Ocean Food Chain Worksheets
Ocean food chain worksheets are a valuable educational resource for students of all ages who want to learn more about the intricate relationships between different organisms in the marine ecosystem. These worksheets provide an engaging way to explore the various entities and subjects involved in the ocean food chain, allowing students to gain a deeper understanding of how energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
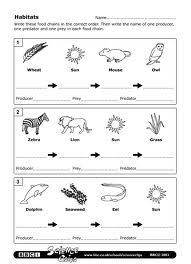
What is the first step in the ocean food chain?
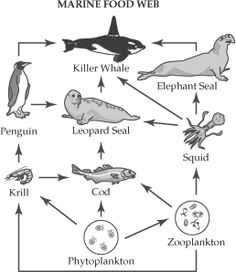
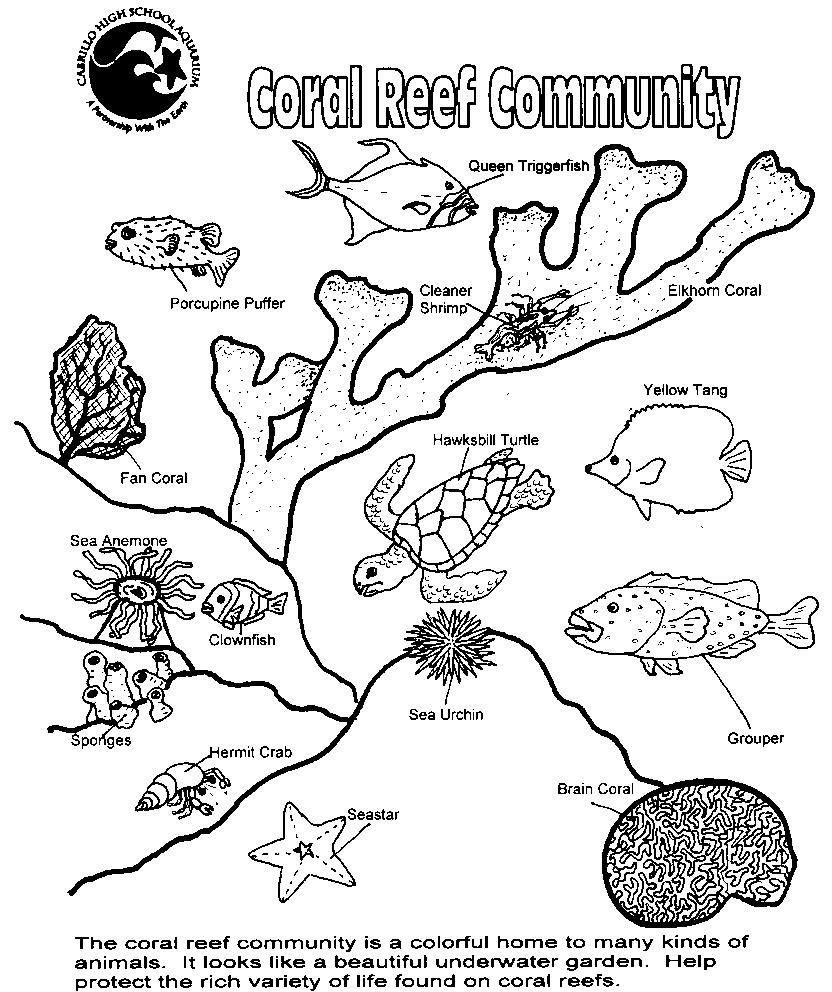
The first step in the ocean food chain is usually phytoplankton, which are microscopic marine algae that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and serve as the primary food source for many marine organisms.
Name an example of a primary producer in the ocean food chain.
Phytoplankton is an example of a primary producer in the ocean food chain. Phytoplankton are tiny, plant-like organisms that photosynthesize and form the base of the marine food web, converting sunlight into energy and initiating the flow of nutrients through the ecosystem.
What are primary consumers in the ocean food chain?
Primary consumers in the ocean food chain are organisms that feed directly on producers, which are usually phytoplankton and seaweeds. Examples of primary consumers in the ocean include zooplankton, small fish, crustaceans, and some types of sea urchins and snails. These organisms play a crucial role in transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels in the marine ecosystem.
Give an example of a secondary consumer in the ocean food chain.
An example of a secondary consumer in the ocean food chain is a dolphin. Dolphins feed on smaller fishes and invertebrates such as squid and octopus, making them a predator at the second trophic level of the food chain.
What role do decomposers play in the ocean food chain?
Decomposers in the ocean food chain break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. They are essential for the breakdown of organic matter, turning it into simpler compounds that can be used by other organisms. Without decomposers, the balance of nutrients in the ocean would be disrupted, affecting the entire food chain.
What happens to the energy as you move up the ocean food chain?
As you move up the ocean food chain, energy is transferred from one organism to another. The energy initially comes from producers, such as phytoplankton, through photosynthesis. Herbivores, such as small fish, consume the producers and transfer some of that energy. Carnivores, such as larger fish or marine mammals, then consume the herbivores and further pass on the energy. However, with each transfer of energy, some energy is lost as heat or used for the organism's metabolism, resulting in less energy being available at each higher trophic level. Overall, the energy decreases as you move up the ocean food chain.
How are predators and prey connected in the ocean food chain?
Predators and prey are connected in the ocean food chain through a relationship of consumption and energy transfer. Predators hunt and consume prey for food, which provides them with energy to survive and reproduce. This continuous cycle of predation helps regulate the population sizes of various species in the ocean ecosystem and ensures the transfer of energy throughout the food chain, ultimately maintaining the balance and health of the marine environment.
What happens if one species in the ocean food chain becomes extinct?
If one species in the ocean food chain becomes extinct, it can create a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem. The loss of that species can disrupt the balance of the food chain, leading to overpopulation of certain species, decline in others, and potential collapse of the ecosystem. This can impact the abundance of other species, their predators, and ultimately affect the overall health and biodiversity of the ocean ecosystem.
How does pollution affect the ocean food chain?
Pollution in the ocean can negatively impact the ocean food chain by contaminating water, reducing oxygen levels, and introducing harmful chemicals and toxins. This pollution can disrupt the balance and health of ecosystems, leading to habitat destruction, species decline, and ultimately affecting the entire food chain. Phytoplankton, the base of the ocean food chain, can be particularly vulnerable to pollution, affecting the entire ecosystem's ability to support marine life and ultimately causing cascading effects on higher trophic levels, including fish, marine mammals, and humans who rely on seafood for sustenance.
Name three human activities that can disrupt the ocean food chain.
Overfishing, pollution from agricultural runoff and plastic waste, and climate change-induced ocean warming and acidification are three human activities that can disrupt the ocean food chain by reducing biodiversity, impacting ecosystems, and potentially leading to the collapse of vital marine species.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments