such as small molecules (1-6 carbons), medium-sized molecules (7-20 carbons), and large molecules (greater than 20 carbons).
What are the properties of organic compounds?
Organic compounds are primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, and occasionally other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus. They are characterized by covalent bonds between their atoms, which form a variety of molecular structures such as chains, rings, and branches. Organic compounds are typically combustible, soluble in organic solvents, and have lower melting and boiling points compared to inorganic compounds. They often exhibit diverse chemical reactions, such as combustion, addition, substitution, and fermentation, making them essential for life and a wide range of industries.
How do organic compounds contribute to the diversity of life?
Organic compounds are essential building blocks of life, providing the molecular basis for the vast diversity of living organisms. From carbohydrates and lipids for energy storage and structural support, to proteins for enzymatic functions and cellular processes, and nucleic acids for genetic information, organic compounds play crucial roles in shaping the complexity and variety of life forms on Earth. Their versatile chemical properties allow for the formation of endless combinations and structures, enabling organisms to adapt to diverse environments and evolve over time, ultimately contributing to the incredible diversity of life we see today.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments