Momentum Conservation Worksheet with Answers
Are you a physics student struggling to grasp the concept of momentum conservation? Look no further! This blog post is specifically designed to guide you through a momentum conservation worksheet with answers, making it easier for you to understand and apply this fundamental principle in your studies. With clear explanations and worked examples, you'll gain a solid understanding of the topic and be well-prepared for any related questions or assessments in your coursework.
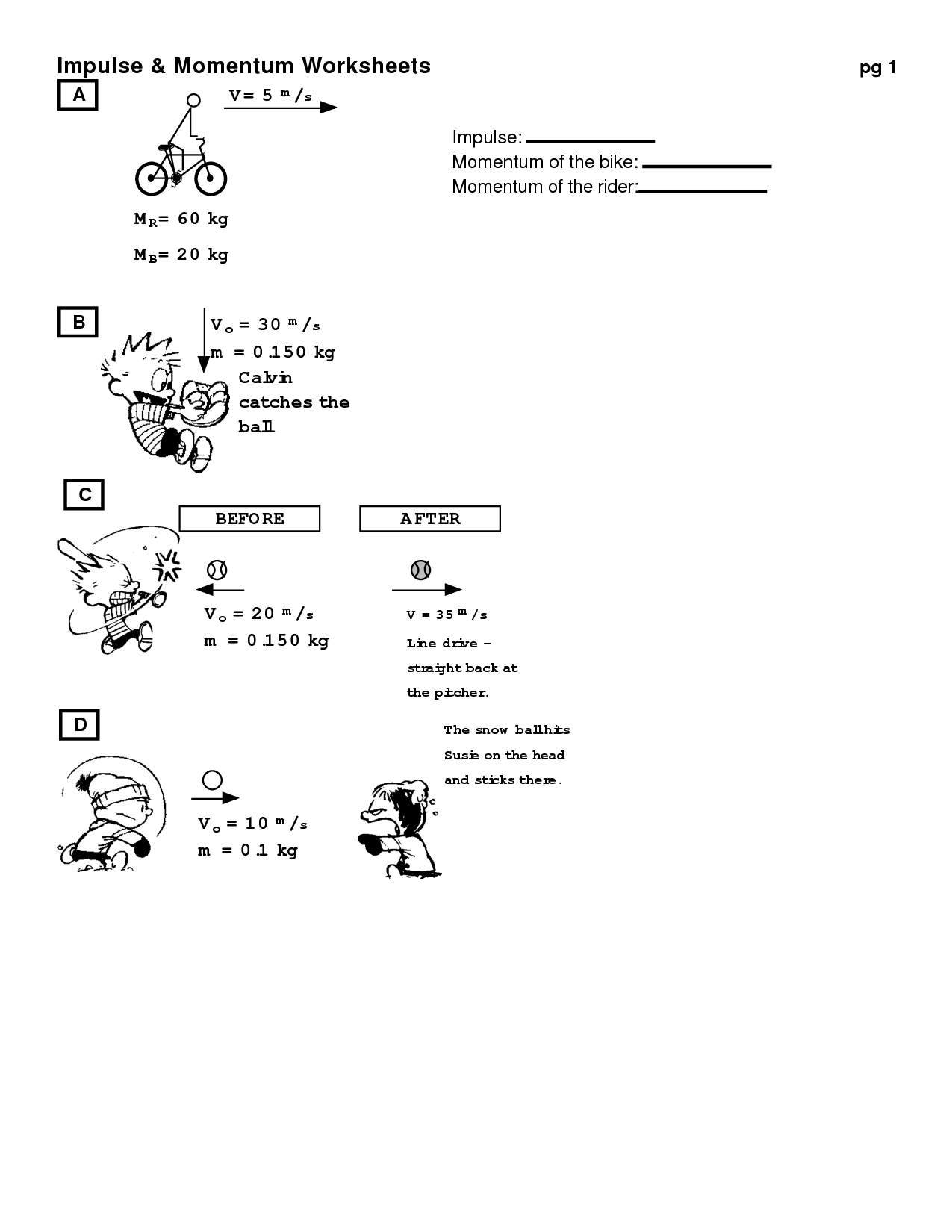
Table of Images 👆
- Momentum Worksheets with Answers
- Conservation of Momentum Worksheet Answers
- Momentum Worksheet Answer Key
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Energy Transformation Worksheet Answer Key
- Impulse-Momentum Worksheet with Answer Key
- Conceptual Physics Worksheet Answers
- Momentum and Impulse Worksheet with Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is momentum conservation?
Momentum conservation is a fundamental principle in physics that states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act on it. This means that in a system where there are no external forces present, the total momentum before an event is equal to the total momentum after the event. This principle is derived from Newton's laws of motion and is a powerful tool in analyzing and predicting the outcomes of various physical interactions and processes.
Momentum conservation is the principle that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant unless external forces act upon it.
Yes, momentum conservation states that in the absence of external forces, the total momentum of a closed system remains constant. This means that the total momentum before an event must equal the total momentum after the event. It is a fundamental principle in physics that helps explain and predict the motion of objects in different scenarios.
What are some examples of situations where momentum is conserved?
Some examples of situations where momentum is conserved include collisions between billiard balls, the swinging of a pendulum, the recoil of a gun after firing a bullet, and the interaction between objects in space where there is no external force acting upon them. In each of these scenarios, the total momentum before the interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction, demonstrating the conservation of momentum.
Collision of billiard balls, bouncing of a basketball, rocket propulsion, and the recoil of a gun.
These are all examples of Newton's third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In the collision of billiard balls, the force exerted by one ball on the other is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. When a basketball bounces, it pushes against the ground with a force equal to the force of gravity acting on it. Rocket propulsion works on the principle of pushing exhaust gases backward, resulting in forward propulsion. Similarly, the recoil of a gun is caused by the equal and opposite reaction to the force of the bullet being expelled.
Explain why momentum is considered a vector quantity.
Momentum is considered a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction. The direction of an object's momentum is determined by the direction of its velocity. This means that in addition to knowing how fast an object is moving (magnitude), we also need to know in which direction it is moving to fully describe its momentum. This makes momentum a vector quantity as opposed to a scalar quantity, which only has magnitude.
Momentum is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction. It follows the same laws of vector addition as other vector quantities.
Yes, that is correct. Momentum is a vector quantity as it not only possesses a magnitude (which is given by the product of an object's mass and velocity) but also a direction (which is the same as the direction of the object's velocity). This dual nature of momentum allows us to apply vector addition principles to analyze the effects of multiple forces acting on an object and calculate the resultant momentum.
How is momentum calculated?
Momentum is calculated by multiplying an object's mass by its velocity. Mathematically, momentum (p) is equal to mass (m) times velocity (v), expressed as p = m * v. The SI unit for momentum is kilogram meters per second (kg m/s).
Momentum is calculated by multiplying an object's mass by its velocity.
Correct. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. It is a vector quantity that indicates the motion and direction of an object. Mathematically, momentum (p) is represented as p = m * v, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
State the law of conservation of momentum.
The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant before and after any interaction or event within the system, as long as no external forces are acting on it. This means that the total momentum of all objects in the system before an event is equal to the total momentum of all objects in the system after the event, regardless of any internal forces or collisions that may occur.
The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant before and after any interaction or collision.
Yes, that is correct. According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of a closed system is constant if there are no external forces acting upon it. This means that in a collision or interaction between objects, the total momentum before the event must be equal to the total momentum after the event. This principle is a fundamental concept in physics and is used to analyze the outcomes of various interactions and collisions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments