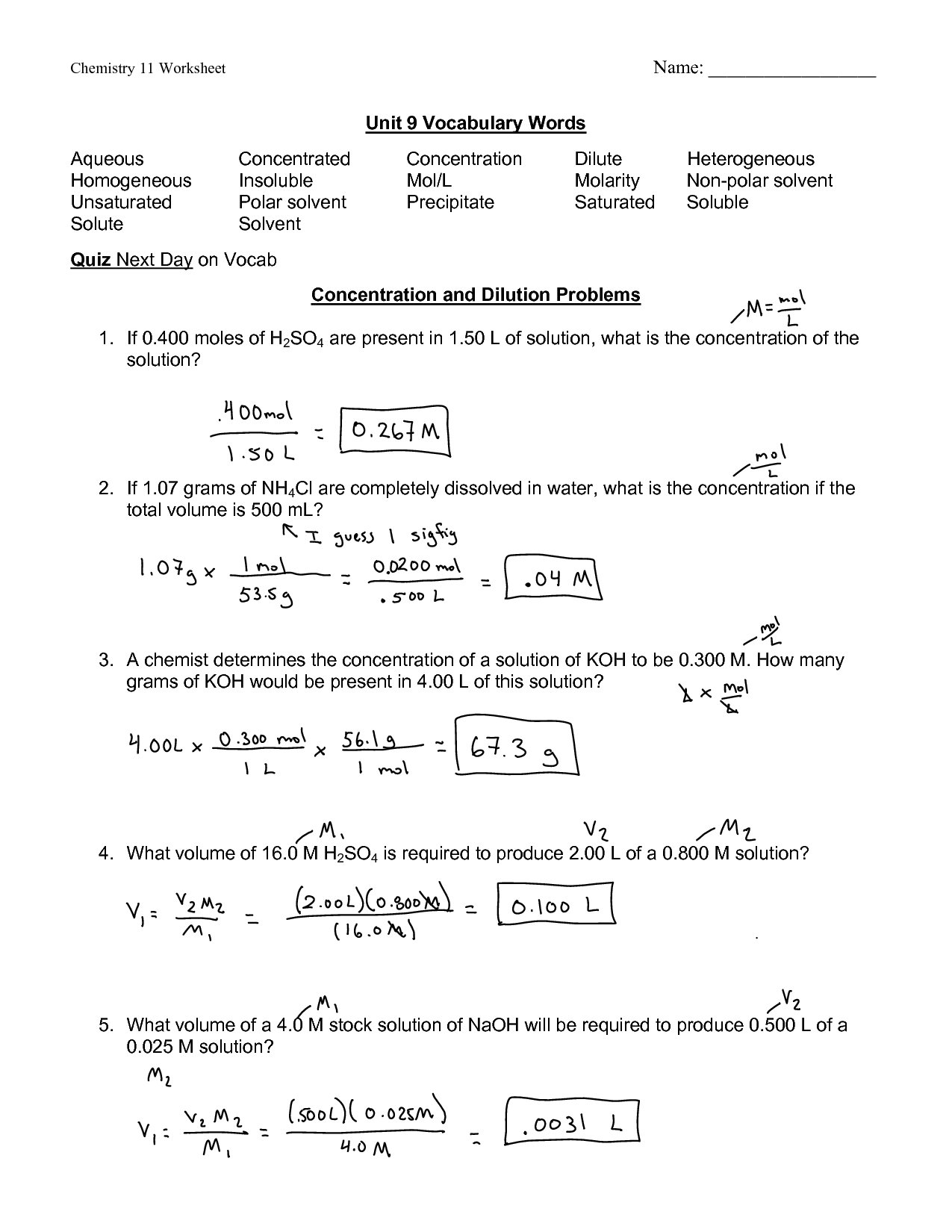
Molarity Worksheet with Answers
This blog post provides a comprehensive molarity worksheet with answers. It is perfect for students studying chemistry or anyone needing additional practice with molarity calculations. The worksheet covers essential topics such as Molarity and Molecular Weight, Diluting Solutions, and Stoichiometry. By completing this worksheet, readers can reinforce their understanding of these concepts and improve their problem-solving skills in molarity calculations.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is molarity?
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, expressed as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is a common unit of concentration used in chemistry to quantify the amount of a substance dissolved in a given volume of solvent.
How is molarity calculated?
Molarity is calculated by dividing the moles of solute by the volume of solution in liters. The formula for molarity (M) is: M = moles of solute / liters of solution. This calculation helps determine the concentration of a solute in a given volume of solution and is commonly used in chemistry to measure the strength of a solution.
What is the formula to convert moles to molarity?
The formula to convert moles to molarity is: Molarity (M) = moles of solute (mol) / volume of solution (L). This formula is used to calculate the concentration of a solution in moles of solute per liter of solution.
What is the formula to convert volume to molarity?
The formula to convert volume to molarity is: Molarity (M) = moles of solute (mol) / volume of solution in liters (L).
Why is molarity important in chemistry?
Molarity is important in chemistry because it helps in accurately determining the concentration of a solution, which is crucial for performing experiments, making solutions, and calculating reaction rates. It allows chemists to easily measure and compare the amounts of solutes in different solutions, ensuring precision in reactions and experiments. Additionally, molarity is used to calculate stoichiometry in chemical reactions, which aids in understanding the relationships between reactants and products.
What are some units used to express molarity?
The units used to express molarity are moles of solute per liter of solution, typically represented as mol/L or M.
How does molarity affect the concentration of a solution?
Molarity directly affects the concentration of a solution by representing the number of moles of solute in a liter of solvent. As the molarity of a solution increases, the concentration of the solute in the solution also increases. Therefore, a higher molarity indicates a higher concentration of the solute in the solution, while a lower molarity indicates a lower concentration.
How does molarity affect the colligative properties of a solution?
Molarity directly affects the colligative properties of a solution, as colligative properties are dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Increasing the molarity of a solution increases the number of solute particles present, which in turn enhances colligative properties such as boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure. This relationship is described by various equations, such as Raoult's Law and the van't Hoff factor, which demonstrate the direct relationship between molarity and the colligative properties of a solution.
How can molarity be used to dilute a solution?
To dilute a solution using molarity, you would need to use the formula C1V1 = C2V2, where C1 is the initial concentration of the solution, V1 is the initial volume of the solution, C2 is the desired final concentration, and V2 is the final volume of the diluted solution. By rearranging the formula, you can calculate the volume of the initial solution needed to achieve the desired final concentration. This allows you to add the necessary amount of solvent to dilute the solution while maintaining the desired concentration.
How does temperature affect molarity?
Temperature can affect molarity by changing the volume of a solution due to thermal expansion or contraction. This can cause the concentration of a solute to appear to change even though the amount of solute remains constant. Additionally, temperature can impact the solubility of certain solutes, affecting their molarity in a solution. Overall, it's important to consider temperature when working with molarity calculations to ensure accurate results.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments