Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a student looking for an effective study tool to enhance your understanding of nuclear chemistry? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets as a valuable learning resource for this complex subject. By providing clear and concise questions, worksheets can help you grasp important concepts and reinforce your knowledge of nuclear chemistry.
Table of Images 👆
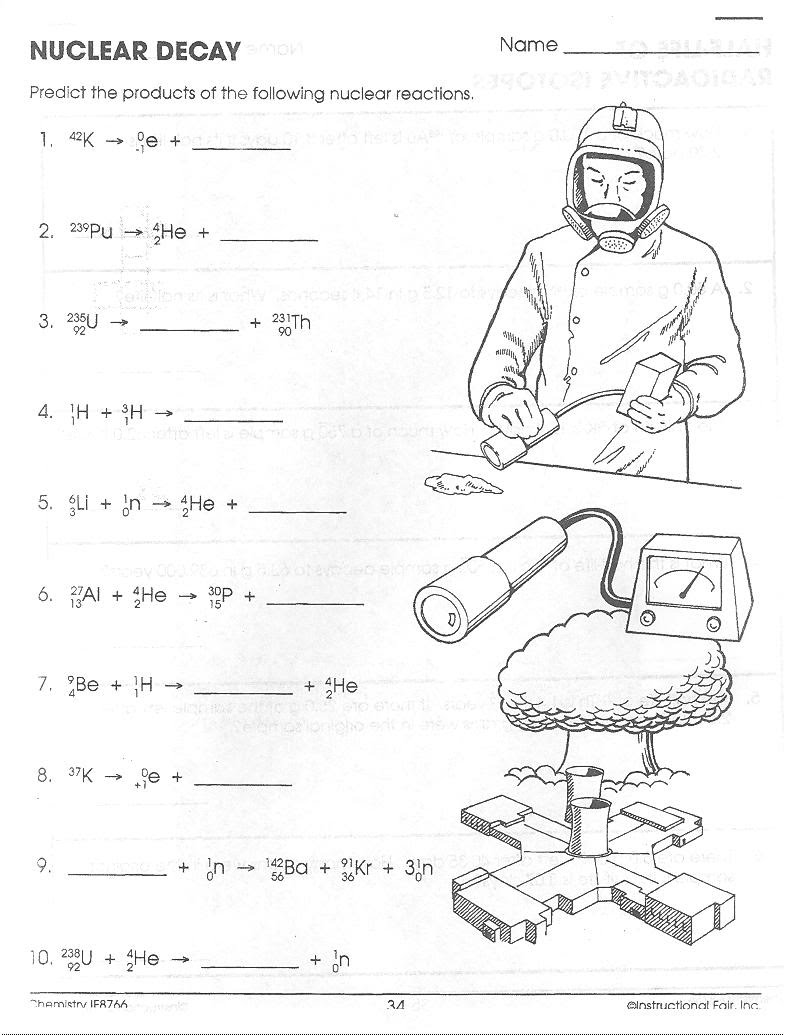
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet Answers
- Ph Calculations Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
- Chemistry Worksheet Matter 1 Answer Key
- Chapter 8 Chemistry Review Answers
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion Worksheet Answers
- Matter Worksheet Answer Key
- Enzyme Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
- Intensified Algebra Worksheets
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 11 Worksheet 1 Chemistry
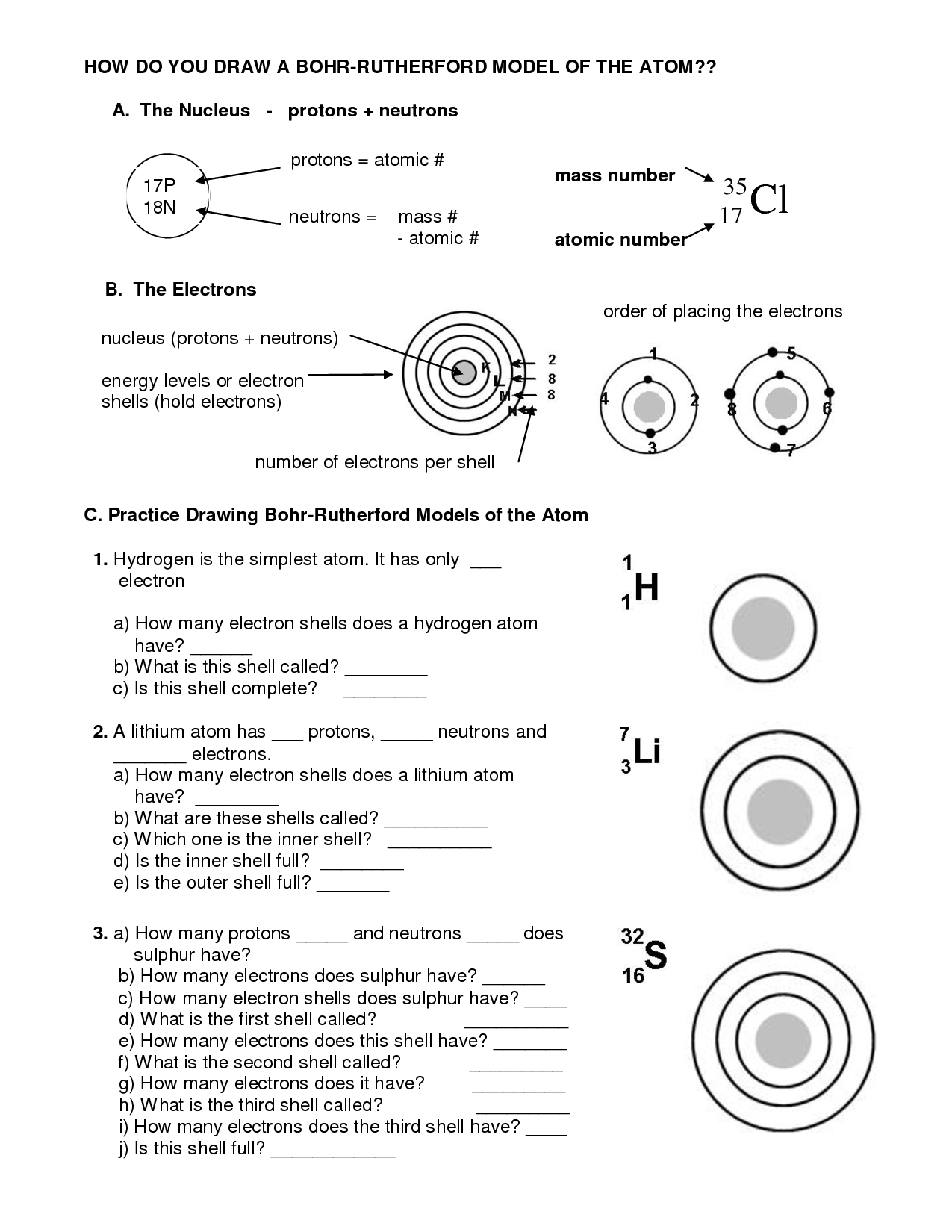
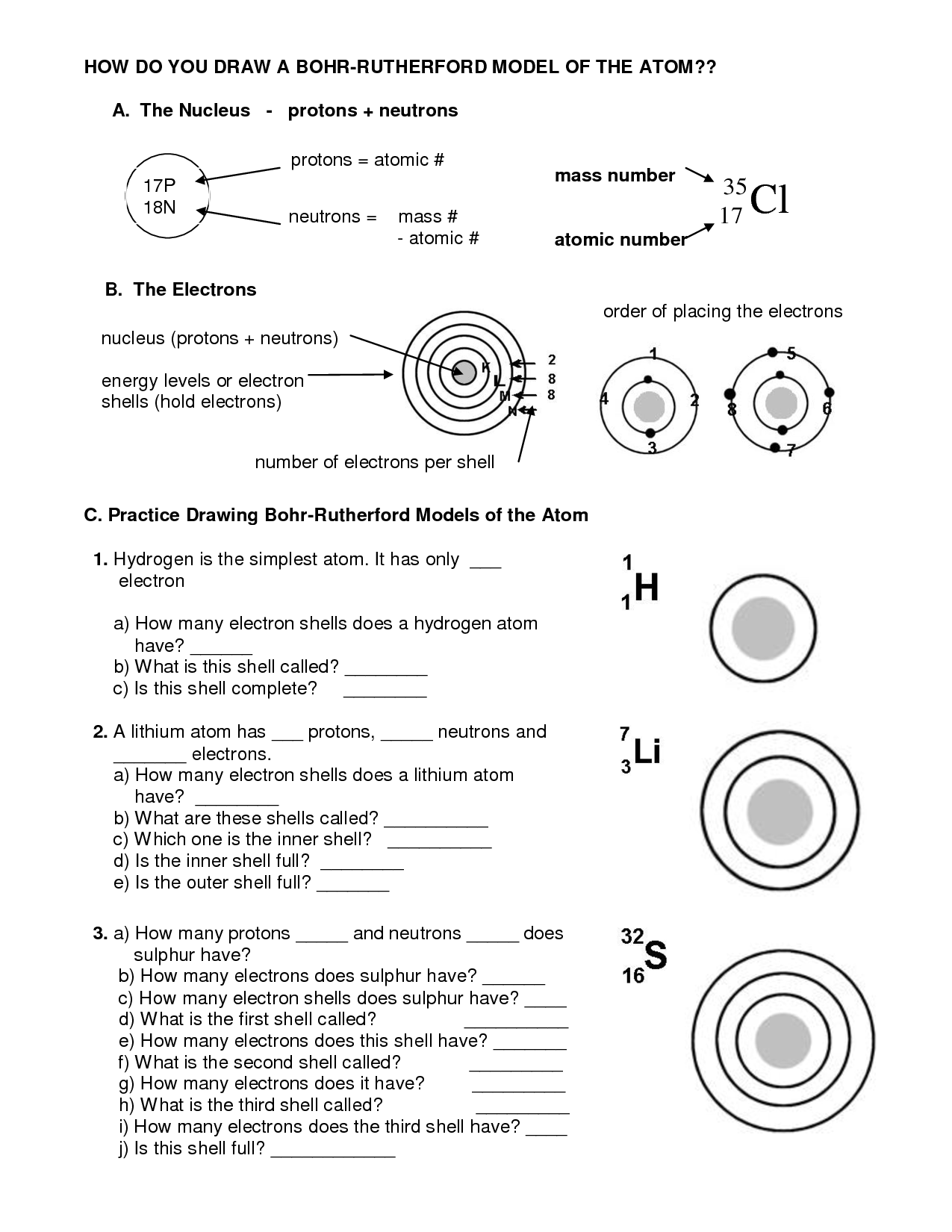
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
More Chemistry Worksheets
Chemistry Lab Equipment WorksheetChemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
Chemistry Conversion Factors Worksheet
Fun Chemistry Worksheets
What is nuclear chemistry?
Nuclear chemistry is the subfield of chemistry that deals with the properties, behavior, and interactions of atomic nuclei. It involves processes such as nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and the use of nuclear technology in various applications such as energy production, medicine, and research. The study of nuclear chemistry helps us understand the structure of atomic nuclei and the forces that govern their behavior, leading to advancements in various scientific and technological fields.
What is a nuclear reaction?
A nuclear reaction is a process in which the nucleus of an atom is changed through interactions with other atomic nuclei or particles, resulting in the creation or destruction of different isotopes of the element, release of energy, and often the emission of radiation. These reactions can occur spontaneously in radioactive materials or can be induced in a controlled manner in nuclear power plants or nuclear weapons.
What is a radioactive isotope?
A radioactive isotope is an unstable form of an element that undergoes radioactive decay, emitting radiation in the form of alpha or beta particles, or gamma rays. This decay process results in the release of energy and the transformation of the isotope into a different element. Radioactive isotopes are commonly used in various applications such as medical imaging, cancer treatment, dating archaeological artifacts, and generating electricity in nuclear power plants.
How is a nuclear fission reaction different from a nuclear fusion reaction?
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions differ in the way they release energy. In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom is split into smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy, while in nuclear fusion, two smaller atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, also releasing a significant amount of energy. Fission is the process used in current nuclear power plants, while fusion is still in the experimental stages for energy production. Each reaction has its own set of challenges and benefits in terms of safety, waste management, and efficiency.
What is half-life in the context of radioactive decay?
Half-life in the context of radioactive decay refers to the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to undergo decay, resulting in the transformation of unstable parent atoms into stable daughter atoms. It is a constant property specific to each radioactive isotope and is used to measure the rate of decay and the stability of the material. As each half-life passes, half of the remaining radioactive atoms will decay, resulting in a gradual decrease in the amount of the original radioactive material present in the sample.
How does the process of radioactive decay occur?
Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. This process is random and cannot be predicted for any individual atom. The decay changes the original atom into a different element or isotope with a more stable configuration, as it seeks to reach a more balanced or lower energy state.
What are the different types of radiation emitted during radioactive decay?
The different types of radiation emitted during radioactive decay are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons and have low penetration capability. Beta particles are high-energy electrons or positrons with higher penetration capability than alpha particles. Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation with the highest penetration capability and are often emitted alongside alpha and beta particles during radioactive decay.
How can nuclear reactions be used in medicine?
Nuclear reactions can be used in medicine for various applications, such as in nuclear imaging techniques like positron emission tomography (PET) scans and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scans to visualize internal structures and diagnose diseases. In addition, radioisotopes produced through nuclear reactions can be used for radiation therapy to treat certain types of cancer by targeting and destroying cancer cells. These applications demonstrate the important role of nuclear reactions in advancing medical diagnosis and treatment.
What are the potential risks and benefits associated with nuclear power plants?
Nuclear power plants offer benefits such as low greenhouse gas emissions, high energy output, and energy security. However, they also come with risks such as potential accidents leading to radioactive releases, long-term storage of radioactive waste, high cost of construction and decommissioning, as well as concerns regarding nuclear proliferation and terrorism. It is essential to carefully weigh these risks and benefits when considering the use of nuclear power as part of the energy mix.
How does nuclear chemistry influence our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe?
Nuclear chemistry plays a crucial role in our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe by explaining how elements were formed in the early universe through processes like nucleosynthesis during the Big Bang and in stars through fusion reactions. Studying nuclear reactions and decay also provides insights into the age of the universe and the abundance of different elements, helping scientists piece together the complex history of cosmic evolution. Additionally, radioactive isotopes serve as cosmic clocks, allowing researchers to date ancient celestial bodies and events, further deepening our understanding of the universe's origins.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments