Momentum Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are a valuable resource for anyone seeking to sharpen their understanding of a specific subject or entity. Whether you're a student looking to solidify your grasp on a challenging concept or a teacher in need of a supplementary tool for your classroom, worksheets offer a structured approach to learning that encourages engagement and promotes effective knowledge retention.
Table of Images 👆
- Impulse and Momentum Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
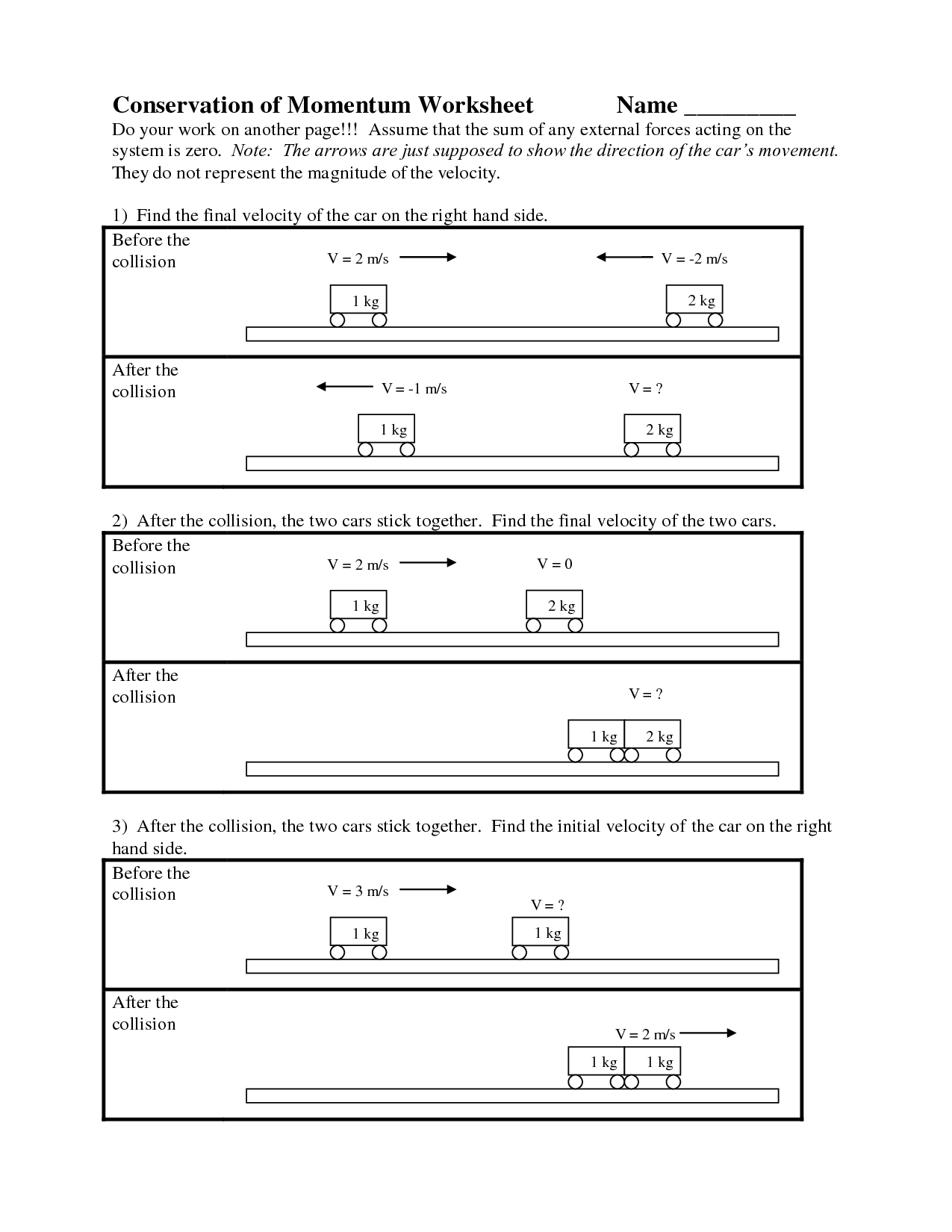
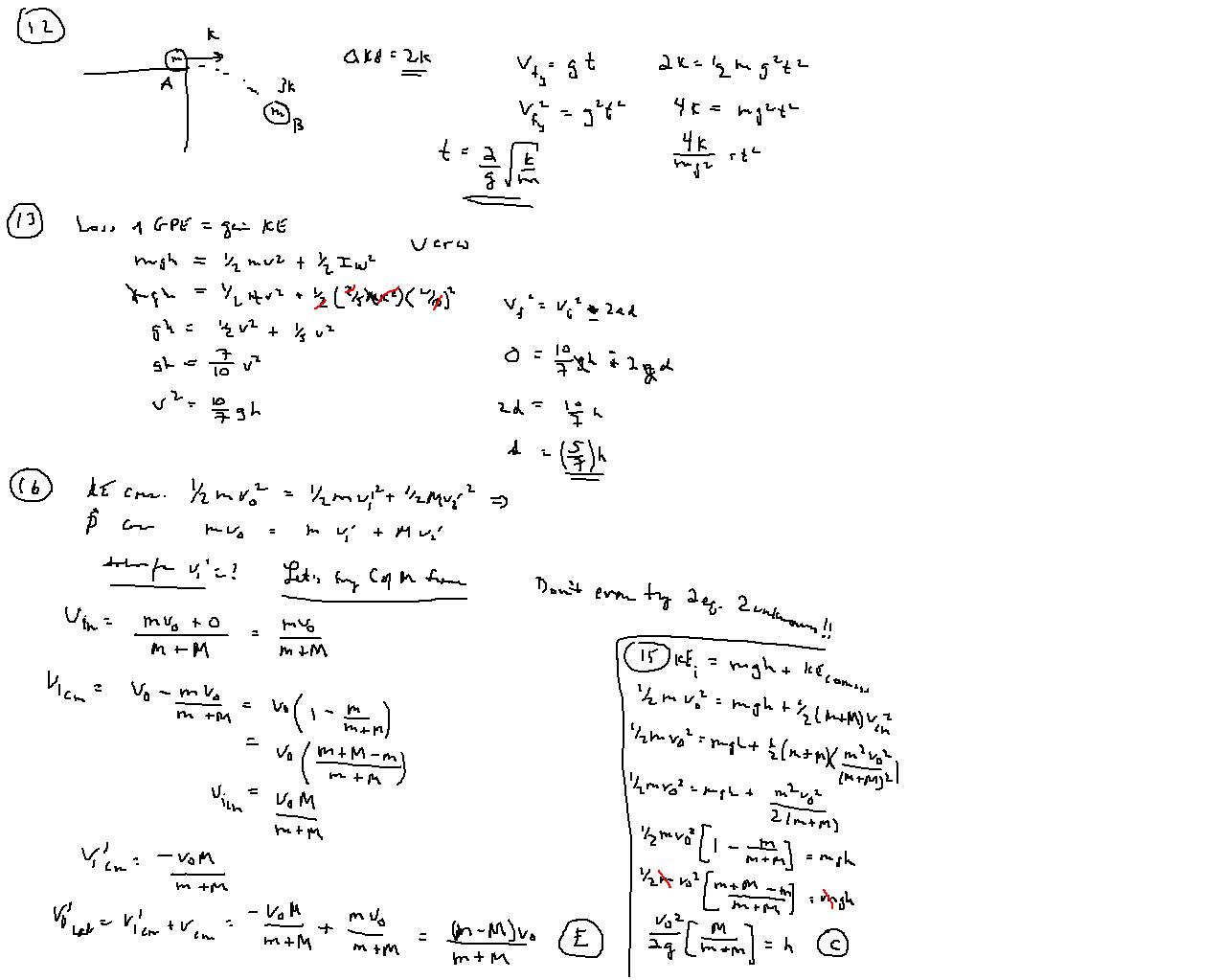
- Momentum Conservation Worksheet with Answers
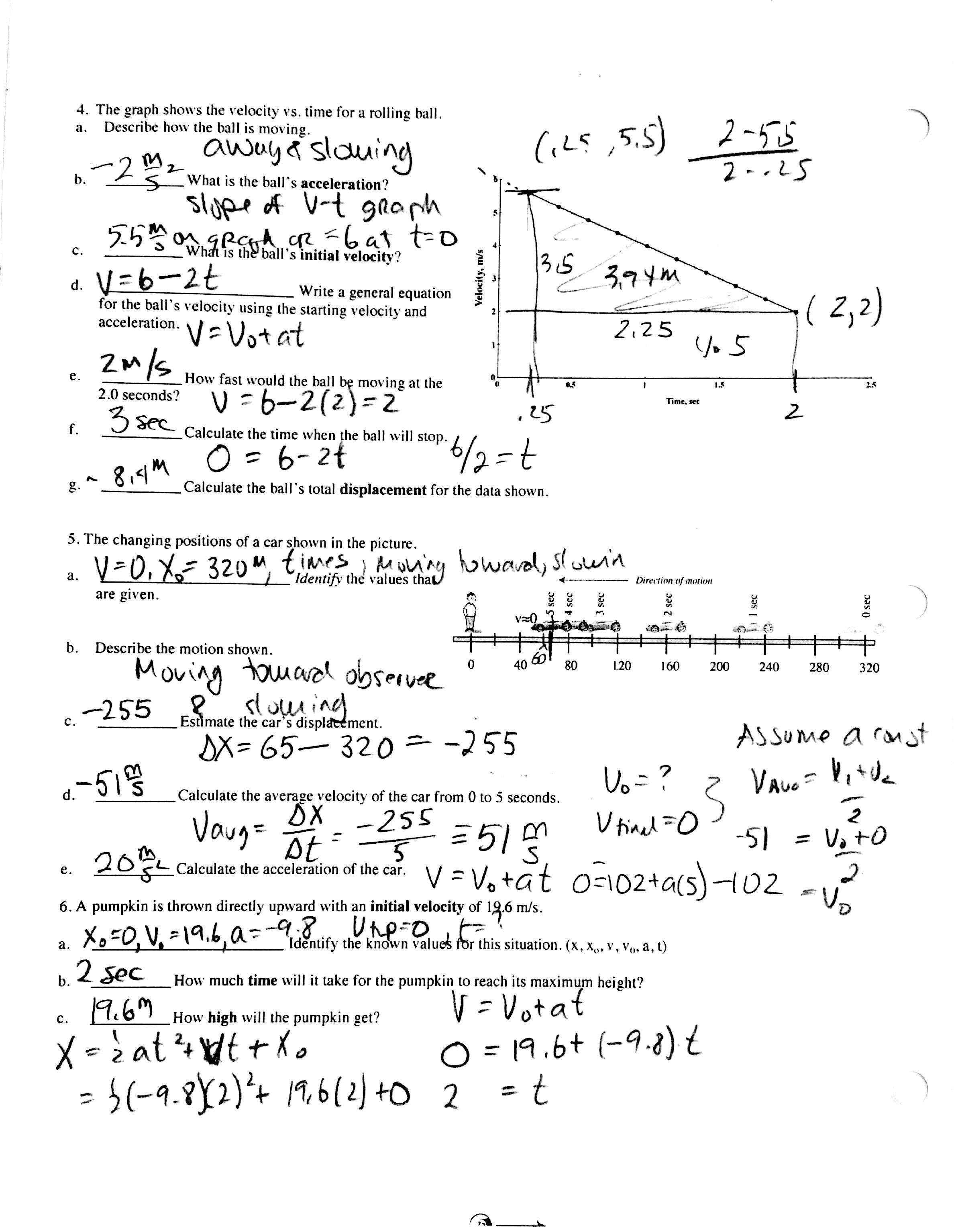
- Physics Kinematics Worksheet Answers
- Physics Problem Sets and Solutions
- Manufacturing Training Worksheet Examples
- Practice Problems Speed Velocity Worksheet
- Momentum and Impulse Worksheet with Answer Key
- Scientific Notation Answer
- Reading Volume Graduated Cylinder Worksheet
- Conceptual Physics Heat Worksheets
- Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key PhET Simulation
- Newtons Second Law Worksheet Answers
- Hydraulic Gear Pump Diagram
- Hydraulic Gear Pump Diagram
- Hydraulic Gear Pump Diagram
- Hydraulic Gear Pump Diagram
- Hydraulic Gear Pump Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
What is momentum?
Momentum is a physical quantity that represents the motion of an object. It is calculated by multiplying an object's mass by its velocity, and it is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Momentum is a crucial concept in physics as it governs how objects interact with each other during collisions and plays a key role in understanding the conservation of energy and momentum in various physical systems.
Momentum is a measure of an object's mass and velocity combined.
Yes, that is correct. Momentum is a vector quantity that is calculated as the product of an object's mass and velocity. It indicates the amount of motion an object possesses, with larger momentum values indicating greater motion.
How is momentum calculated?
Momentum is calculated by multiplying an object's mass by its velocity. The equation for momentum is: momentum = mass x velocity. This means that the momentum of an object is directly proportional to both its mass and velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction, and its units are kilogram meters per second (kg m/s).
Momentum is calculated by multiplying an object's mass by its velocity.
Yes, that is correct. Momentum is the product of an object's mass and its velocity. The formula for momentum is P = m * v, where P is momentum, m is mass, and v is velocity.
What are the SI units of momentum?
The SI units of momentum are kilogram meters per second (kg•m/s).
The SI units of momentum are kilogram-meter per second (kg·m/s).
Yes, the SI units for momentum are kilogram-meter per second (kg·m/s). It is a derived unit that combines the mass of an object in kilograms with its velocity in meters per second to quantify the quantity of motion it possesses.
Is momentum a scalar or vector quantity?
Momentum is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
Momentum is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
Yes, momentum is indeed a vector quantity because it not only has a magnitude, which represents the amount of motion an object possesses, but also a direction indicating the object's motion.This makes momentum a vector quantity, distinguishing it from scalar quantities that have magnitude only.
What is the law of conservation of momentum?
The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces are acting on it. This means that in a collision or interaction between objects, the total momentum before the event is equal to the total momentum after the event, assuming no external forces are present. This principle is a fundamental concept in physics that helps to analyze and predict the motion of objects.
The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act upon it.
The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act upon it.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments