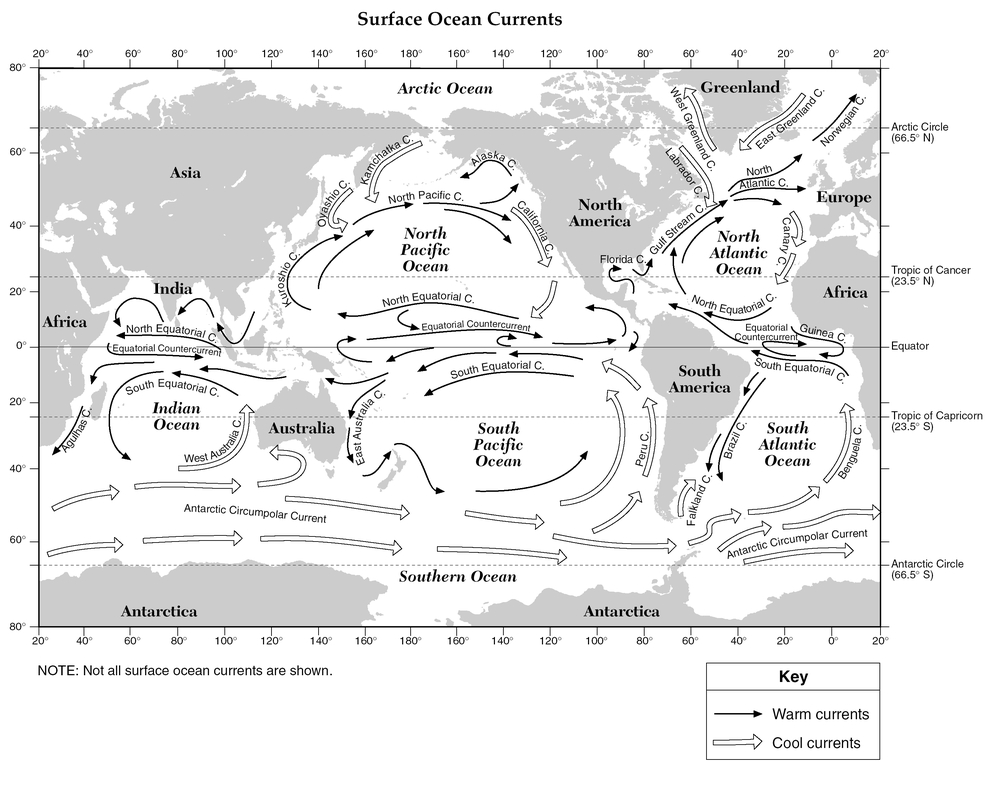
Ocean Currents Map Worksheet
Ocean currents play a crucial role in shaping our planet's climate and marine ecosystems. Understanding their patterns and characteristics is essential for students studying Earth science, geography, or environmental studies. This Ocean Currents Map Worksheet provides an engaging and interactive way for students to explore and analyze the movement of ocean currents around the world.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
Where are cold ocean currents typically found?
Cold ocean currents are typically found closer to the poles in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This is because cold water currents originate from polar regions where the water has been cooled by the surrounding icy conditions, leading to a denser and colder body of water that sinks and flows towards the equator.
Which ocean current is responsible for the Gulf Stream?
The Gulf Stream is primarily driven by the North Atlantic Drift, which is a warm and swift ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows up the Eastern coast of the United States before crossing the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe.
How do ocean currents affect global climate patterns?
Ocean currents play a vital role in regulating global climate patterns by redistributing heat around the planet. Warm ocean currents can bring milder temperatures to coastal regions, while cold ocean currents can cool down adjacent areas. These currents also play a significant role in influencing weather patterns by affecting the moisture content in the air and impacting precipitation levels. Ultimately, ocean currents help to transport heat and nutrients across vast distances, creating a complex interconnected system that significantly influences the Earth's climate.
Which ocean current brings warm water to the western coast of South America?
The ocean current that brings warm water to the western coast of South America is the Peru Current, also known as the Humboldt Current. This cold, nutrient-rich current flows northward along the coast, leading to the cooling effect known as the Humboldt Upwelling.
What causes the formation of ocean currents?
Ocean currents are largely driven by a combination of wind, temperature, salinity gradients, and the Coriolis effect. Winds push surface waters, creating surface currents, while differences in water density due to varying temperatures and salinity levels result in vertical and horizontal movements. The Coriolis effect, caused by the Earth's rotation, affects the direction of ocean currents by deflecting them to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere, ultimately shaping the complex circulation patterns we see in the oceans.
How do ocean currents influence marine life and ecosystems?
Ocean currents play a crucial role in shaping marine life and ecosystems by influencing the distribution of nutrients, temperature, and salinity in the water. These currents help transport essential nutrients and plankton to different parts of the ocean, providing food for various marine species. They also affect the migration patterns of marine animals and determine the connectivity between different populations. Additionally, ocean currents can impact the larval dispersal of organisms, affecting their survival and genetic diversity. Overall, ocean currents are essential for maintaining the balance and health of marine ecosystems.
What are the main factors that influence the direction and strength of ocean currents?
The main factors that influence the direction and strength of ocean currents include wind patterns, the rotation of the Earth (Coriolis effect), temperature and salinity gradients, coastal topography, and the shape of the ocean basins. Wind patterns drive surface currents, while the Coriolis effect deflects them, resulting in circular currents in each hemisphere. Variations in temperature and salinity create density gradients that drive vertical movements and deep currents. Coastal topography can funnel or deflect currents, while the shape of ocean basins can affect the speed and direction of flow. Collectively, these factors work together to shape the complex system of ocean currents around the world.
How do ocean currents transport heat around the Earth?
Ocean currents transport heat around the Earth by redistributing warm water from the equator to the poles and cooler water from the poles to the equator. This process helps regulate global temperatures by transferring heat energy from regions that receive more sunlight to regions that receive less sunlight, ultimately contributing to the Earth's climate system.
What is the impact of ocean currents on weather phenomena such as hurricanes?
Ocean currents play a critical role in shaping weather patterns, including the formation and intensity of hurricanes. Warm ocean currents provide the necessary energy and moisture for hurricanes to strengthen, while cold ocean currents can weaken them. For example, the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean can fuel the development of hurricanes by providing warm water and favorable conditions for convection. Similarly, the Pacific Ocean's El Niño and La Niña phenomena, which are linked to changes in ocean currents, can influence the frequency and intensity of hurricanes in the region. Overall, understanding the interactions between ocean currents and weather phenomena is essential for predicting and preparing for the impacts of hurricanes and other extreme weather events.
How do scientists study and track ocean currents?
Scientists study and track ocean currents using a variety of methods, including satellite imagery, moored buoys equipped with sensors, underwater vehicles, and drifting floats. Satellite-derived data help to identify surface currents, while moored buoys provide information on temperature, salinity, and current patterns at different depths. Underwater vehicles such as gliders and floats equipped with sensors can collect data on currents in real time, offering detailed insights into their behavior. By combining data gathered from these different sources, scientists are able to model and track ocean currents, providing valuable information for understanding climate patterns, marine ecosystems, and potential hazards like oil spills and pollution dispersion.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments