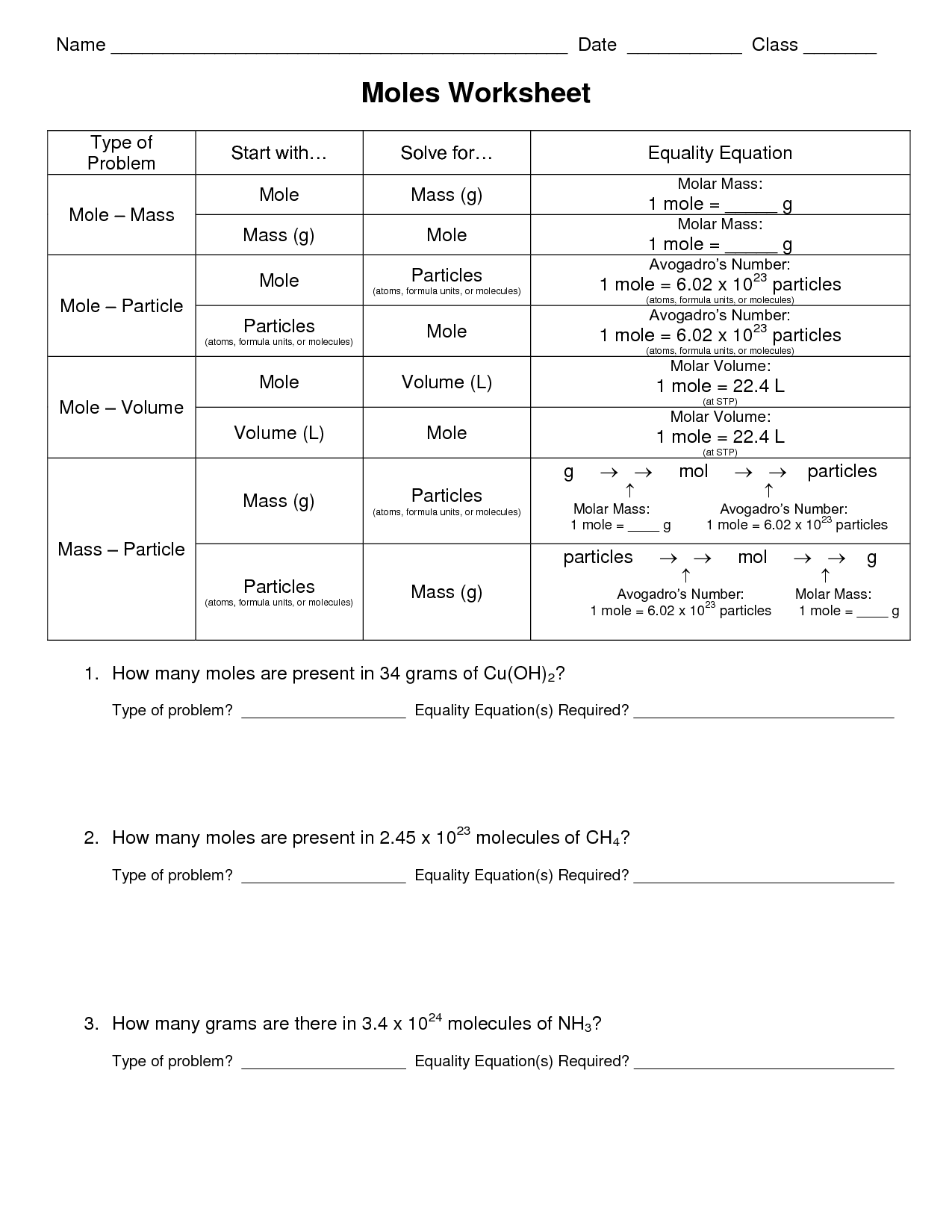
Moles and Mass Worksheet Answers
Are you a student or teacher in need of moles and mass worksheet answers? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with a comprehensive set of answers to help you master the concept of moles and mass. Whether you're a high school student preparing for an exam or a chemistry teacher looking for supplementary materials for your students, this post has got you covered. So let's dive in and explore the world of moles and mass together!
Table of Images 👆
- Moles and Molar Mass Worksheet
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Answer Key
- Mass Mole Conversion Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
- The Mole and Gram Formula Mass Worksheet Answers
- Molar Mass Moles and Avogadros Number Worksheet
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Answers
- Mole to Mass Stoichiometry Problems Answers
- Moles and Mass Worksheet Answers PDF
- Mole Molecules and Grams Worksheet Answer Key
- Mole Conversion Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a mole?
A mole is a unit used in chemistry to represent a specific amount of a substance. It is defined as the amount of a substance that contains Avogadro's number of atoms, ions, or molecules, which is approximately 6.02 x 10^23. One mole of a substance is equal to its molar mass in grams, making it a useful tool for measuring and comparing quantities of different substances in chemical reactions.
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to represent a certain number of particles (6.022 x 10^23) of a substance.
Yes, that is correct. A mole is a unit used in chemistry to measure the amount of a substance. It represents Avogadro's number, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23 particles, whether they are atoms, molecules, ions, or any other type of particle.
What is Avogadro's number?
Avogadro's number, denoted as \(N_{\rm A}\), is a fundamental constant in chemistry and physics that represents the number of constituent particles, such as atoms or molecules, in one mole of a substance. It is approximately \(6.022 \times 10^{23}\) particles per mole. This number allows scientists to bridge the macroscopic world of grams and moles with the microscopic world of atoms and molecules, aiding in calculations involving chemical reactions and the composition of matter.
Avogadro's number is the number of atoms, molecules, or formula units in one mole of a substance, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23.
Avogadro's number, approximately 6.022 x 10^23, represents the number of atoms, molecules, or formula units present in one mole of a substance. It serves as a crucial conversion factor in chemistry, allowing scientists to relate the mass of a substance to the number of its particles, facilitating various calculations and measurements in the field of chemistry.
What is molar mass?
Molar mass is a physical property defined as the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. It is calculated by summing the atomic masses of the elements in the chemical formula of a compound or molecule. Molar mass is used in various calculations in chemistry, such as determining the amount of a substance present in a given quantity or in stoichiometry calculations.
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams/mole. It is calculated by summing up the atomic masses of all the atoms in the chemical formula of the substance.
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. It is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the atoms present in the chemical formula of the substance.
How is the molar mass of an element determined?
The molar mass of an element is determined by adding up the atomic mass of each individual atom in the element, calculated based on the atomic number and mass number of the element's isotopes as found on the periodic table. This sum gives the molar mass in grams per mole (g/mol) of that particular element.
The molar mass of an element is determined by finding the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes, considering their relative abundances.
The molar mass of an element is determined by calculating the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes, taking into account their respective abundances.
How is the molar mass of a compound calculated?
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the elements present in a molecule and then multiplying that sum by the number of atoms of each element in the compound. This value is expressed in grams per mole and is an important parameter in various chemical calculations and reactions.
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by summing the molar masses of all the atoms in the chemical formula of the compound.
Yes, that is correct. The molar mass of a compound is determined by adding up the atomic masses of all the elements present in the compound, as indicated by the chemical formula. Each element's atomic mass can be found on the periodic table, and once all the masses are added up, the total sum is the compound's molar mass.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments