Labeling Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Are you on the hunt for a reliable and comprehensive resource to help you navigate the complexities of meiosis? Look no further! In this blog post, we are excited to introduce the Labeling Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key, designed specifically for students and enthusiasts who are eager to enhance their understanding of this crucial biological process. With a clear focus on providing accurate and detailed information, this worksheet will serve as an invaluable tool for anyone looking to delve deeper into the fascinating world of meiosis.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis Matching Worksheet Answer Key
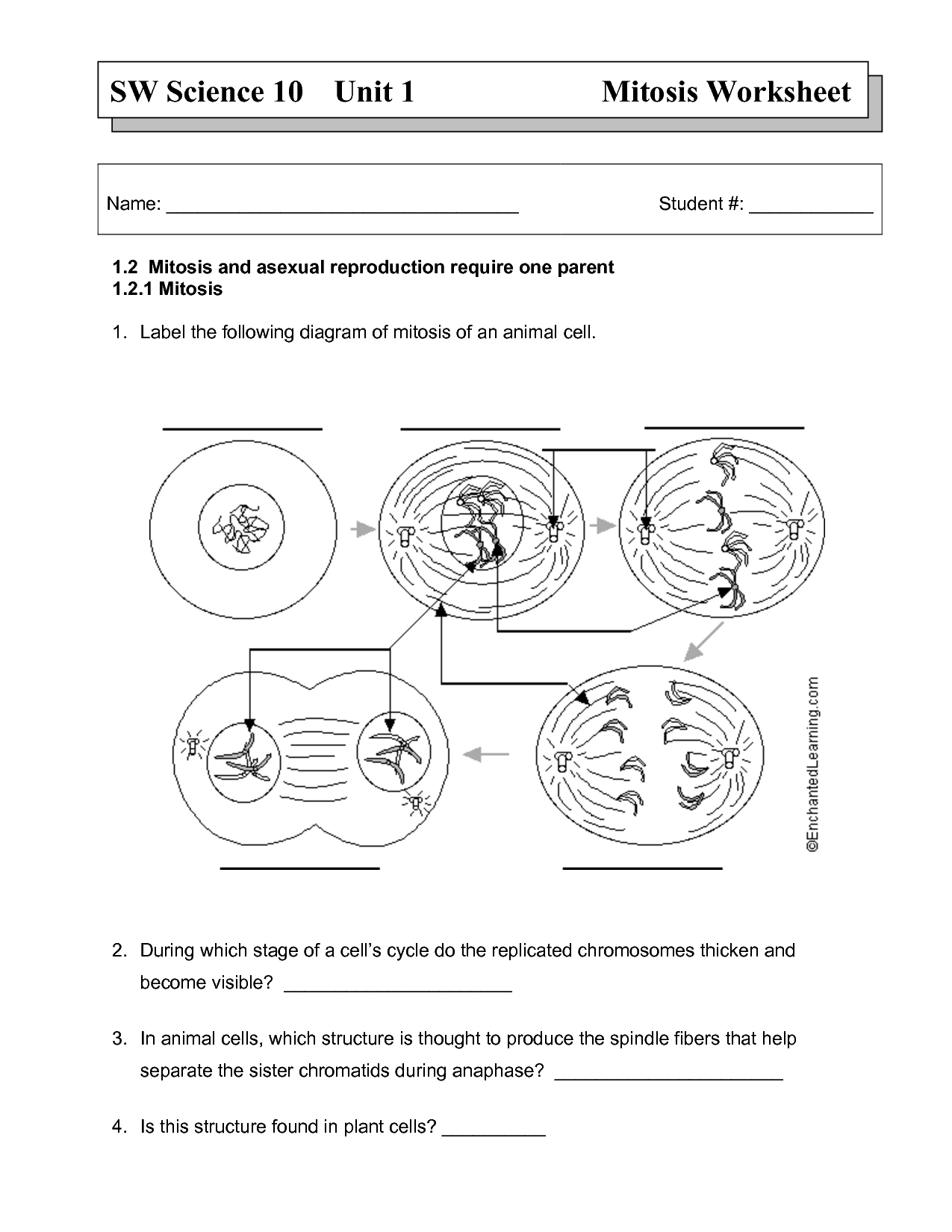
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Evolution Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
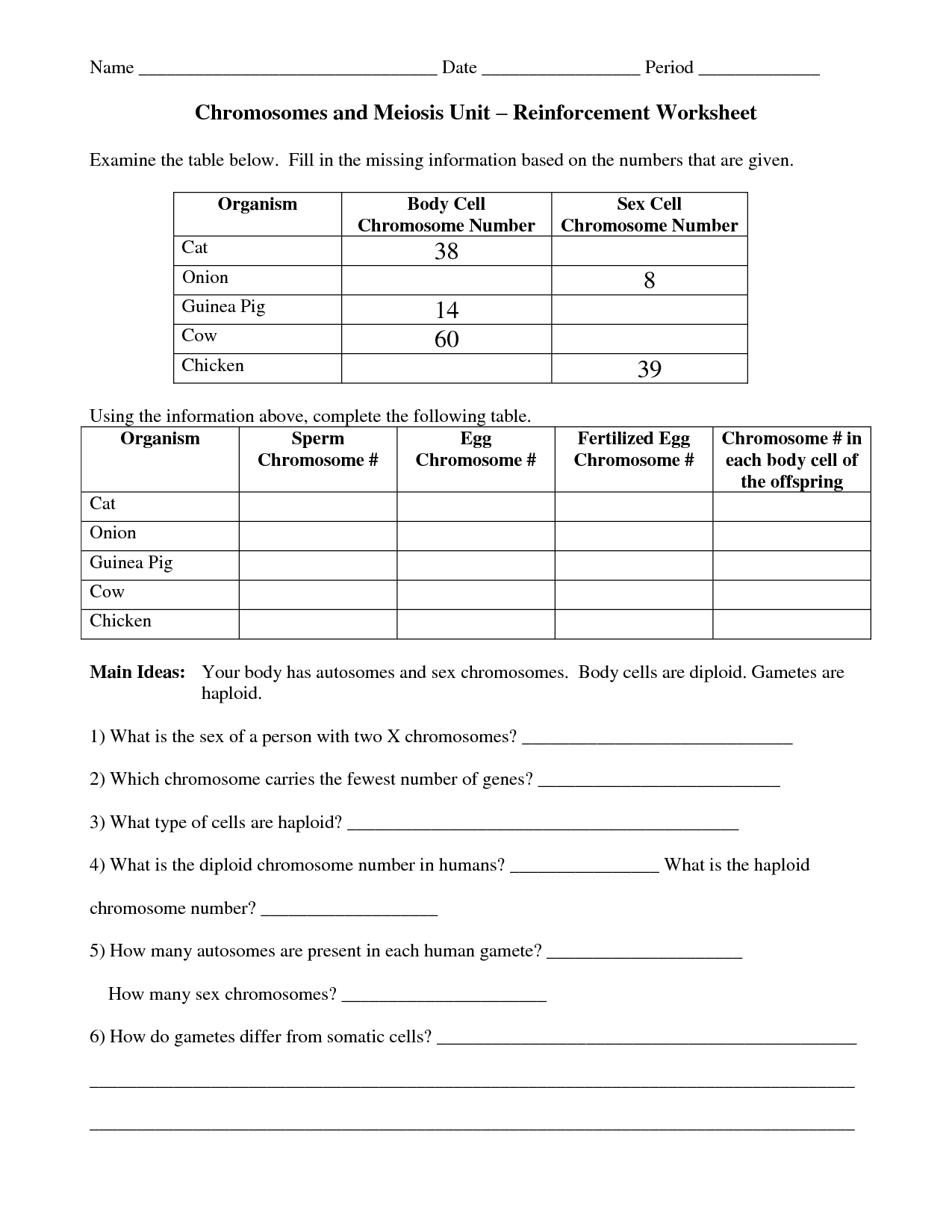
- Chromosomes and Meiosis Reinforcement Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis versus Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis Stages Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- 11 4 Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, resulting in the formation of gametes (eggs and sperm). It involves two rounds of division, producing four genetically unique daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to produce genetically diverse gametes (sperm and egg cells) for sexual reproduction. Meiosis ensures genetic variation by randomly shuffling genetic information and reducing the chromosome number by half, allowing for offspring with unique combinations of genetic traits.
How many divisions occur during meiosis?
Two divisions occur during meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, while meiosis II involves the separation of sister chromatids. These divisions result in the formation of four haploid daughter cells with genetic diversity.
How many daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis?
Four daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that contain the same genes, one from each parent. They are similar in size, shape, and genetic content, and are involved in the process of genetic recombination during meiosis. Homologous chromosomes carry the same genetic information, but can have different versions of the same gene (alleles), which may lead to variations in traits.
What is crossing over and when does it occur?
Crossing over is a process during meiosis where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, leading to genetic recombination. This occurs during prophase I of meiosis, specifically when homologous chromosomes pair up and physically exchange segments of DNA, creating new combinations of alleles that are passed on to offspring.
What is the significance of genetic variation in meiosis?
Genetic variation in meiosis is crucial for offspring diversity and adaptation. During meiosis, genetic recombination and random segregation of chromosomes lead to the creation of unique combinations of alleles in gametes, increasing genetic diversity. This variability is essential for natural selection to act upon, allowing organisms to evolve and better adapt to changing environments. Additionally, genetic variation plays a key role in preventing inbreeding and maintaining the health and viability of populations by reducing the likelihood of harmful genetic disorders.
What are haploid cells?
Haploid cells are cells that contain a single set of chromosomes, which represents half of the genetic material found in diploid cells. In humans, haploid cells are the result of meiosis, the cell division process that reduces the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) in order to produce gametes such as sperm and egg cells for sexual reproduction.
What is the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
Meiosis I is the first division in the cell division process of meiosis, where homologous chromosomes pair up, exchange genetic material, and separate, resulting in two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. In contrast, meiosis II is the second division in meiosis where the two daughter cells from meiosis I divide again, separating sister chromatids and producing a total of four haploid daughter cells, each with a unique combination of genes. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis but with haploid cells.
What is the final result of meiosis?
The final result of meiosis is the formation of four haploid daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. This process is essential for the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in sexually reproducing organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments