Logical Fallacies Worksheets High School
Logical fallacies worksheets provide a valuable tool for high school students to develop critical thinking and analytical skills. These worksheets present various examples of logical fallacies and challenge students to identify the specific type of fallacy employed. By engaging with these exercises, students gain a deeper understanding of the principles of logical reasoning and become more adept at recognizing faulty arguments in everyday life.
Table of Images 👆
- Inductive Deductive Reasoning Worksheet
- Printable Logic Puzzle Worksheets High School
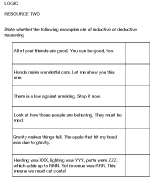
- Logical Fallacies Worksheet
- University of Phoenix Process Design Matrix
- Logic Problem Worksheets
- Fallacy Worksheets and Answer Keys
- Identifying Fallacies Worksheet
- High School Math Worksheets
- Predicting Outcomes Worksheets
- Analogies Worksheets Middle School
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a logical fallacy?
A logical fallacy is a flaw in reasoning that makes an argument invalid or unsound. It refers to errors in logic that weaken an argument's credibility, often leading to false or misleading conclusions. Common examples of logical fallacies include ad hominem attacks, straw man arguments, and slippery slope reasoning. Identifying and avoiding logical fallacies is essential for constructing persuasive and rational arguments.
How are logical fallacies used to manipulate arguments?
Logical fallacies are used to manipulate arguments by presenting faulty reasoning in order to deceive or persuade others. By employing fallacious arguments, individuals can appeal to emotions, mislead listeners, distract from the main point, or create confusion. This manipulation can be intentional to win a debate or persuade an audience, or unintentional due to a lack of critical thinking skills. Ultimately, using logical fallacies undermines the credibility and validity of an argument by relying on flawed reasoning instead of evidence and sound logic.
Give an example of the ad hominem fallacy.
An example of the ad hominem fallacy would be during a political debate when one candidate attacks their opponent's character or personal life instead of addressing their arguments or policies. For instance, if a candidate says, "You shouldn't trust my opponent because they have a history of dishonesty and marital infidelity," instead of discussing the opponent's proposed plans for healthcare reform.
What is the straw man fallacy?
The straw man fallacy is a type of argumentative fallacy where someone distorts or misrepresents their opponent's argument to make it easier to attack, thus creating a straw man or a weakened version of the original argument. By attacking this distorted version, they avoid addressing the actual points being made, leading to a deceptive and ineffective form of argumentation.
Explain the slippery slope fallacy.
The slippery slope fallacy is a logical fallacy where someone argues that a certain action will inevitably lead to a series of events that result in a negative outcome, without providing sufficient evidence to support this chain of events. It is assuming that one event will lead to another based on a series of unlikely or exaggerated assumptions, rather than considering the complexities of the situation or potential alternate outcomes. Ultimately, the slippery slope fallacy oversimplifies cause and effect relationships and can be used to manipulate or distort arguments by ignoring nuance and context.
Provide an example of the appeal to authority fallacy.
An example of the appeal to authority fallacy is when a celebrity endorses a product, so people believe it must be effective or worth buying simply because the celebrity said so. This logic is flawed because the celebrity may not have expertise in the product's effectiveness or may have been paid for the endorsement, making their opinion not a reliable basis for a purchasing decision.
What is the false dichotomy fallacy?
The false dichotomy fallacy is a type of logical fallacy where a situation is presented as if there are only two mutually exclusive options or outcomes when, in reality, there are more possibilities or nuances available. This fallacy oversimplifies complex issues, leading to a misleading or inaccurate representation of the choices at hand.
Explain the hasty generalization fallacy.
The hasty generalization fallacy occurs when an individual draws a conclusion about a whole group based on insufficient or biased evidence from a small sample. This fallacy overlooks the diversity within the group and fails to consider other factors that may influence the situation. It can lead to inaccurate or unfair judgments that do not represent the entire group accurately, undermining the validity of the argument or belief being presented.
Give an example of the appeal to emotion fallacy.
An example of the appeal to emotion fallacy is a politician using images of crying children to manipulate voters into supporting a particular policy without presenting factual evidence or logical arguments to justify it. By appealing to fear or sympathy, the politician is attempting to sway the audience's emotions instead of engaging in a rational debate based on facts and reason.
What is the circular reasoning fallacy?
Circular reasoning is a logical fallacy where the conclusion of an argument is essentially the same as the premise. In other words, the argument assumes what it is trying to prove, leading to a self-reinforcing loop where the conclusion is based on the initial assumption and the initial assumption is supported by the conclusion. This results in no real evidence or valid reasoning being presented to support the argument, making it logically invalid and unpersuasive.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments