Logical Fallacies Worksheet
Are you a student or a teacher who wants to improve your critical thinking and argumentation skills? Look no further than the Logical Fallacies Worksheet! Designed to help you identify and understand different types of logical fallacies, this worksheet is a valuable tool for anyone seeking to strengthen their ability to spot flawed reasoning and construct persuasive arguments. Whether you're tackling a school project, preparing for a debate, or simply interested in sharpening your thinking skills, this worksheet is perfect for you.
Table of Images 👆
- Logical Fallacies Examples
- Logical Fallacies Worksheets High School
- Rhetorical Fallacies Worksheet Middle School
- Fallacy Worksheet Practice
- False Dilemma Fallacy Examples
- False Analogy Fallacies Examples
- Inductive Deductive Reasoning Worksheet
- Fallacy Worksheets and Answer Keys
- Premise-Conclusion Examples
- Identifying Fallacies Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
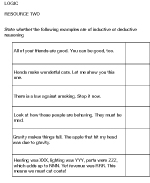
What is a logical fallacy?
A logical fallacy is a flaw in reasoning that makes an argument invalid or unsound. It is a mistake in the structure of an argument that can deceive or mislead the audience in reaching a conclusion. Logical fallacies can come in different forms such as appeals to emotion, false cause-effect relationships, ad hominem attacks, and circular reasoning. Identifying and understanding logical fallacies is important in critical thinking and debate to ensure sound and rational arguments are made.
How do logical fallacies impact arguments and reasoning?
Logical fallacies can distort arguments and reasoning by introducing errors in logic that deceive the audience into accepting faulty conclusions. They can weaken the credibility of an argument by relying on flawed reasoning rather than sound evidence and rational thinking. This can lead to a breakdown in communication and understanding, as well as undermining the overall effectiveness and persuasiveness of the argument. It is important to be aware of logical fallacies in order to critically evaluate claims and ensure that arguments are based on valid reasoning.
What are the different types of logical fallacies?
There are many types of logical fallacies, including ad hominem attacks (attacking the person instead of their argument), straw man arguments (misrepresenting someone's argument to make it easier to attack), appeal to authority (claiming something is true because someone famous or important said it), slippery slope (arguing that one thing will lead to a series of extreme consequences), and false cause (assuming that because one event follows another, the first caused the second). Other common fallacies include appeal to emotion, begging the question, and bandwagon.
Can you provide an example of a fallacy of presumption?
One example of a fallacy of presumption is the "Begging the Question" fallacy, where someone's argument is based on an assumption that has not been proven or is still in question. For instance, if someone says "Paranormal activity is real because I have experienced it myself, and my experiences are always real," they are presuming that their experiences are always accurate and truthful without providing any substantial evidence to support the claim that paranormal activity is real.
What is a fallacy of relevance?
A fallacy of relevance occurs when an argument's premises are not directly related to the conclusion being argued. This means that the evidence presented is not actually supporting the conclusion, making the argument invalid. Examples of fallacies of relevance include appeals to authority, ad hominem attacks, and red herrings, where the evidence presented distracts from the actual issue at hand.
What is a fallacy of ambiguity?
A fallacy of ambiguity is a type of logical fallacy where the meaning of a term or statement is unclear, making it difficult to evaluate the validity of the argument. This can occur through the use of vague language, ambiguous phrasing, or shifting definitions of terms, leading to confusion or misunderstanding in the logic presented.
Can you give an example of a fallacy of defective induction?
One example of a fallacy of defective induction is when a person concludes that all members of a group share a certain characteristic based on a small sample size. For instance, someone may generalize that all lawyers are untrustworthy because they had a negative experience with one lawyer. This faulty reasoning oversimplifies a complex group and leads to an inaccurate and biased conclusion.
What is a fallacy of causation?
A fallacy of causation occurs when a conclusion is drawn about causation based on a correlation or coincidence, without sufficient evidence to support the claim that one event caused another. This fallacy assumes that correlation equals causation, when in reality there may be other factors at play that are responsible for both events or that the correlation is purely coincidental. It is important to critically analyze the relationship between events and avoid making unwarranted assumptions about causation based solely on correlation.
Can you provide an example of a fallacy of diversion?
A common example of a fallacy of diversion is the red herring fallacy, where someone introduces irrelevant information or argument to divert attention away from the main issue being discussed. For instance, during a debate about climate change and its impact on the environment, someone might bring up a completely unrelated topic like how much money is spent on space exploration in order to steer the conversation away from the core issue at hand.
How can recognizing logical fallacies improve critical thinking skills?
Recognizing logical fallacies can improve critical thinking skills by helping individuals identify flawed reasoning in arguments, enabling them to evaluate information more effectively and make sound judgments. By understanding common fallacies such as ad hominem attacks or appeals to authority, individuals can avoid being swayed by misleading or invalid arguments, leading to more informed decision-making and the ability to construct stronger, well-reasoned arguments themselves. This heightened awareness of logical fallacies enhances the ability to think critically, question assumptions, and engage with information more analytically.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments