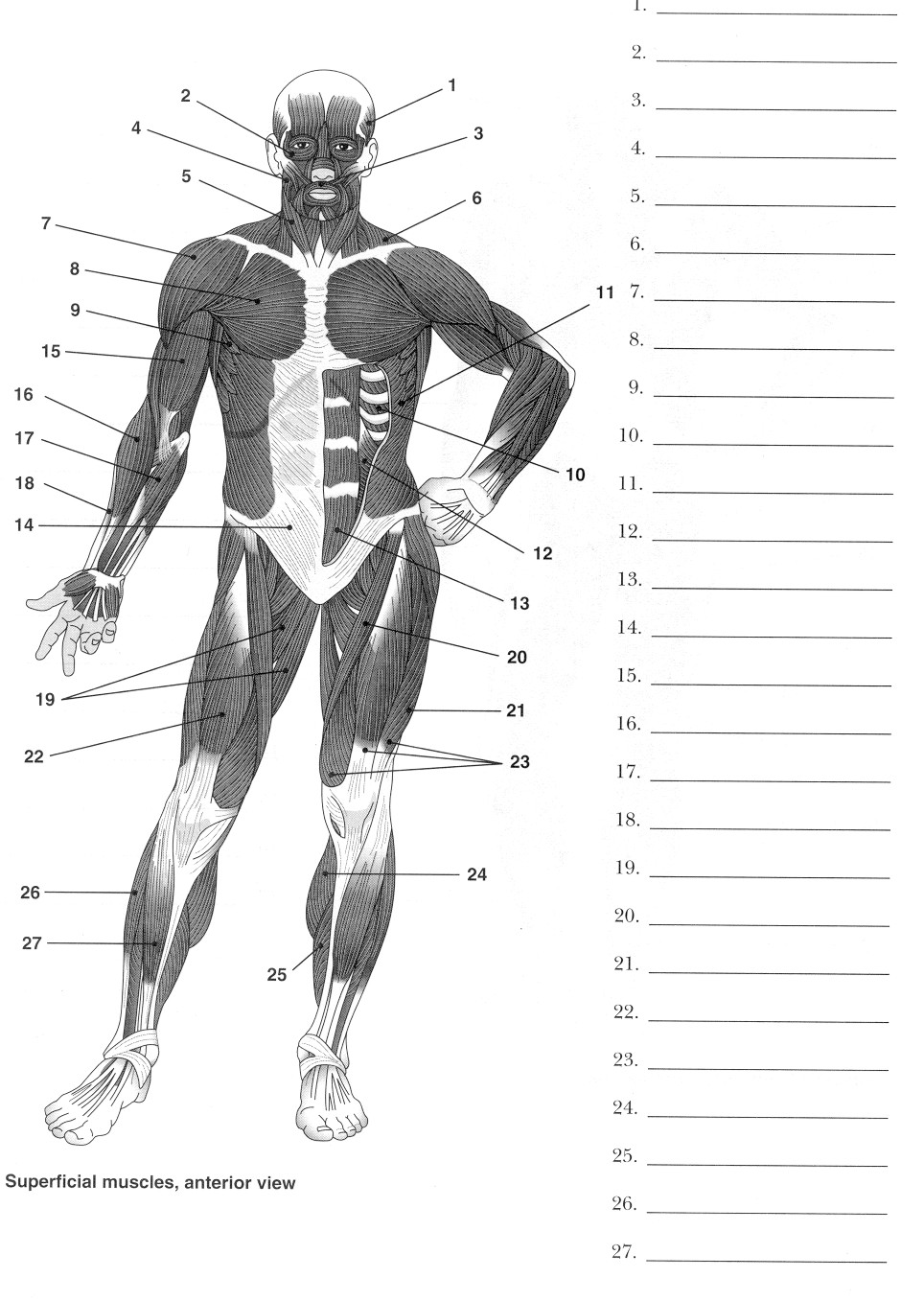
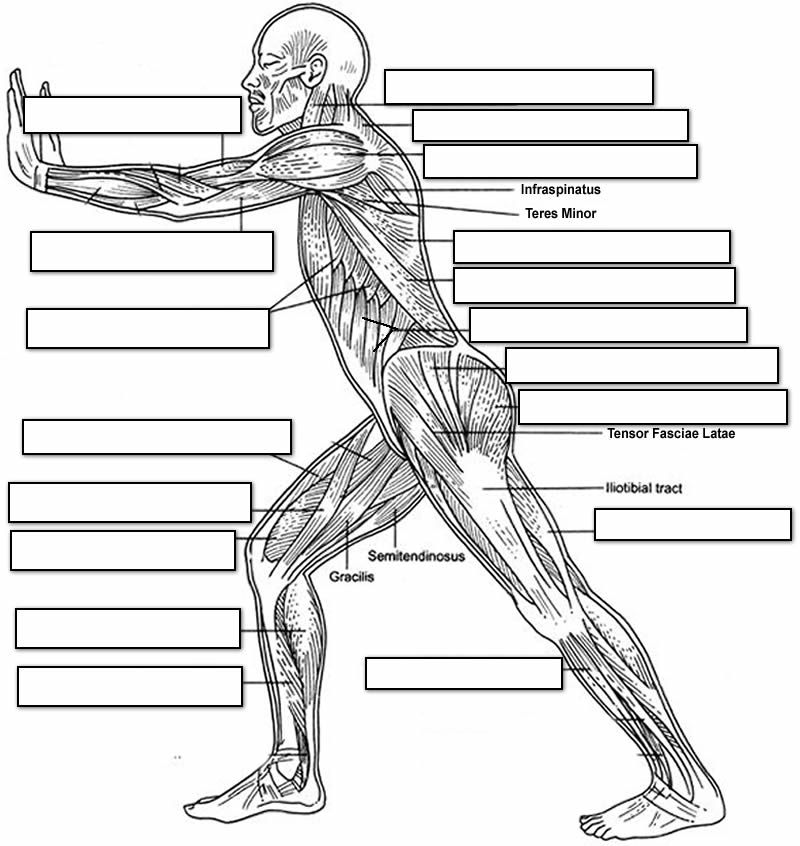
Muscle Review Worksheet
Are you looking for a way to reinforce your knowledge of muscle anatomy and function? Look no further than the Muscle Review Worksheet. Designed to cater to students and individuals interested in biology or physical education, this worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of muscle structure and how it relates to movement and body mechanics. By utilizing this worksheet, you will be able to solidify your understanding of key concepts and enhance your ability to identify and label different muscle groups.
Table of Images 👆
- Label Muscles Worksheet
- The Muscular System Worksheets Answer Key Chapter 6
- Muscle Tissue Worksheet Answers
- Muscular System Worksheets High School
- 7th Grade Body Systems Worksheets
- Anatomy and Physiology Worksheet Answers
- Nervous System Worksheet Answers
- Human Body Muscles
- The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Tissue Worksheet
- Joint Worksheets Skeletal System
- Human Body Muscle Diagram Worksheet
- Muscle Tissue Worksheet
- Immune System Worksheet Answers
- Muscle Physiology Worksheet
- Muscles Worksheet Answer Key
- Muscles Study Guide Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is responsible for voluntary movements, cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood, and smooth muscle is found in internal organs and controls involuntary movements such as digestion and blood vessel constriction.
What is the main function of skeletal muscles?
The main function of skeletal muscles is to create movement by contracting and pulling on the skeleton, enabling us to perform voluntary actions like walking, running, lifting objects, and making facial expressions. Additionally, skeletal muscles also help maintain posture, stabilize joints, generate heat, and protect internal organs.
What is the structure of a muscle fiber?
A muscle fiber is a long, cylindrical cell with multiple nuclei located around the periphery. It is composed of several key components, including myofibrils, sarcoplasmic reticulum, transverse (T) tubules, and mitochondria. The myofibrils contain the contractile proteins actin and myosin, which are responsible for muscle contraction. The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium ions that are essential for muscle contraction. Transverse (T) tubules are invaginations of the cell membrane that help transmit signals for muscle contraction. Mitochondria provide energy in the form of ATP for muscle function.
How are muscles attached to bones?
Muscles are attached to bones via tendons, which are strong, fibrous connective tissues that connect muscle to bone. Tendons are made up of collagen fibers and their main function is to transfer the force generated by the muscle to the bone, allowing for movement of the skeleton. This connection between muscles and bones enables movement and provides stability to the joints in the human body.
How do muscles contract?
Muscles contract when motor neurons release neurotransmitters at the neuromuscular junction, leading to the generation of an action potential along the muscle fiber. This action potential triggers the release of calcium ions inside the muscle cell, allowing the actin and myosin filaments to interact and slide past each other, causing muscle contraction. This process is governed by the sliding filament theory, where the myosin heads pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, ultimately shortening the muscle fiber and generating mechanical force.
What is the role of the neuromuscular junction in muscle contraction?
The neuromuscular junction is a synaptic connection between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber, where acetylcholine is released from the neuron, binding to receptors on the muscle fiber membrane, causing depolarization and the initiation of an action potential that leads to muscle contraction. This junction is crucial for transmitting signals from the nervous system to the muscular system, ultimately enabling muscle movement and control.
What is the sliding filament theory?
The sliding filament theory is a theory that explains how muscle contractions occur in the body. It states that during muscle contraction, myosin filaments slide over actin filaments, causing the sarcomeres (the basic unit of muscle contraction) to shorten. This sliding action is powered by the interaction between myosin and actin, with ATP providing the energy for the process. As the myosin filaments pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, the muscle fibers contract, generating force and movement.
What causes muscle fatigue?
Muscle fatigue can be caused by a variety of factors including the build-up of metabolic byproducts such as lactic acid, depletion of energy stores like ATP and glycogen, accumulation of reactive oxygen species, and disruptions in muscle cell ion concentrations. Additionally, muscle fatigue can also occur due to inadequate blood flow, nerve signals, and muscle damage.
What is the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions?
Isotonic muscle contractions involve the muscle changing length as it contracts, such as during activities like lifting weights. On the other hand, isometric muscle contractions occur when the muscle contracts but doesn't change length, like when holding a plank position. The main difference is that isotonic contractions involve movement and a change in muscle length, while isometric contractions involve no movement or change in muscle length.
How does muscle tissue repair and regenerate?
Muscle tissue repairs and regenerates through a process called muscle remodeling, where damaged muscle fibers are broken down and replaced by new muscle fibers. Initially, inflammatory cells clear out the damaged tissue, followed by the activation and proliferation of satellite cells that differentiate into myoblasts and fuse to form new muscle fibers. This process is aided by factors like growth factors, hormones, and nutrients that support muscle repair and growth. Over time, the new muscle fibers mature and integrate into the existing muscle structure, contributing to muscle tissue repair and regeneration.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments