Molecules and Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a science teacher looking for a reliable resource to reinforce students' understanding of molecules and atoms? Look no further! We understand the importance of providing a comprehensive and structured learning experience for your students. That's why we have created a Molecules and Atoms Worksheet Answer Key that covers various essential concepts and ensures students grasp the material effectively. With this answer key, both you and your students can easily track progress and identify areas that need further exploration.
Table of Images 👆
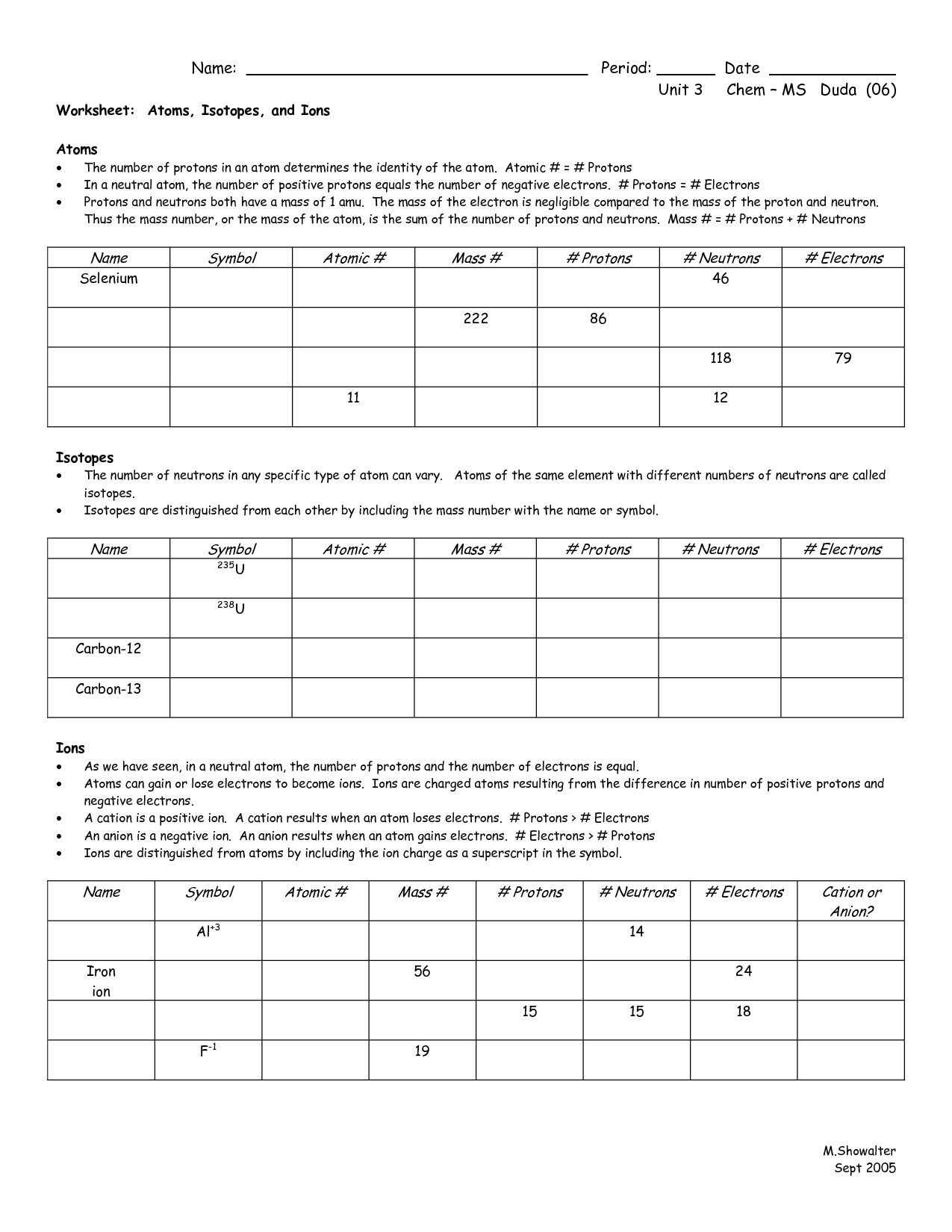
- Atoms Ions and Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
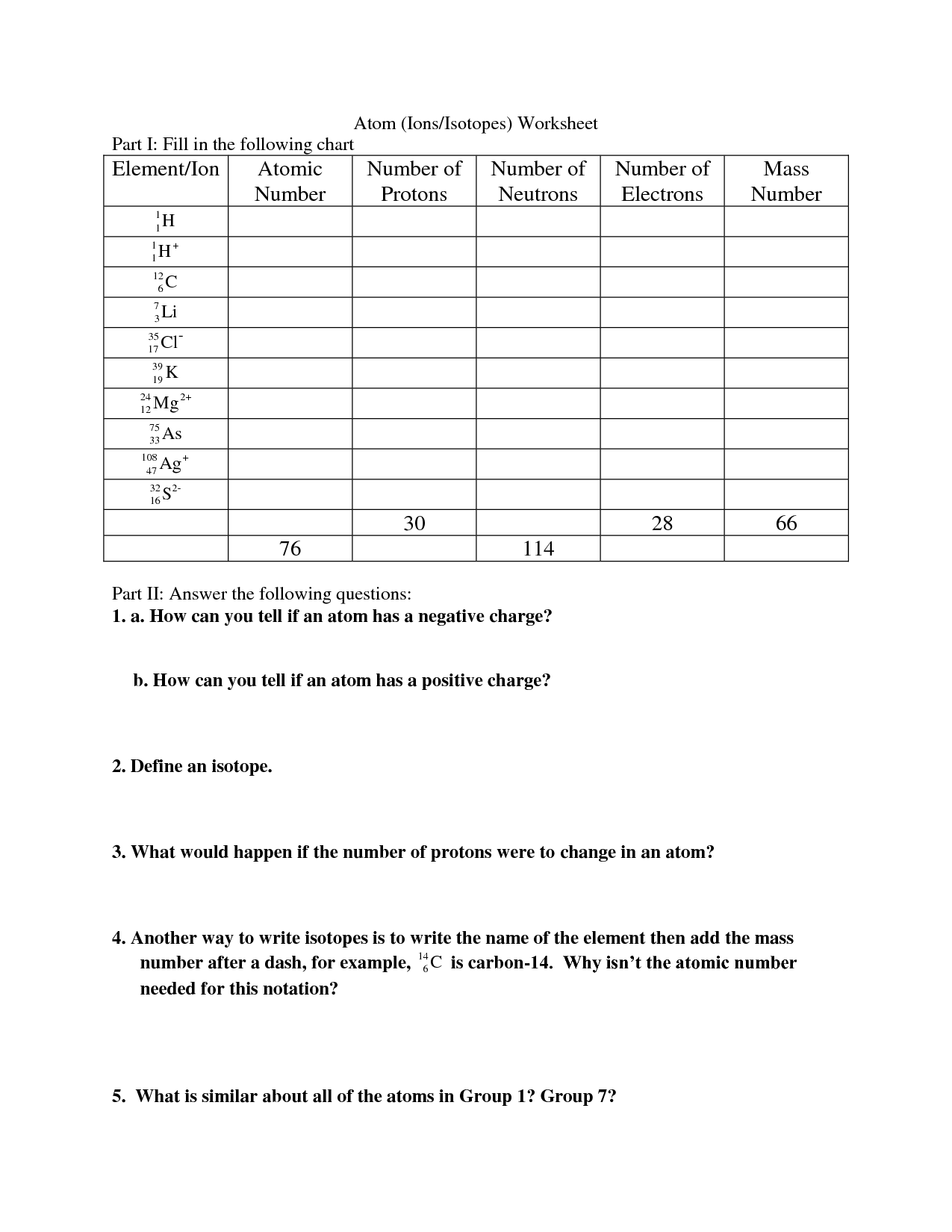
- Atoms and Molecules Worksheet Answers
- Isotopes and Ions Practice Worksheet Answers
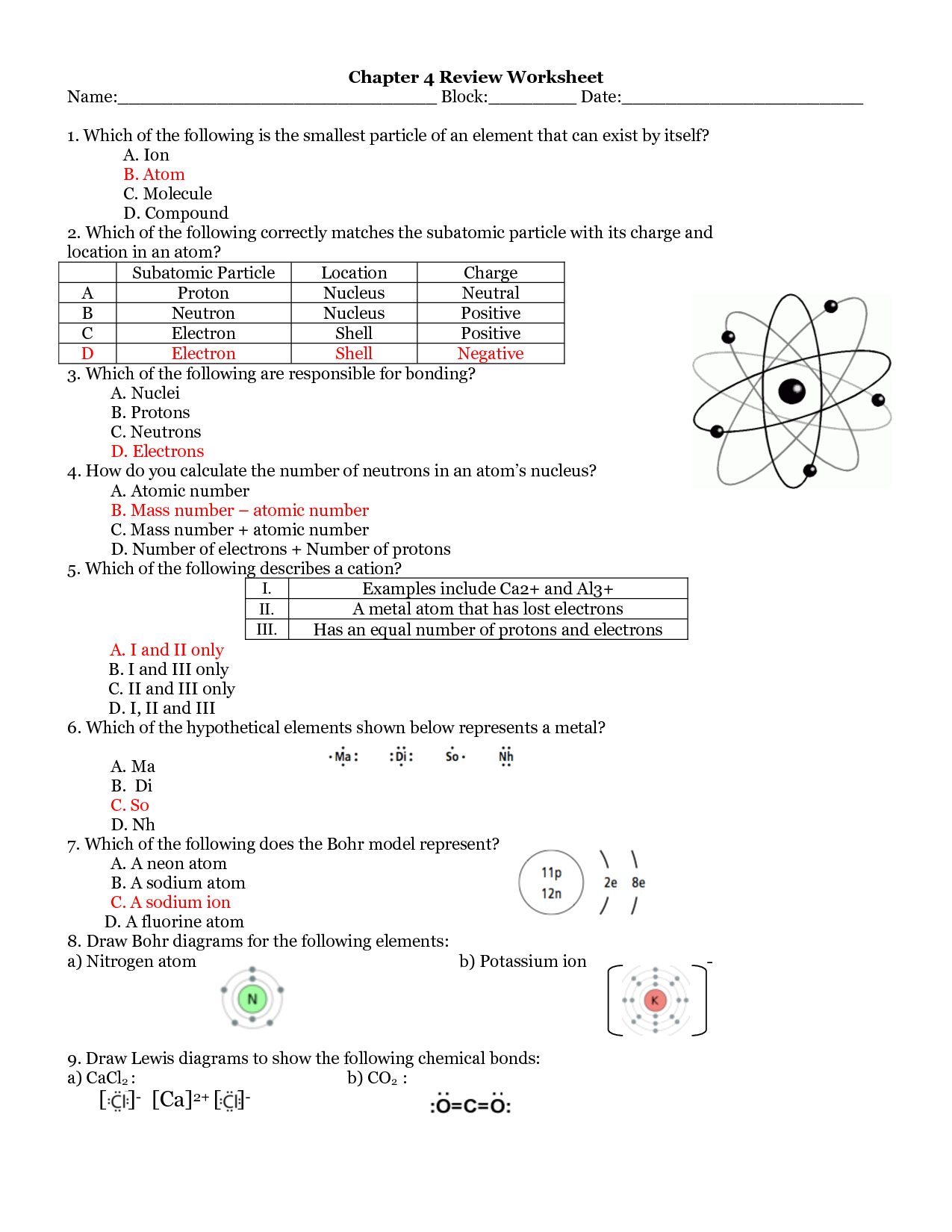
- Atoms and Ions Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Bill Nye Atoms Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms Answer Key
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
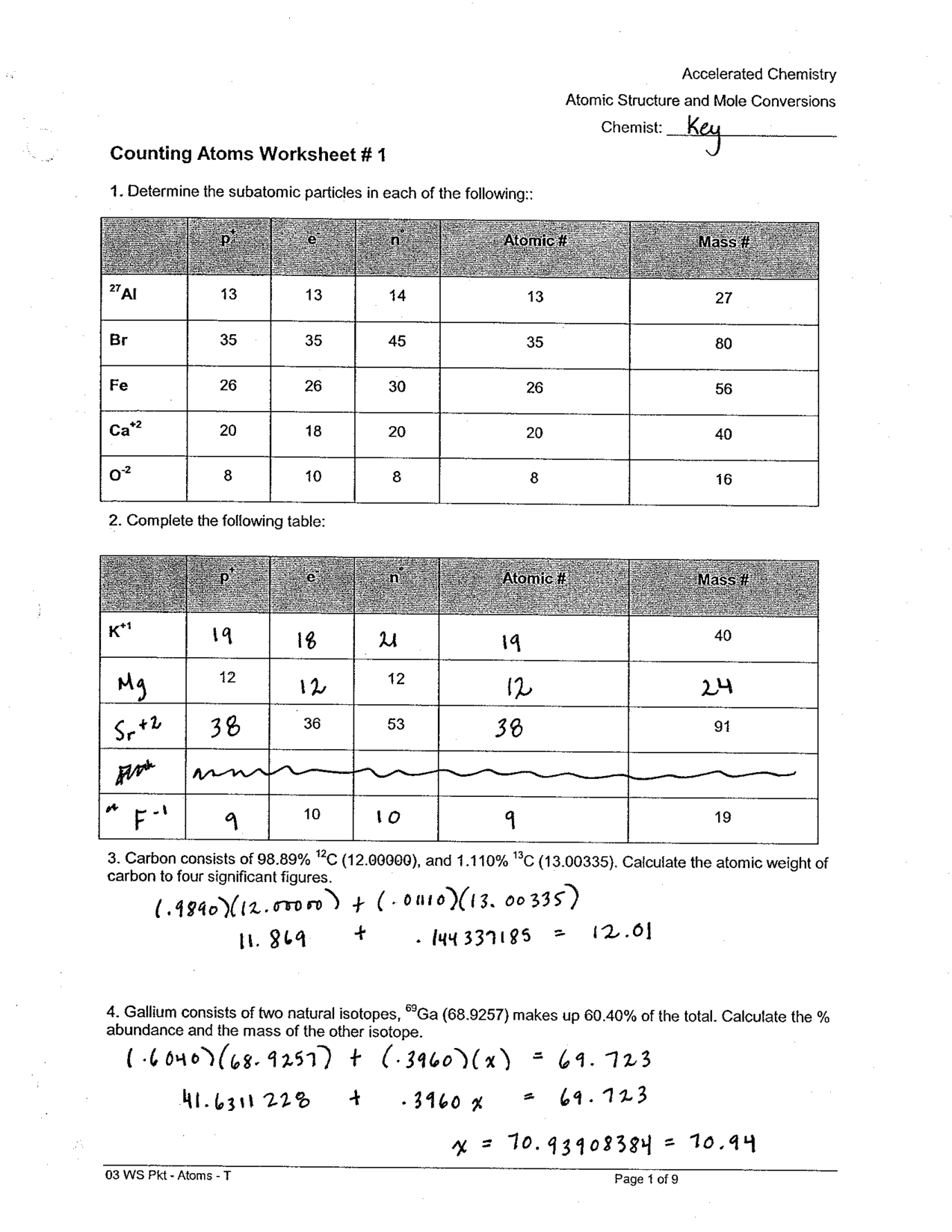
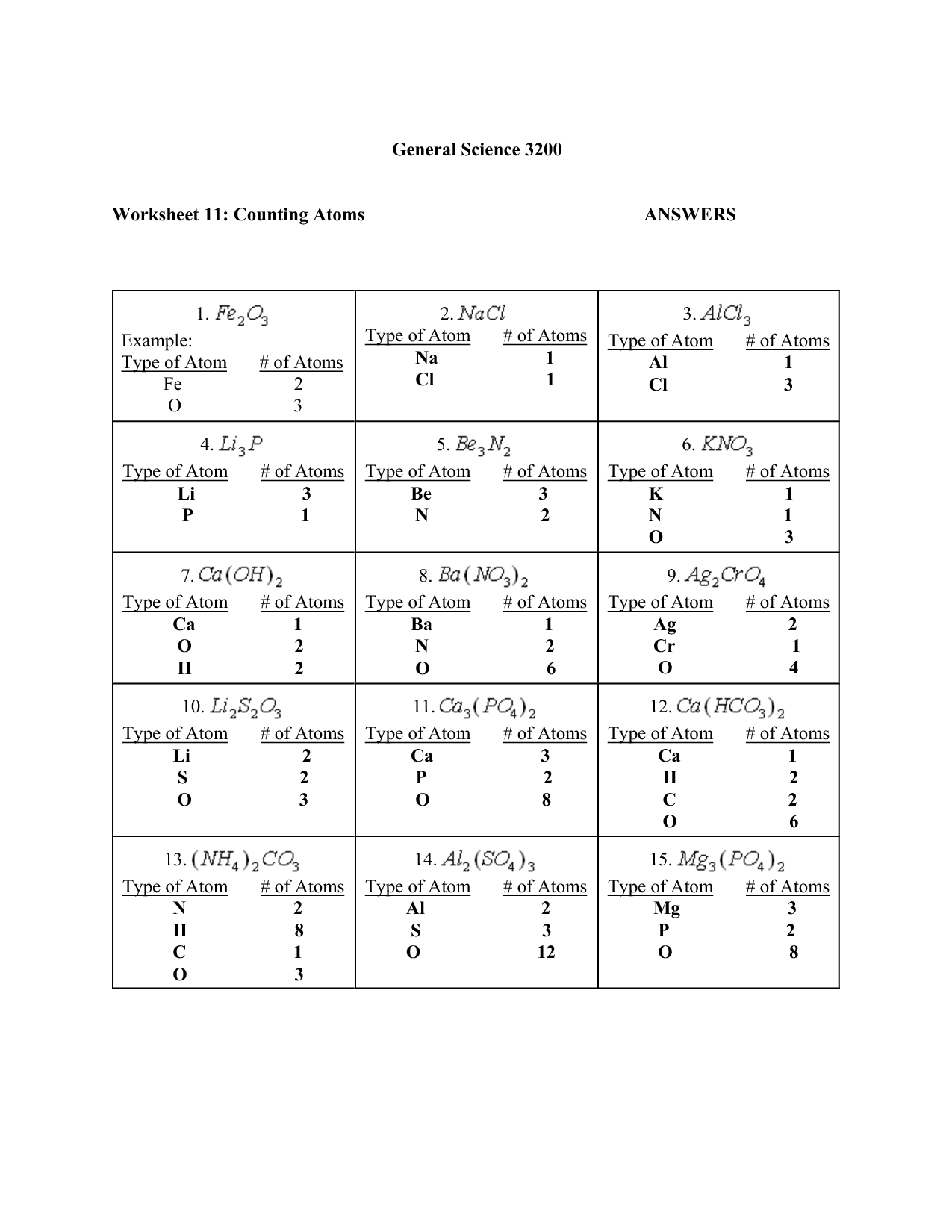
- Counting Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
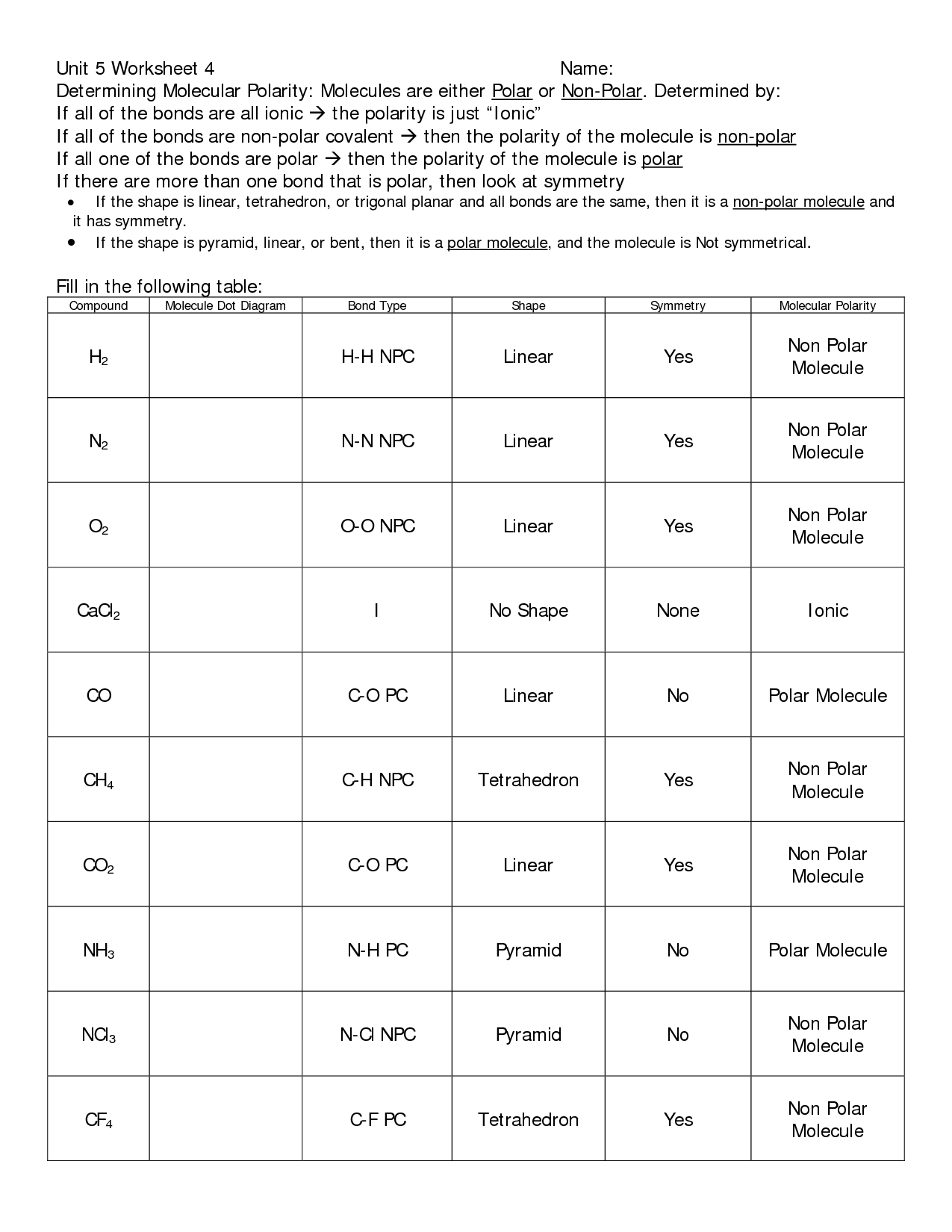
- Polar Bonds and Molecules Worksheet Review Answers Section
- Counting Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
- Mole Molecules and Grams Worksheet Answer Key
- Counting Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
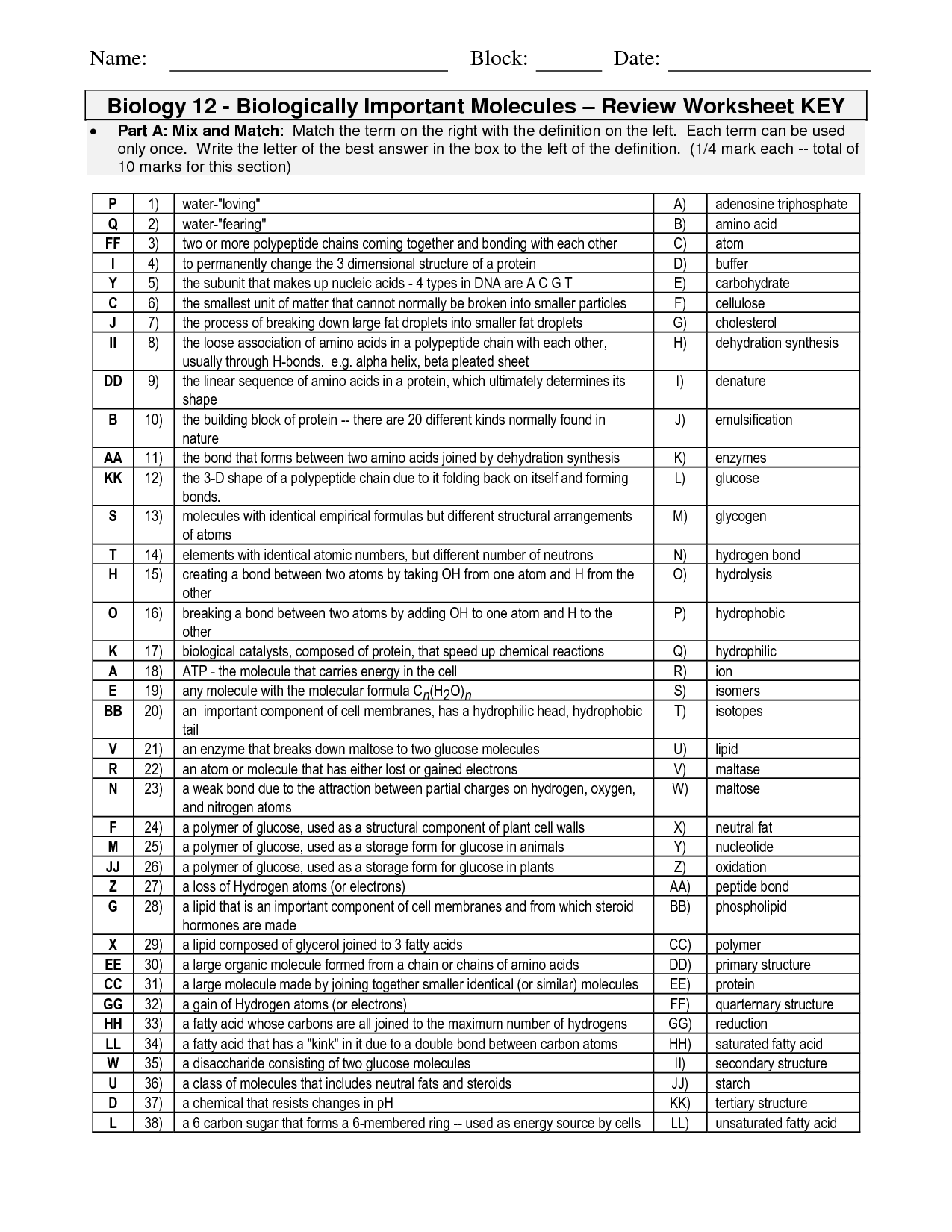
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Counting Atoms and Molecules Worksheet
- Atom Structure Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a dense nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons that orbit the nucleus. Atoms combine to form molecules through chemical bonding, and they are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
What are the three subatomic particles found in an atom?
The three subatomic particles found in an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of that element. It uniquely identifies each element and determines its chemical properties.
How is an element's atomic mass calculated?
An element's atomic mass is calculated by taking the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element, with each isotope's abundance taken into account. This isotope abundance multiplied by isotope mass calculation is summed up to give the atomic mass of the element, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or grams per mole (g/mol).
What is a molecule?
A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction. It can be made up of either the same type of atoms (e.g., O2 for oxygen) or different types of atoms (e.g., H2O for water).
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, such as oxygen or hydrogen, that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means. In contrast, a compound is a substance composed of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions, such as water (H2O) or carbon dioxide (CO2). So, the key difference between an element and a compound is that elements are made up of one type of atom, while compounds are made up of different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
How are chemical reactions represented in a chemical equation?
Chemical reactions are represented in a chemical equation by using chemical symbols to show the substances involved (reactants) on the left side of the equation and the substances produced (products) on the right side, separated by an arrow. Coefficients are used to balance the equation, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides, thereby following the law of conservation of mass.
What is the law of conservation of mass?
The law of conservation of mass states that the total mass of a closed system remains constant over time, regardless of physical or chemical changes that occur within the system. In other words, mass cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be rearranged or transformed into different forms through chemical reactions or physical changes.
How does the arrangement of atoms in a molecule affect its properties?
The arrangement of atoms in a molecule affects its properties by influencing its shape, size, polarity, and reactivity. Different arrangements can lead to variations in physical properties such as melting and boiling points, as well as chemical properties such as stability and reactivity in different environments. For example, the arrangement of atoms in a molecule can determine whether it is soluble in water, how it interacts with other molecules, and its overall behavior in chemical reactions.
How does the number of valence electrons in an atom influence its reactivity?
The number of valence electrons in an atom influences its reactivity by determining how easily it can either gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Atoms with full valence shells are typically more stable and less reactive, while atoms with incomplete valence shells are more likely to participate in chemical reactions in order to achieve a stable electron configuration.Atoms with fewer valence electrons tend to lose electrons and form positive ions, while atoms with more valence electrons tend to gain electrons and form negative ions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments