Mechanical Energy Worksheet
Worksheets are a valuable tool for individuals seeking to enhance their understanding of mechanical energy. Designed to provide a structured and interactive learning experience, these worksheets offer a clear explanation of key concepts and practical examples to reinforce understanding. Whether you are a student looking to deepen your knowledge or a teacher seeking additional resources for your lesson plans, these worksheets offer an engaging way to grasp the entity and subject of mechanical energy.
Table of Images 👆
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets
- Centripetal Acceleration Worksheet
- Roller Coaster Energy Worksheet
- Simple Machines Worksheet
- Energy Worksheet 1st Grade Activities
- Forms of Energy Worksheets 2nd Grade
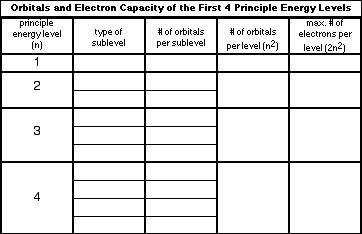
- Electron Configuration Worksheet
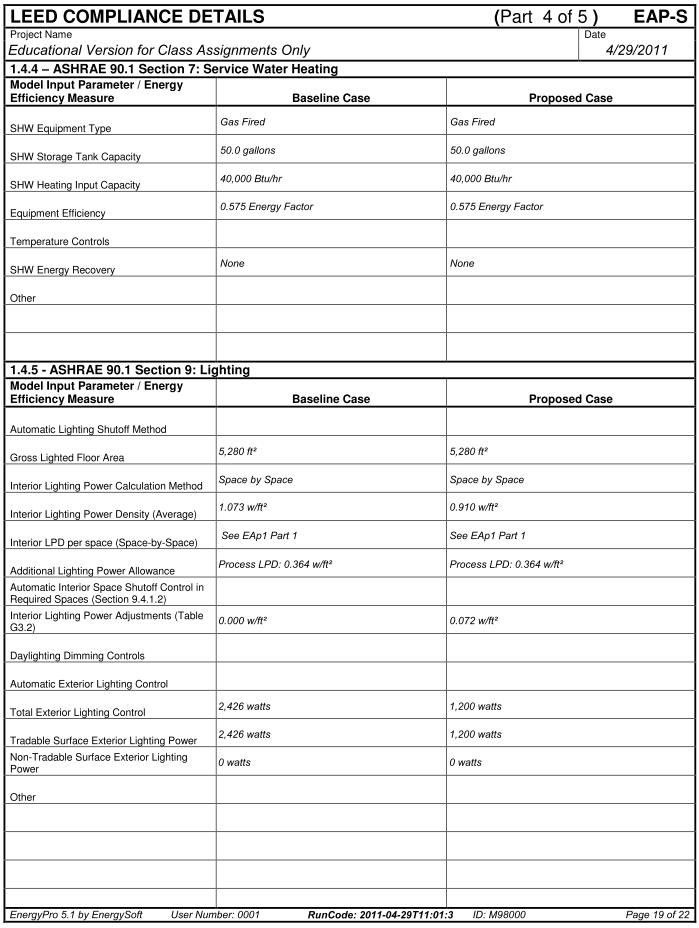
- Title 24 Energy Compliance Forms
- Joe Weatherly NASCAR
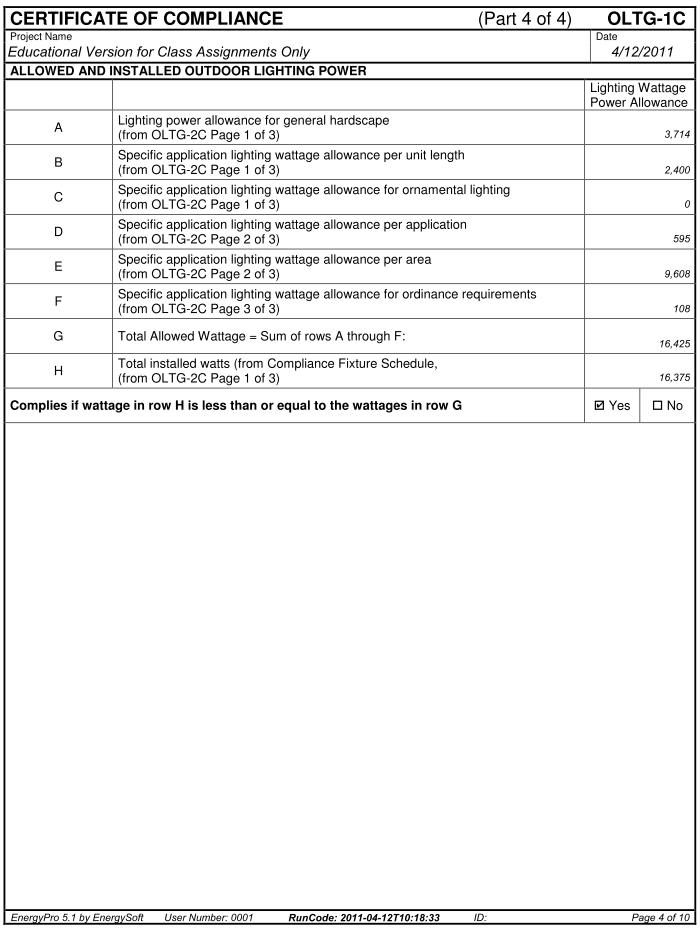
- Lighting Compliance Certificate
- Far Side Cartoons
- Far Side Cartoons
- Far Side Cartoons
- Far Side Cartoons
- Far Side Cartoons
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
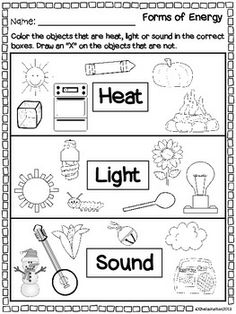
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is mechanical energy?
Mechanical energy is the total sum of potential energy and kinetic energy within a system due to its motion and position. Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses based on its position or configuration, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion that an object possesses. Combined, these two forms of energy make up the mechanical energy of an object or system.
What are the two main forms of mechanical energy?
The two main forms of mechanical energy are kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, while potential energy is the energy stored in an object based on its position or condition, like gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy.
Describe the concept of potential energy.
Potential energy is a form of energy that an object possesses due to its position or configuration. It is stored energy that has the capacity to do work in the future. The amount of potential energy an object has depends on its position in a force field, such as gravity or a spring. When the object's position changes, its potential energy also changes accordingly. This energy can be converted into kinetic energy when the object moves or when the forces acting on it change.
Explain kinetic energy and its relationship to motion.
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object has is directly proportional to its mass and the square of its velocity. In simpler terms, the faster an object moves and the more massive it is, the greater its kinetic energy will be. As an object accelerates or decelerates, its kinetic energy changes accordingly, demonstrating the direct relationship between kinetic energy and the motion of an object.
How is gravitational potential energy calculated?
Gravitational potential energy (GPE) is calculated using the formula GPE = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2 on Earth), and h is the height above the reference level. This formula represents the energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
What factors affect the amount of potential energy an object has?
The amount of potential energy an object has is primarily affected by its mass, height, and the force of gravity acting on it. The potential energy of an object increases with its mass and height above a reference point, as more mass or height means more gravitational potential energy stored in the object. Gravity plays a crucial role as the force that pulls the object downward and determines the amount of potential energy it possesses.
Describe the conservation of mechanical energy.
The conservation of mechanical energy states that in a closed system where only conservative forces are acting, the total mechanical energy (the sum of kinetic and potential energy) remains constant over time. This means that energy can change form from potential to kinetic and vice versa, but the total amount of mechanical energy in the system remains unchanged. This principle is based on the law of energy conservation, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed.
Explain how mechanical energy can be transferred or transformed.
Mechanical energy can be transferred from one object to another through mechanisms such as collisions, conduction, and convection. It can also be transformed between different forms such as potential energy (stored energy) and kinetic energy (energy of motion). For example, when a ball is thrown into the air, mechanical energy is transferred from the person throwing it to the ball as it gains kinetic energy. As the ball reaches its highest point, this kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy due to its height.
What role does friction play in mechanical energy?
Friction plays a significant role in mechanical energy by often converting mechanical energy into thermal energy. When two surfaces come in contact and rub against each other, friction causes resistance and generates heat due to the work done against the frictional force. This results in a loss of usable mechanical energy, as some of it is converted into heat energy, reducing the overall efficiency of the system.
Give an example of a real-life scenario where mechanical energy is present.
A real-life scenario where mechanical energy is present is when a car is in motion. In this scenario, the car possesses both kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (stored energy due to its position). As the car moves, the engine converts chemical energy from fuel into mechanical energy that propels the vehicle forward. The interaction between the car's mechanical components like the engine, wheels, and transmission systems all contribute to the overall mechanical energy present in the moving car.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments