Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answers
Are you a biology student who is struggling to understand the concept of macromolecules? Do you find it difficult to grasp the relationship between different types of molecules, such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids? Look no further, as this blog post will provide you with the essential information you need to ace your next macromolecules quiz. In this post, we will be discussing the importance of using worksheets as a tool to enhance your understanding of macromolecules and provide you with a clear and concise way to review and reinforce the information.
Table of Images 👆
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Nomenclature Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Label and Nutrition Worksheet Macromolecules
- Label and Nutrition Worksheet Macromolecules
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Worksheet Answers
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
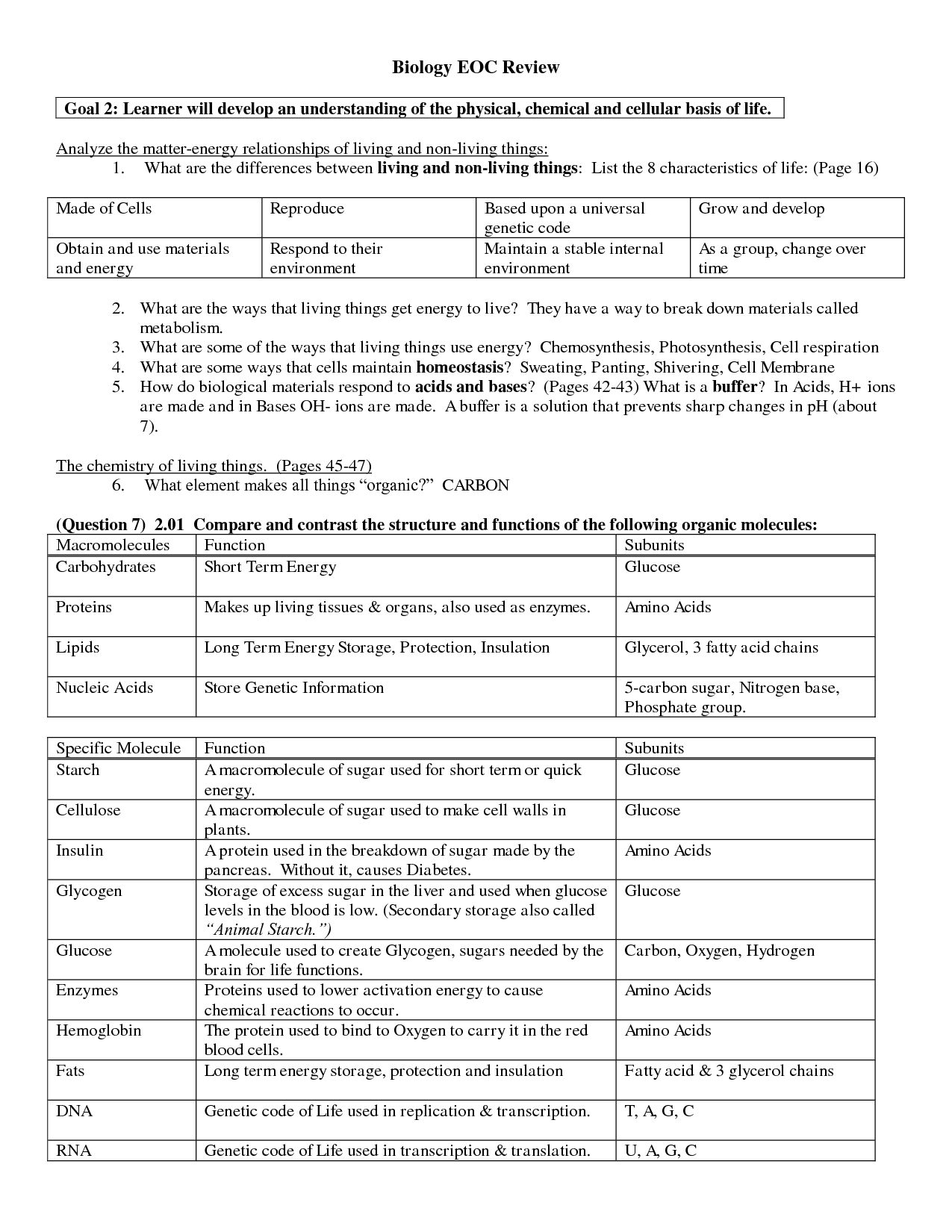
What are the four major classes of macromolecules?
The four major classes of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules are essential components of all living organisms and play key roles in various biological processes, such as energy storage, cell structure, enzymatic reactions, and genetic information storage and transfer.
Describe the structure and function of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are biomolecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, usually in a ratio of 1:2:1. They are classified into three main groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for living organisms, with functions ranging from providing energy for cellular processes to acting as structural components in cell walls. They are also involved in cell signaling, intercellular interactions, and can be used as energy storage molecules in the form of glycogen or starch.
Explain how lipids are different from other macromolecules.
Lipids are different from other macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids because they are primarily hydrophobic molecules, meaning they do not dissolve in water. Unlike proteins, which are made up of amino acids, and carbohydrates, which are composed of sugars, lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids serve various functions in cells and organisms, including energy storage, insulation, and forming cellular membranes. Additionally, lipids are the most energy-dense macromolecules, providing more energy per gram when broken down compared to proteins and carbohydrates.
What are the primary functions of proteins?
Proteins serve several essential functions in the body, including serving as structural components in cells and tissues, aiding in communication between cells, regulating chemical reactions as enzymes, transporting molecules such as oxygen in the bloodstream, and providing immunity through antibodies. Additionally, proteins play a role in muscle contraction, metabolism, and hormone regulation, making them crucial for overall health and functioning of the body.
Describe the structure and function of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids are complex biomolecules made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. These nucleotides are linked together to form long chains, with the sugar-phosphate backbone providing structural support. The nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids can be adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine (in DNA), or uracil (in RNA), and they form specific base pairs. DNA carries genetic information in the form of genes, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by coding for amino acids. Overall, nucleic acids are essential for the storage, transmission, and expression of genetic information in all living organisms.
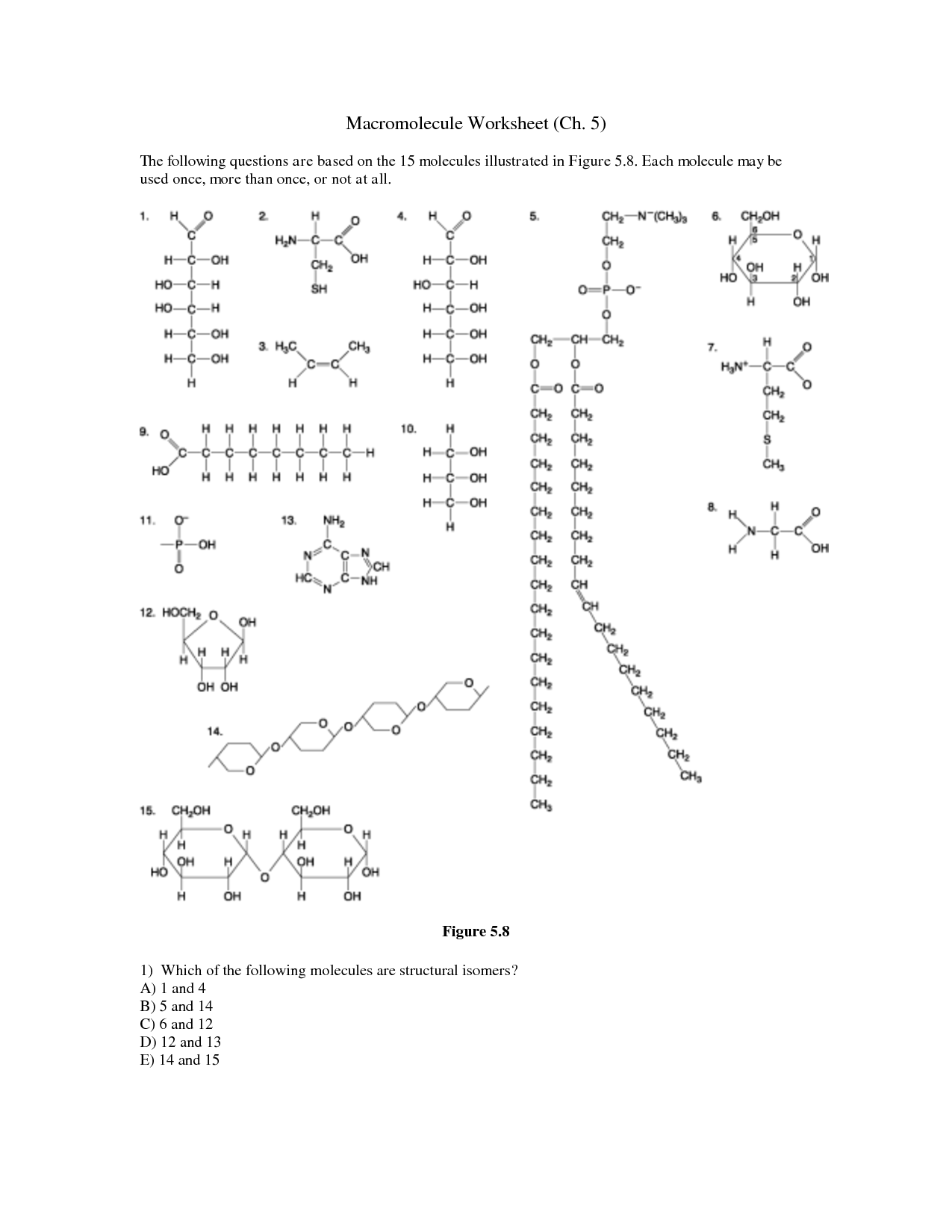
How are monomers and polymers related in macromolecules?
Monomers are smaller molecules that bond together to form polymers, which are large molecules composed of repeating structural units. In macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates, monomers are bonded together through chemical reactions to create larger polymer chains. This process of polymerization is essential for building the complex structures and functions that macromolecules have in living organisms.
What is the role of enzymes in macromolecule synthesis and breakdown?
Enzymes play a crucial role in both macromolecule synthesis and breakdown by acting as biological catalysts. In synthesis, enzymes facilitate the formation of new macromolecules by speeding up chemical reactions that build polymers like nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. On the other hand, enzymes also aid in the breakdown of macromolecules by accelerating the process of decomposition into smaller subunits or molecules. This dual function of enzymes in macromolecule metabolism is vital for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and the overall functioning of living organisms.
Explain the process of dehydration synthesis in macromolecule formation.
Dehydration synthesis is a process in which two molecules are joined together with the removal of a water molecule. During macromolecule formation, such as in proteins and carbohydrates, dehydration synthesis links monomers together to form polymers. An enzyme catalyzes the reaction, bringing two monomers close together and facilitating the removal of a hydroxyl (OH) group from one monomer and a hydrogen (H) atom from the other, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond between the monomers and a water molecule as a byproduct. This process repeats to form long chains of monomers, ultimately creating complex macromolecules.
What is hydrolysis and how does it contribute to macromolecule breakdown?
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the breakdown of a compound by adding water molecules. In the context of macromolecules, hydrolysis plays a crucial role in breaking down polymers such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into their smaller subunits or monomers. For example, proteins are broken down into amino acids, carbohydrates into sugars, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol through hydrolysis reactions. This process is essential for the body to absorb and utilize nutrients efficiently from the food we consume, as well as for the recycling of cellular components.
Describe the importance of macromolecules in living organisms.
Macromolecules are vital in living organisms as they serve as the building blocks of life. Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids are all essential macromolecules that play crucial roles in processes such as cell structure, energy production, molecular signaling, and genetic information transfer. Without these macromolecules, organisms would not be able to function properly or even survive. Their diversity and structural complexity enable them to fulfill a wide range of biological functions necessary for life.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments