Meiosis Practice Worksheet
Are you a biology student struggling to grasp the concepts of meiosis? Look no further! This meiosis practice worksheet provides the perfect opportunity to reinforce your understanding of this complex process. With a focus on entity and subject, this worksheet is designed to help biology students review meiosis with ease.
Table of Images 👆
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Drawing Worksheet
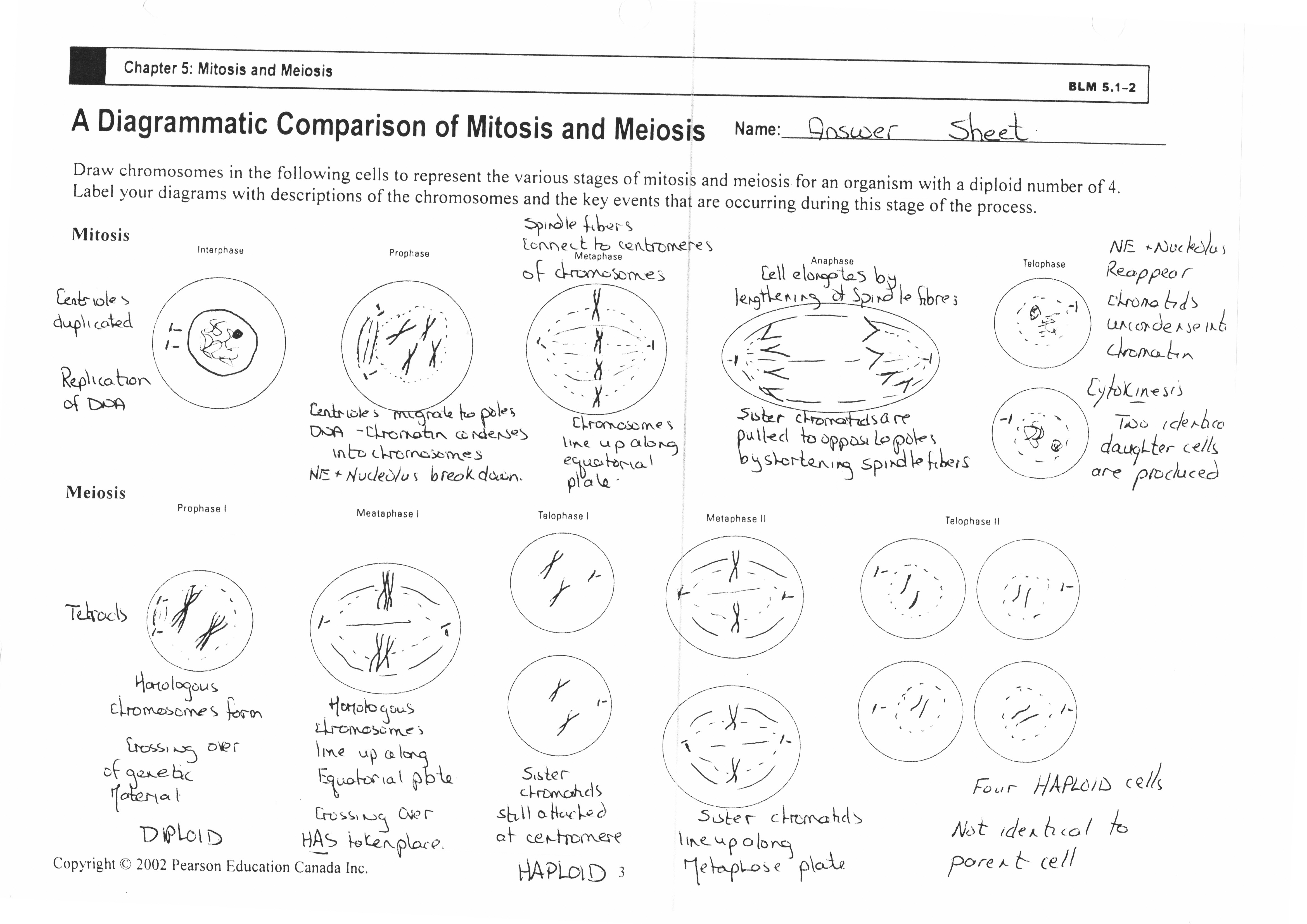
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis and Mitosis Practice 2 Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Mitosis and Meiosis Test Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis versus Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mendel and Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Stages Worksheet
- Mitosis Coloring Worksheet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Quiz
- Mitosis and Meiosis Quiz
- Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Test
- Meiosis Matching Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
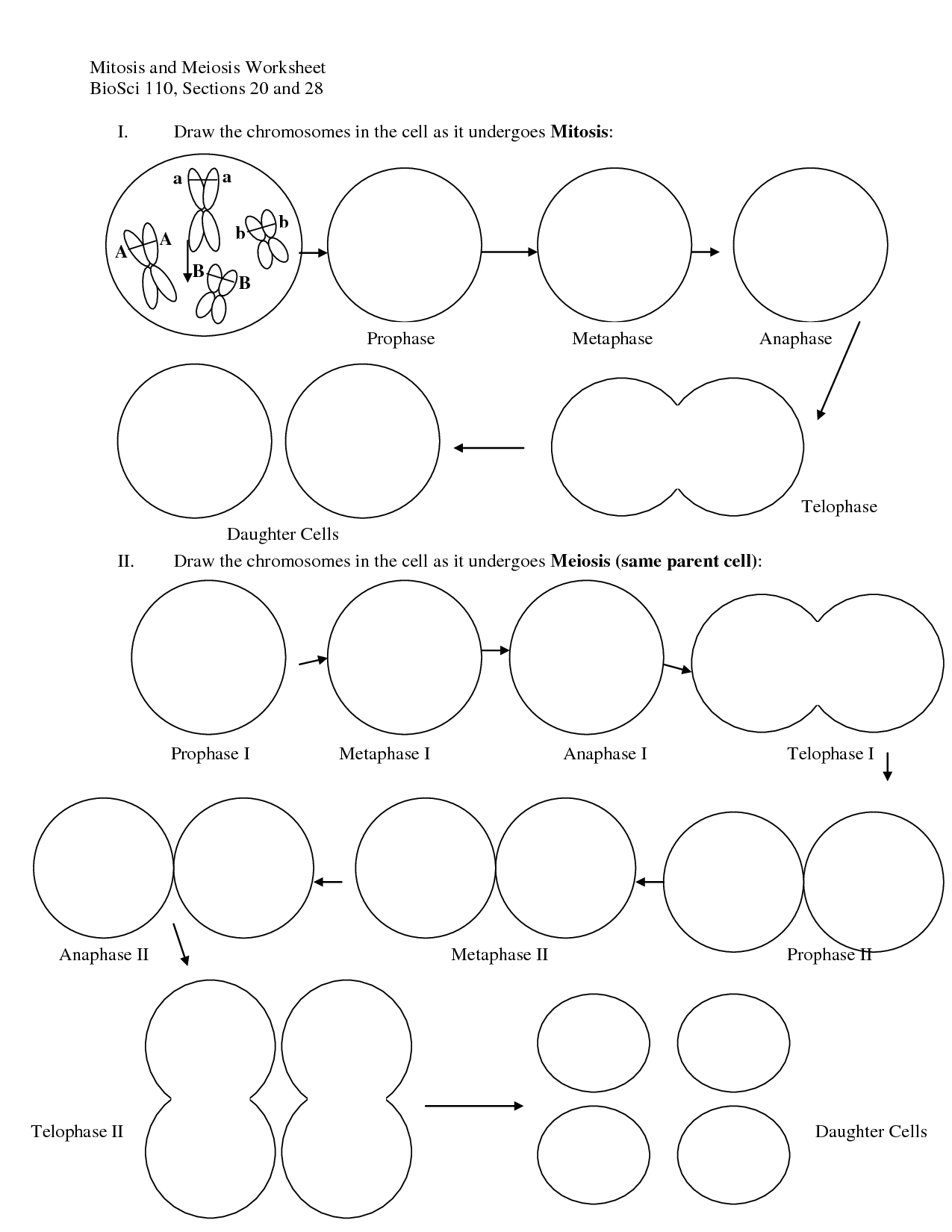
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to produce haploid cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This is essential for sexual reproduction as it ensures genetic diversity by combining genetic material from two different parent organisms. Meiosis also allows for the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in animals and spores in plants, which are crucial for the continuation of the species.
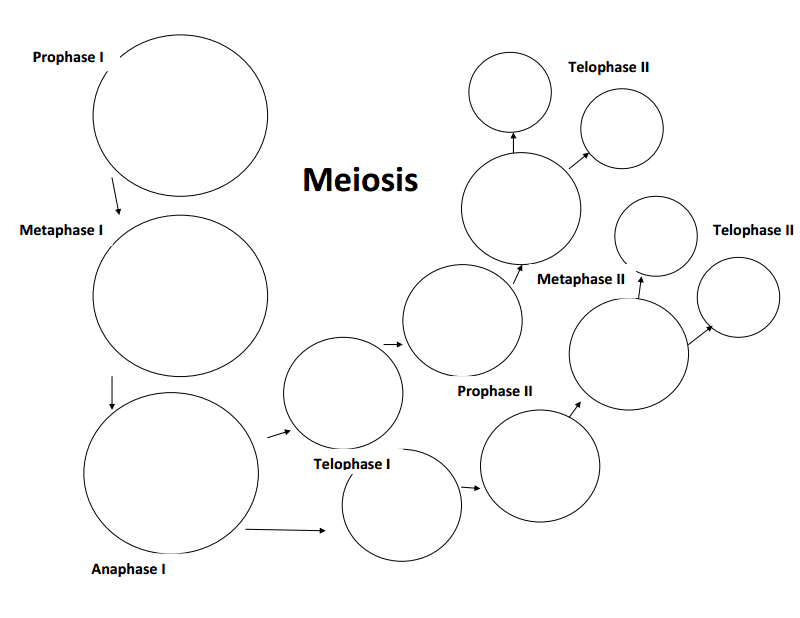
How many rounds of cell division occur during meiosis?
Two rounds of cell division occur during meiosis - meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, resulting in two haploid daughter cells with duplicated chromosomes. In meiosis II, sister chromatids separate, creating four haploid daughter cells with unduplicated chromosomes.
What is the initial number of chromosomes in a diploid cell before meiosis starts?
The initial number of chromosomes in a diploid cell before meiosis starts is 46 in humans, which consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes.
What is the result of meiosis I?
The result of meiosis I is the separation of homologous chromosomes into two separate cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. This process creates genetic variation by shuffling genes between chromosomes, leading to the creation of haploid cells that are genetically unique.
What is the result of meiosis II?
The result of meiosis II is the separation of sister chromatids from each other, resulting in the formation of four haploid daughter cells, each with a single set of chromosomes.
What is the significance of crossing over during meiosis?
Crossing over during meiosis is significant as it promotes genetic diversity by shuffling genetic information between homologous chromosomes. This process results in the exchange of DNA segments between maternal and paternal chromosomes, leading to the creation of new combinations of genes. The genetic variation generated through crossing over enhances the adaptability of offspring to changing environments and contributes to the overall genetic diversity of a population.
What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids?
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that carry the same genes in the same order but may have different versions of those genes. They are inherited from each parent. On the other hand, sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single chromosome that are created during DNA replication. Sister chromatids are held together by a centromere and separate during cell division to form two daughter cells.
How is genetic diversity generated during meiosis?
Genetic diversity is generated during meiosis through several processes such as crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization. Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during prophase I, leading to new combinations of alleles. Independent assortment occurs during metaphase I when homologous chromosomes align and separate randomly, resulting in different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in gametes. Random fertilization then contributes to genetic diversity by the chance fusion of gametes during fertilization, further shuffling genetic material. These processes together ensure that offspring inherit a unique combination of genes, enhancing genetic diversity within a population.
What is the role of spindle fibers in meiosis?
In meiosis, spindle fibers play a crucial role in the separation of homologous chromosomes during the first division (meiosis I) and sister chromatids during the second division (meiosis II). These fibers, composed of microtubules, attach to the centromeres of chromosomes and help to move them to opposite poles of the cell during cell division. This ensures that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity and the formation of haploid gametes.
What is the final outcome of meiosis in terms of chromosome number?
The final outcome of meiosis is the production of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This means that the daughter cells are haploid, containing one set of chromosomes, in contrast to the diploid parent cell that has two sets of chromosomes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments