Ohms Law Practice Worksheet
Are you a student or an electrical enthusiast who wants to strengthen your understanding of Ohm's Law? Look no further! This blog post introduces a practice worksheet designed to help you master this fundamental concept in electronics. Whether you are studying for an exam or simply looking to build your knowledge, this Ohm's Law Practice Worksheet is the perfect tool to enhance your skills and increase your confidence in working with electrical circuits.
Table of Images 👆
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answers
- Ohms Law Practice Problems Worksheet with Answers
- Ohms Law Practice Problems Worksheet with Answers
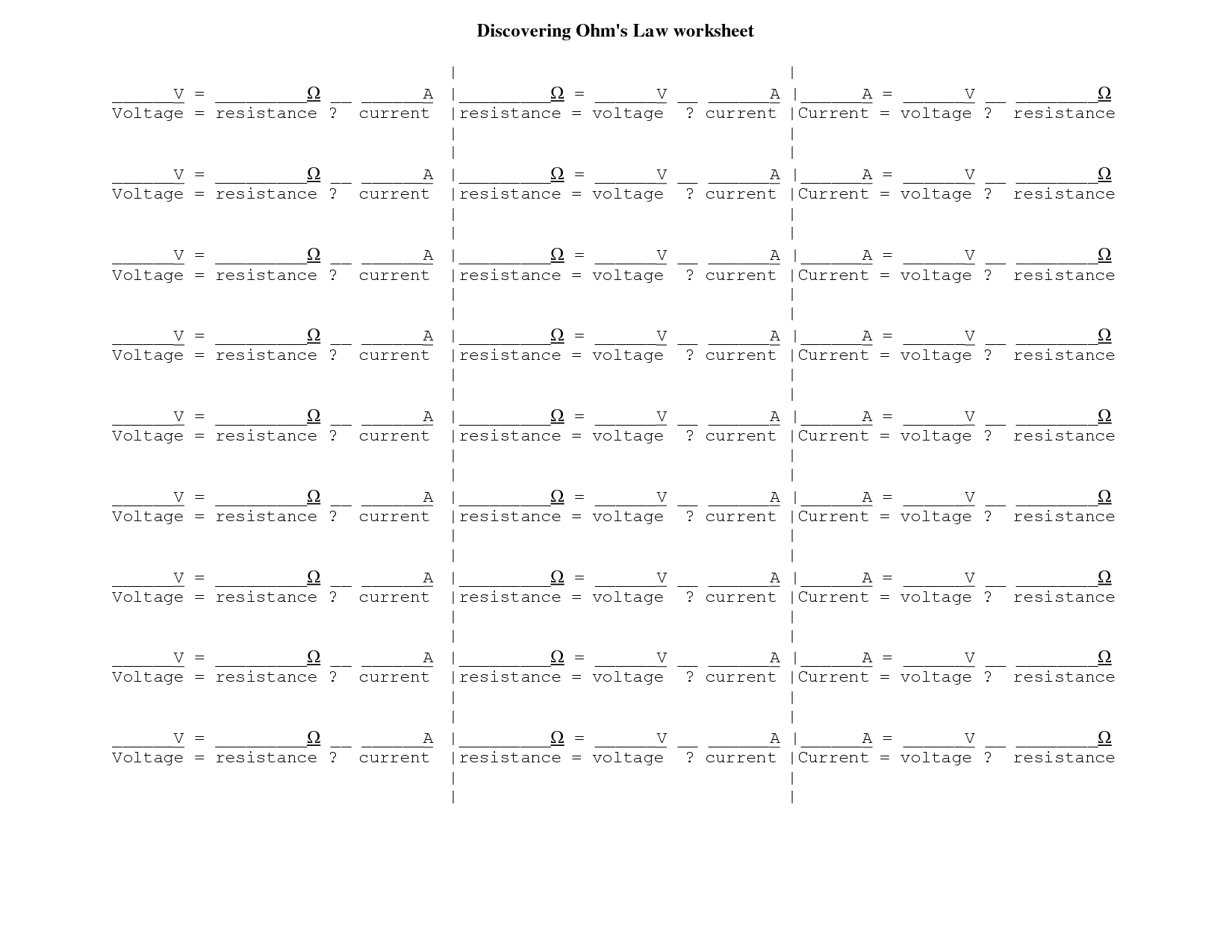
- Ohms Law Practice Problems Worksheet
- Ohms Law Practice Problems Worksheet
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answer Key
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answers
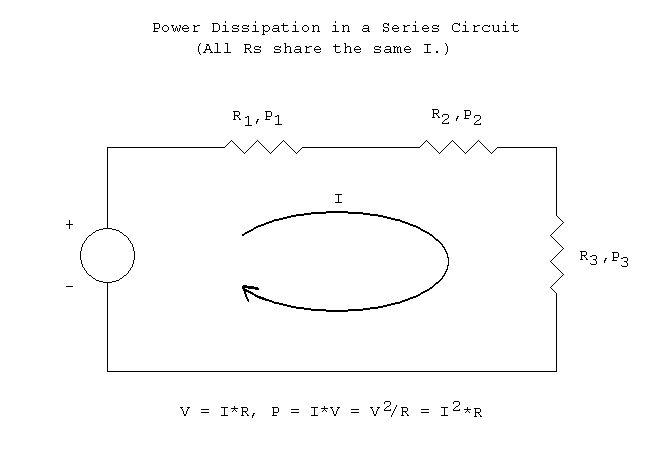
- Ohm S Law Worksheet Series Circuit
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answer Key
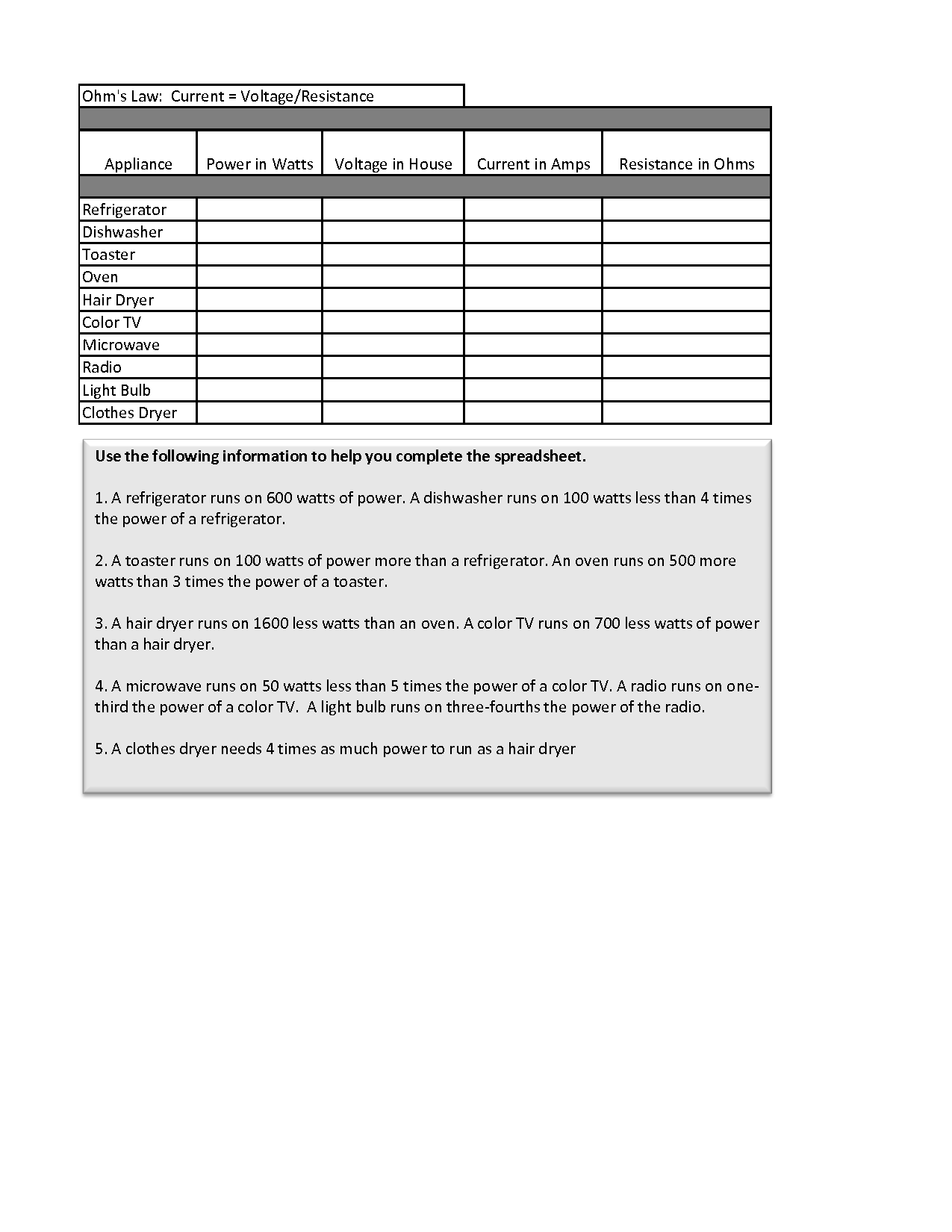
- Ohms Law Calculations Worksheet
- Electric Circuits Worksheet Answers
- Hesss Law Worksheet Answer Key
- Ohms Law Calculations Worksheet
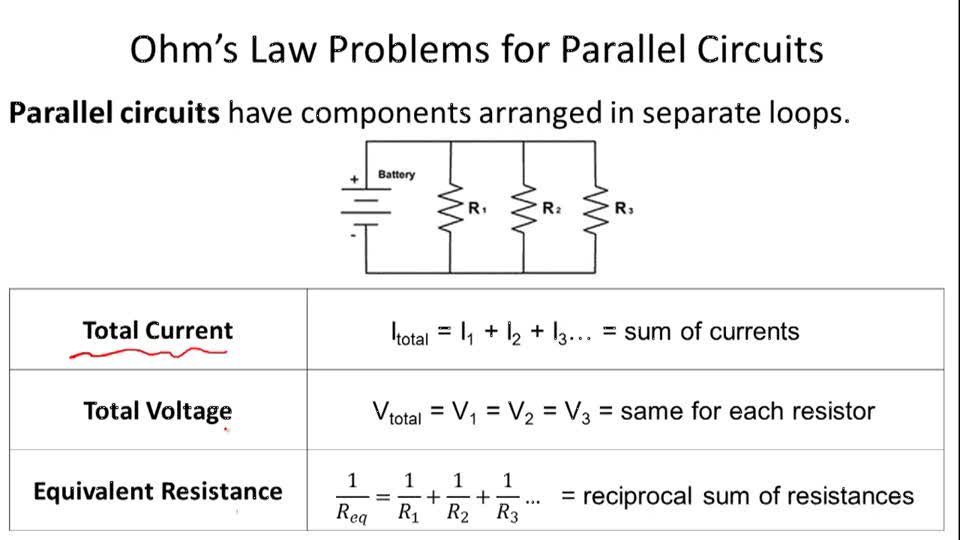
- Ohms Law Parallel Circuit Problems
- Ohms Law Problems Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
Define Ohm's Law.
Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. Mathematically, it is expressed as I = V / R, where I is the current in amperes, V is the voltage in volts, and R is the resistance in ohms.
What is the equation for Ohm's Law?
Ohm's Law is represented by the equation V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
What does the symbol "V" represent in Ohm's Law?
The symbol "V" in Ohm's Law represents the electrical potential difference measured in volts, which is the driving force that pushes electric current through a circuit.
What does the symbol "I" represent in Ohm's Law?
The symbol "I" in Ohm's Law represents the electrical current, which is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is measured in amperes (A) and is a crucial element in calculating the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit.
What does the symbol "R" represent in Ohm's Law?
The symbol "R" in Ohm's Law represents the resistance in an electrical circuit. It is a measure of how much a component resists the flow of electric current and is measured in ohms.
How do you calculate voltage using Ohm's Law?
To calculate voltage using Ohm's Law, you can use the formula V = I * R, where V is the voltage in volts, I is the current in amperes, and R is the resistance in ohms. Simply multiply the current flowing through a circuit by the resistance in that circuit to determine the voltage across it.
How do you calculate current using Ohm's Law?
To calculate current using Ohm's Law, you would divide the voltage (V) across a circuit component by the resistance (R) of that component. The formula is I = V/R, where I represents the current flowing through the component in amperes (A), V is the voltage in volts (V), and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω).
How do you calculate resistance using Ohm's Law?
To calculate resistance using Ohm's Law, you divide the voltage (V) by the current (I). The formula for Ohm's Law is R = V / I, where R represents resistance in ohms, V is voltage in volts, and I is current in amperes. By rearranging the formula, you can also calculate voltage or current if resistance and one of the other variables are known.
What are the units of measurement for voltage, current, and resistance?
The units of measurement for voltage are volts (V), for current are amperes (A), and for resistance are ohms (Ω).
Provide an example of a practical application of Ohm's Law.
An example of a practical application of Ohm's Law is calculating the current flowing through a circuit when given the voltage and resistance values. For instance, if a circuit has a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms, you can use Ohm's Law (I = V/R) to determine that the current flowing through the circuit is 3 amperes. This information is crucial in designing and troubleshooting electrical circuits in various applications such as electronics, automotive systems, and household appliances.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments