Naming Organic Compounds Practice Worksheet
Worksheet activities are a great way to solidify your understanding of organic compounds and their naming conventions. Whether you're a student studying chemistry or an enthusiast looking to deepen your knowledge, this Naming Organic Compounds Practice Worksheet is tailored to help you grasp the concepts of identifying and naming different types of organic compounds accurately and confidently.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheets with Answers
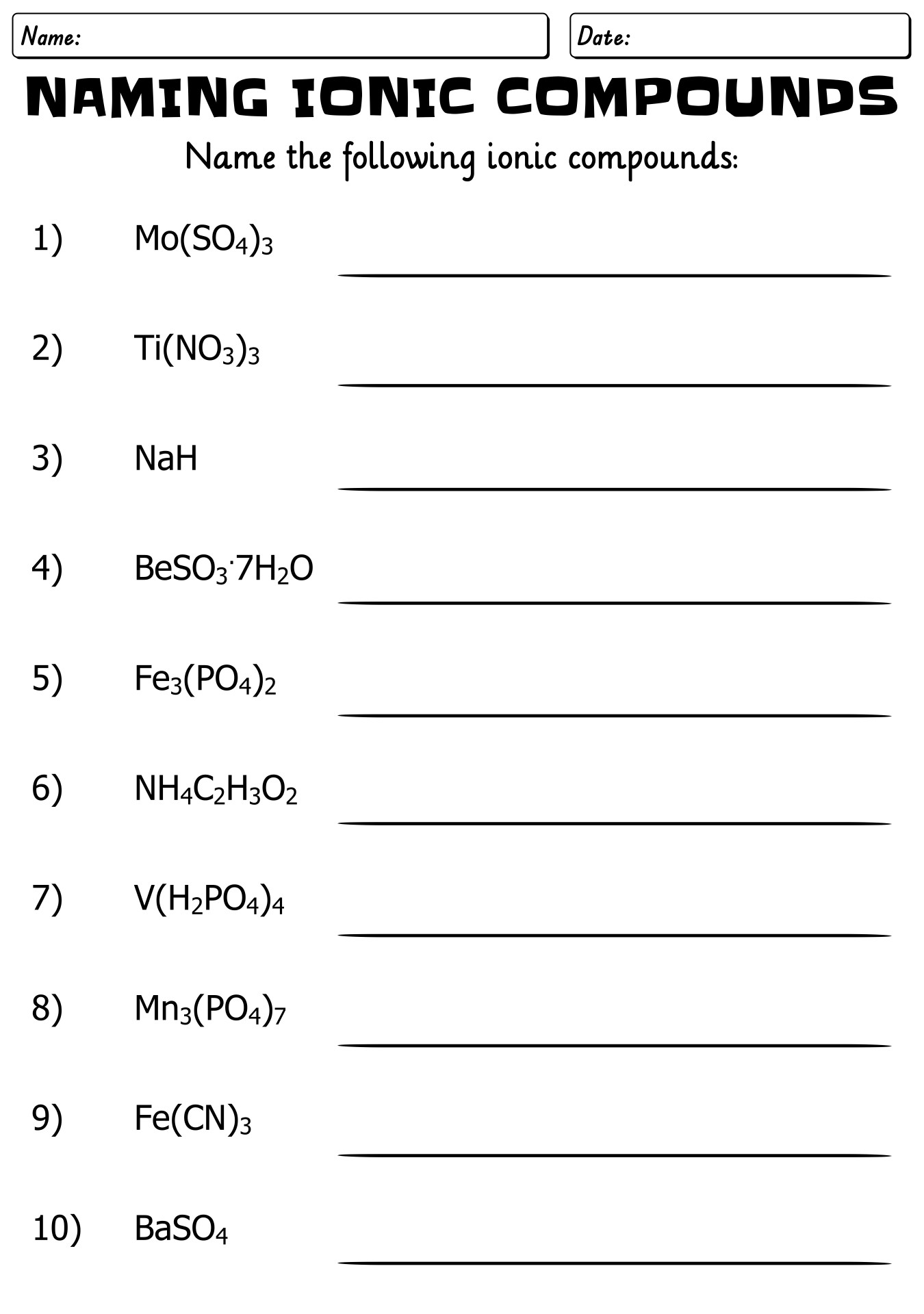
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Molecular Compounds Worksheet
- Organic Chemistry Naming Alkanes Worksheet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheets with Answers
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Practice Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
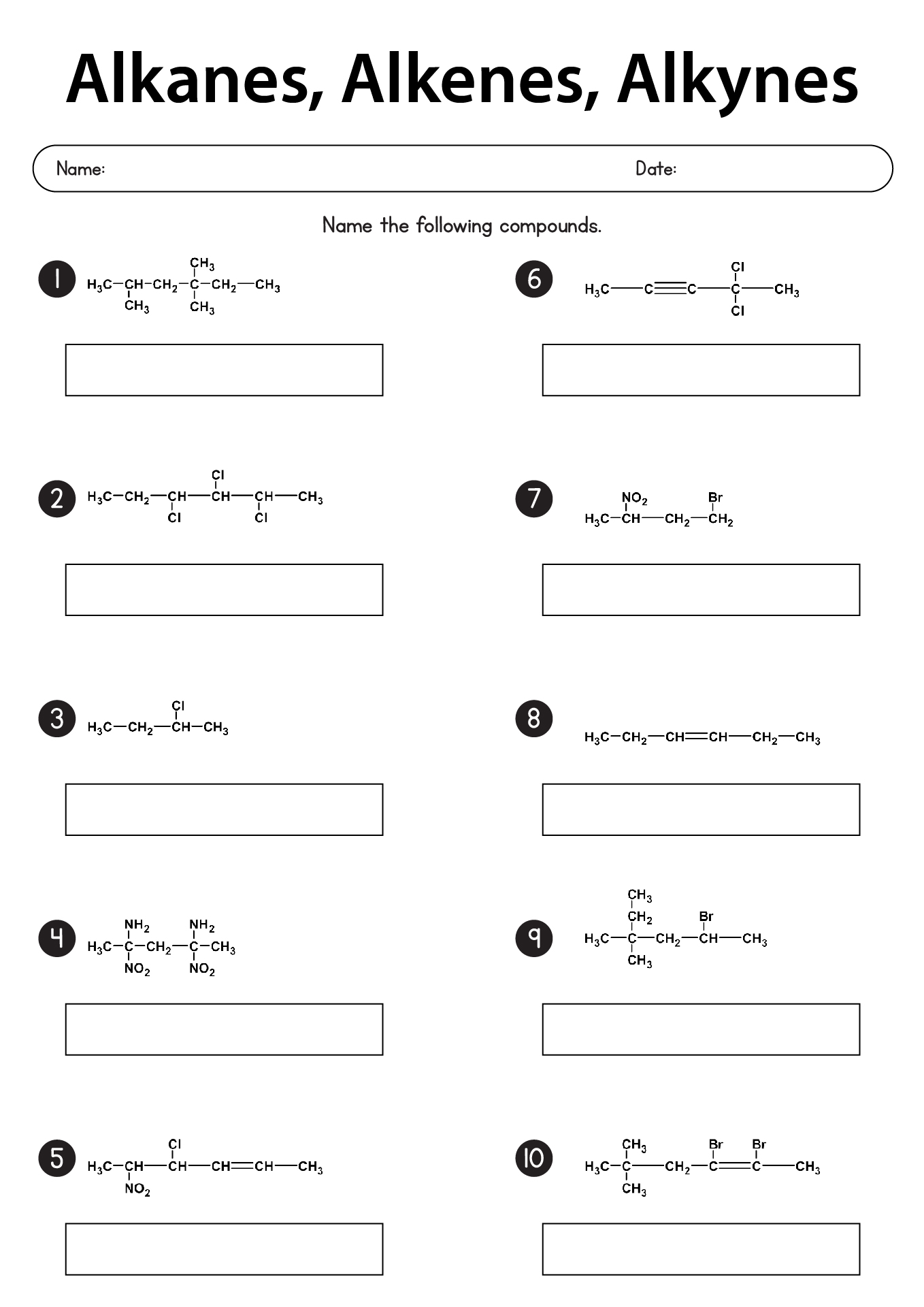
- Naming Alkanes Alkenes and Alkynes
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer

More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
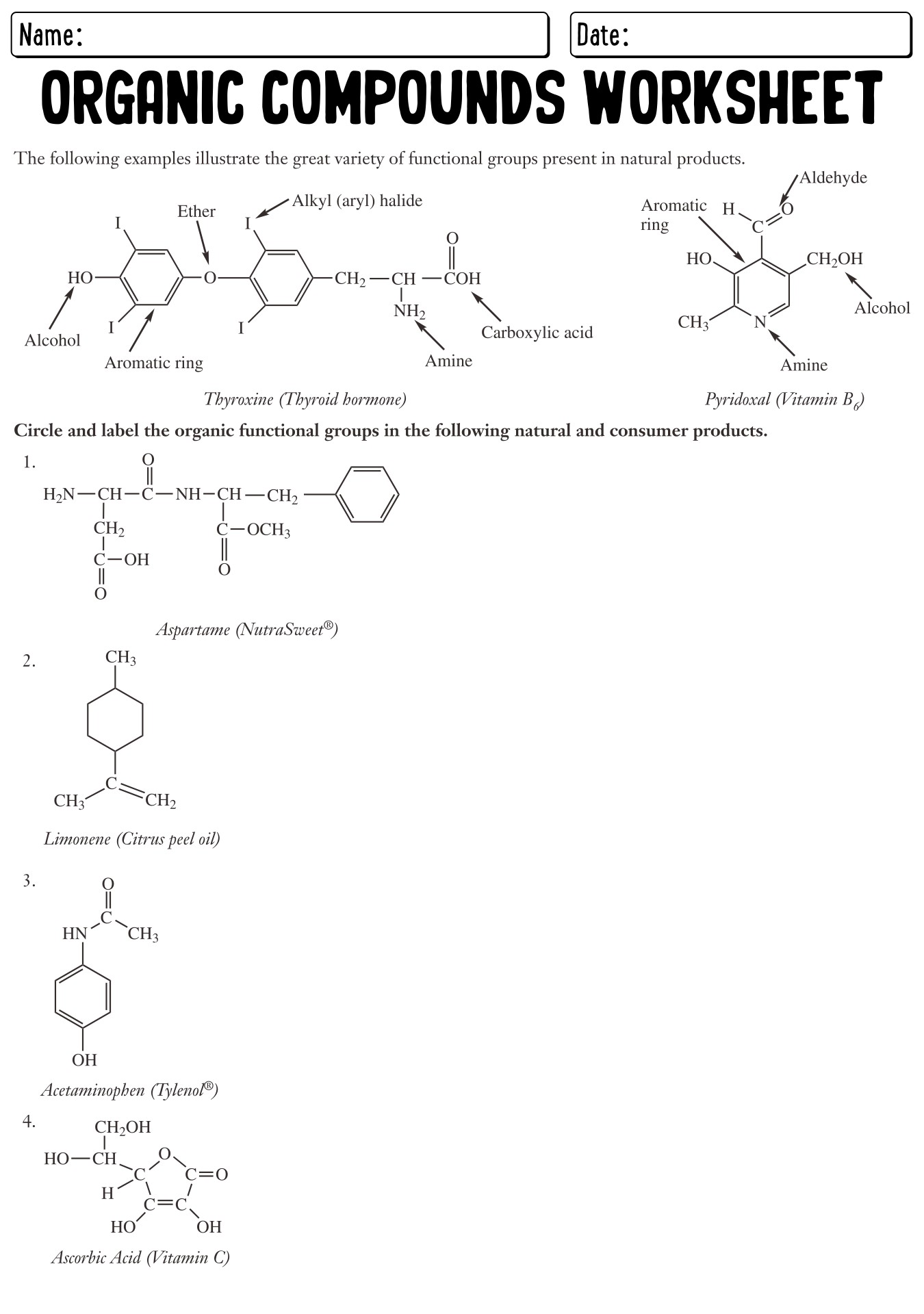
What are organic compounds?
Organic compounds are molecules that contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds, typically derived from living organisms. These compounds can range from simple molecules like methane to complex molecules such as proteins and DNA. Many organic compounds also contain other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that focuses on the study and synthesis of these carbon-containing compounds.
Why is it important to have a systematic way of naming organic compounds?
Having a systematic way of naming organic compounds is important because it allows scientists to easily communicate and understand the structure and properties of different molecules. A systematic naming system, such as the IUPAC system, provides a standardized way to describe organic compounds based on their composition and structure, facilitating accurate representation and interpretation of chemical information. This helps prevent confusion and ensures consistency in naming, making it easier to identify and differentiate compounds in research, education, and practical applications.
What is the role of functional groups in naming organic compounds?
Functional groups are specific atoms or groups of atoms within an organic compound that determine its chemical properties and reactivity. They play a crucial role in naming organic compounds because the presence of a functional group in a molecule gives it a specific name and indicates the type of chemical reactions it can undergo. Functional groups are used as prefixes or suffixes in the systematic nomenclature of organic compounds to classify and identify them based on their structural characteristics and properties.
How does the IUPAC system help to categorize and name organic compounds?
The IUPAC system provides a standardized set of rules for naming organic compounds based on their structure and properties. It helps categorize compounds by classifying them into different functional groups, such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, etc., based on the types of atoms and bonds present in the molecule. By following these rules, chemists can systematically name and identify organic compounds, which aids in communication, research, and teaching within the field of organic chemistry.
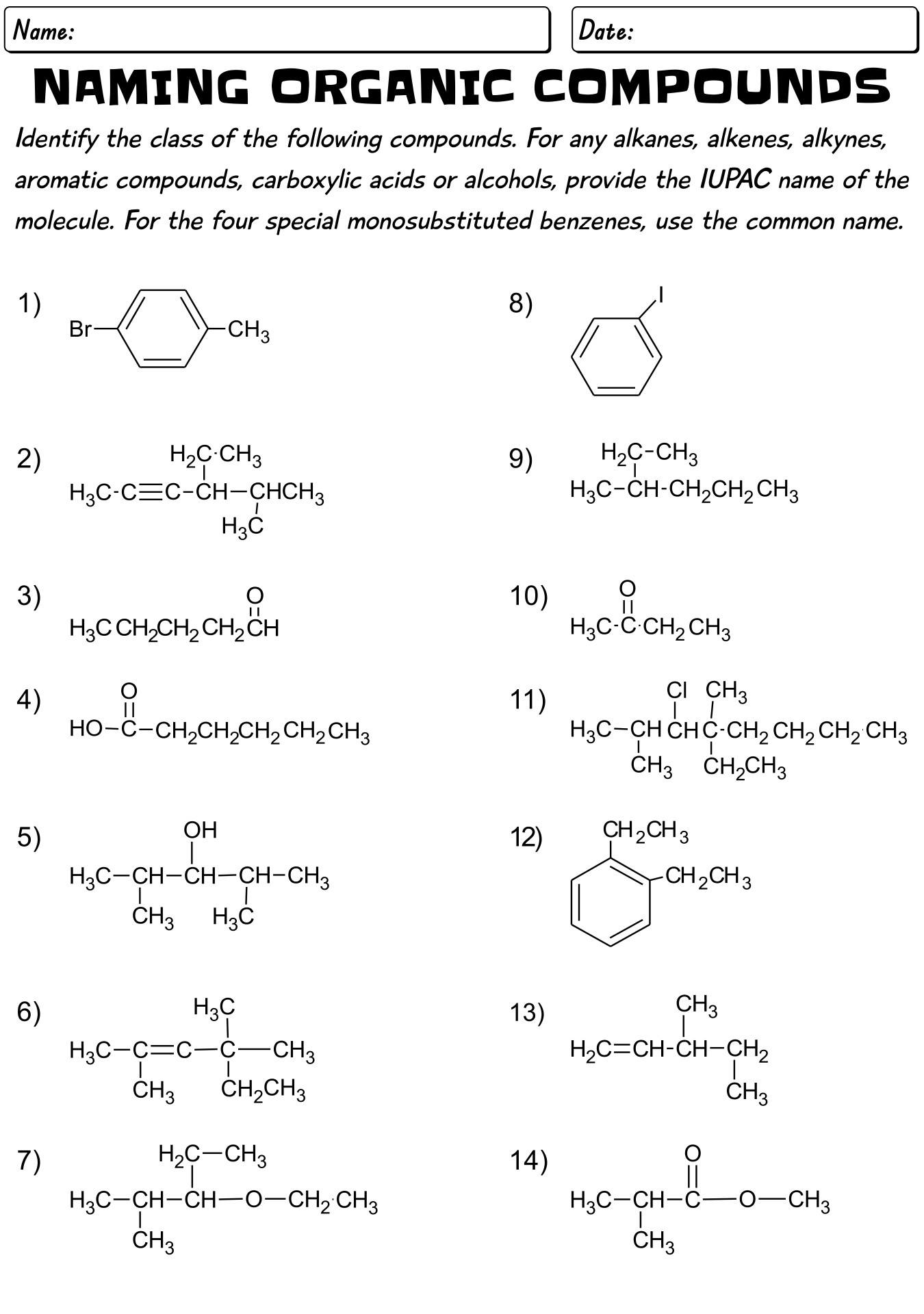
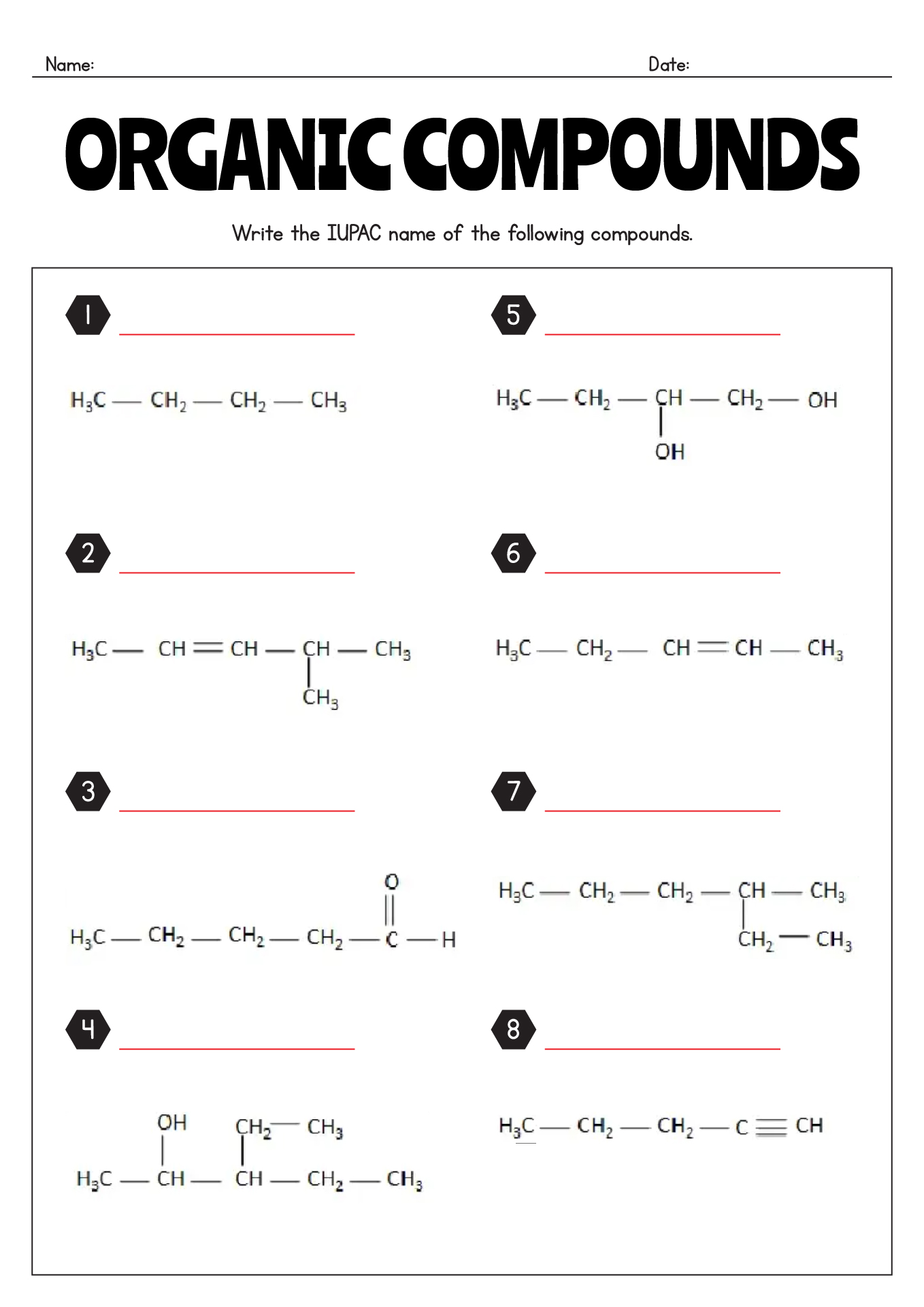
What are the general rules for naming alkanes?
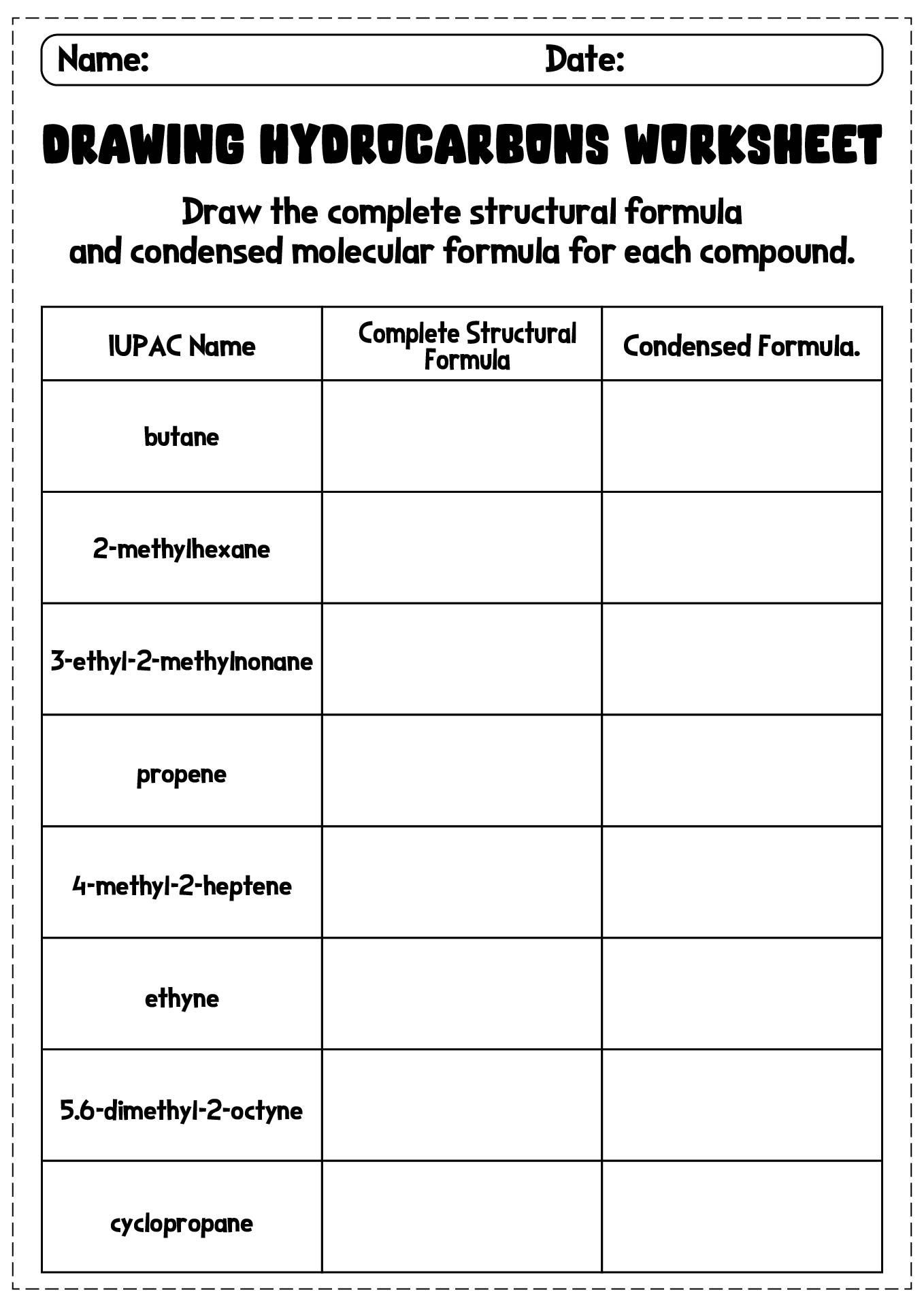
The general rules for naming alkanes involve using prefixes to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain (parent chain) and suffixes based on the type of bond present (-ane for single bonds). Substituents (such as alkyl groups or functional groups) are named as prefixes, and their positions are indicated by numbers. The locants of substituents are chosen to give the lowest set of numbers. The name of the alkane is assembled by arranging the prefixes and suffixes in alphabetical order. Additionally, common names may be used for simple alkanes, where the substituent name is placed before the parent chain name.
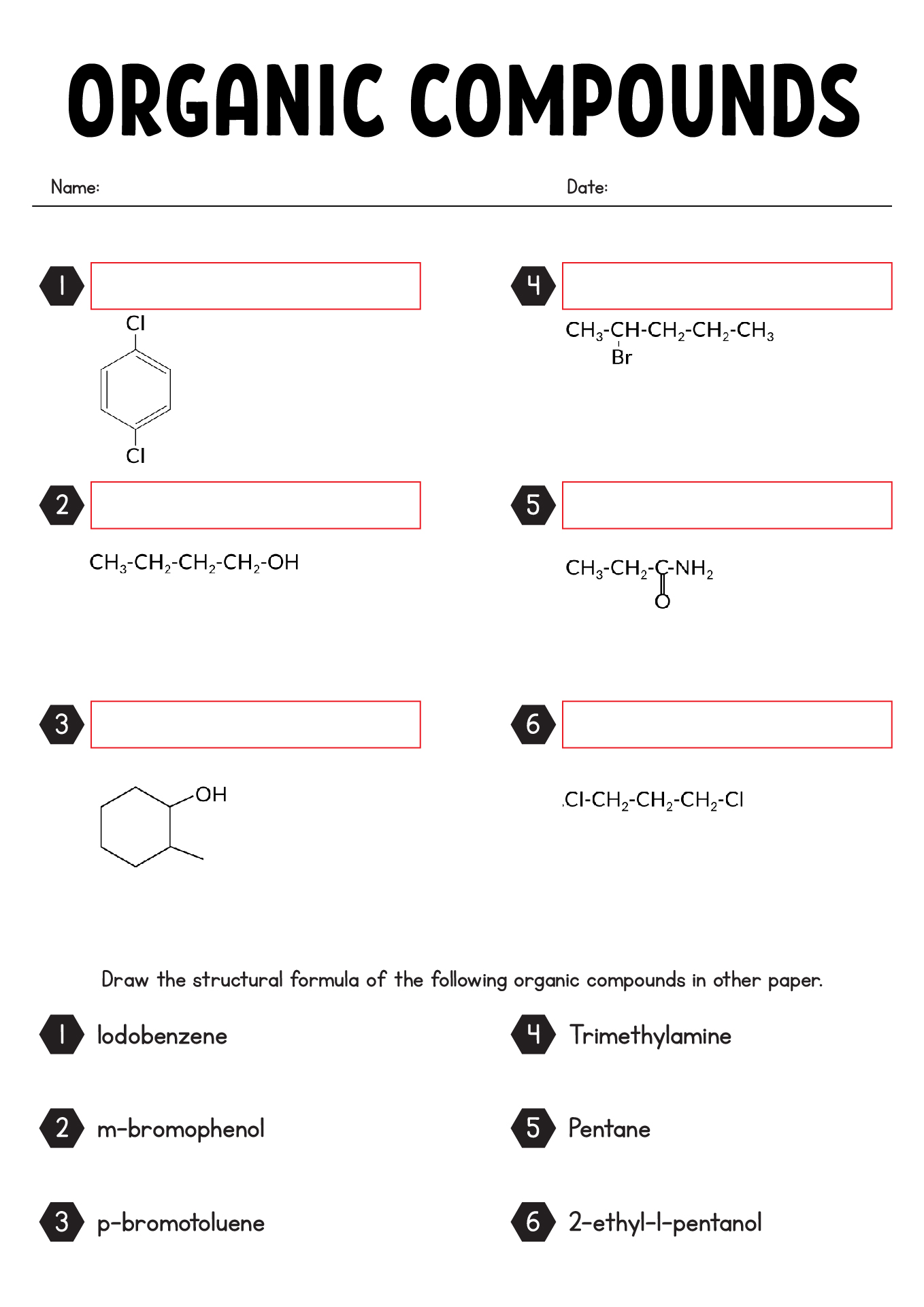
How do you name organic compounds with substituent groups?
Organic compounds with substituent groups are named by identifying the parent structure (usually the longest carbon chain) and then naming and locating the substituent groups along the parent structure. Substituent groups are named based on the number of carbons and their functional groups, and they are listed in alphabetical order when naming the compound. The location of each substituent is indicated by a numerical prefix, with the carbons numbered consecutively to give the lowest possible location numbers to the substituent groups.
What is the difference between naming cyclic and acyclic organic compounds?
The key difference between naming cyclic and acyclic organic compounds lies in the structure of the carbon skeleton. Cyclic compounds contain one or more rings of carbon atoms in their structure, whereas acyclic compounds have an open chain of carbon atoms. In terms of naming, cyclic compounds are identified by the total number of carbon atoms in the ring followed by the prefix "cyclo-," while acyclic compounds are simply named based on the longest carbon chain present in the molecule. This distinction is important as it helps in accurately identifying and classifying different types of organic compounds based on their structure.
How do you indicate the position of a substituent group in the compound's name?
To indicate the position of a substituent group in a compound's name, you typically use a number before the substituent name that corresponds to the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached in the parent chain. The number is separated from the substituent name by a hyphen. This numbering allows for a clear and specific designation of where the substituent is positioned in the compound's structure.
What are some common prefixes and suffixes used in naming organic compounds?
Common prefixes used in naming organic compounds include meth- (1 carbon atom), eth- (2 carbon atoms), prop- (3 carbon atoms), but- (4 carbon atoms), pent- (5 carbon atoms), hex- (6 carbon atoms), hept- (7 carbon atoms), oct- (8 carbon atoms), non- (9 carbon atoms), and dec- (10 carbon atoms). Common suffixes include -ane (single bonds only), -ene (double bonds), -yne (triple bonds), -ol (alcohol functional group), -one (ketone functional group), -oic acid (carboxylic acid functional group), and -amine (amine functional group).
What are some examples of complex organic compounds and how are they named?
Some examples of complex organic compounds include glucose, acetaminophen, and DNA. These compounds are named based on the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature system, which assigns a systematic name to each compound based on its structure and functional groups. This naming system follows specific rules to indicate the type and position of atoms within the molecule, allowing for clear and standardized identification of organic compounds.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments