Karyotype Worksheet Answers
Are you struggling to find comprehensive answers for your karyotype worksheet? Look no further as this blog post will provide you with the necessary information! Designed for biology students studying genetics and heredity, this post offers detailed explanations and solutions for karyotype worksheets. Whether you're a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student seeking a deeper understanding of karyotyping, this post is tailored to meet your needs.
Table of Images 👆
- Human Karyotype Worksheet
- Human Karyotype Lab Answer Key
- Human Karyotype Form Answers
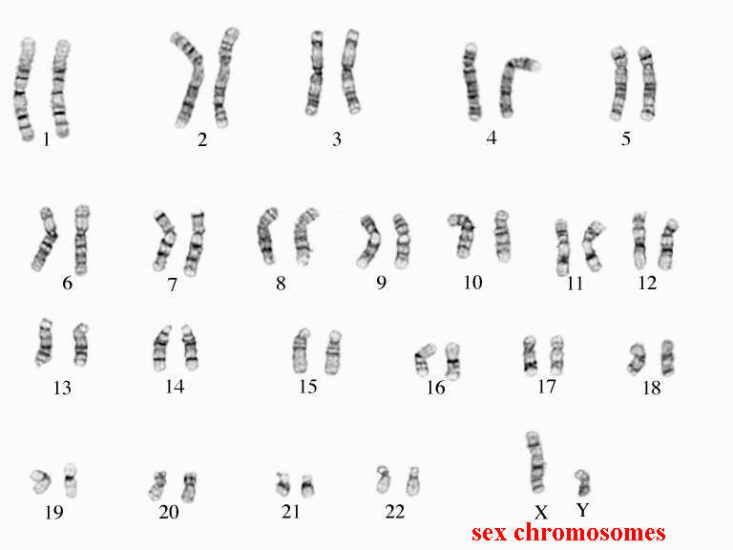
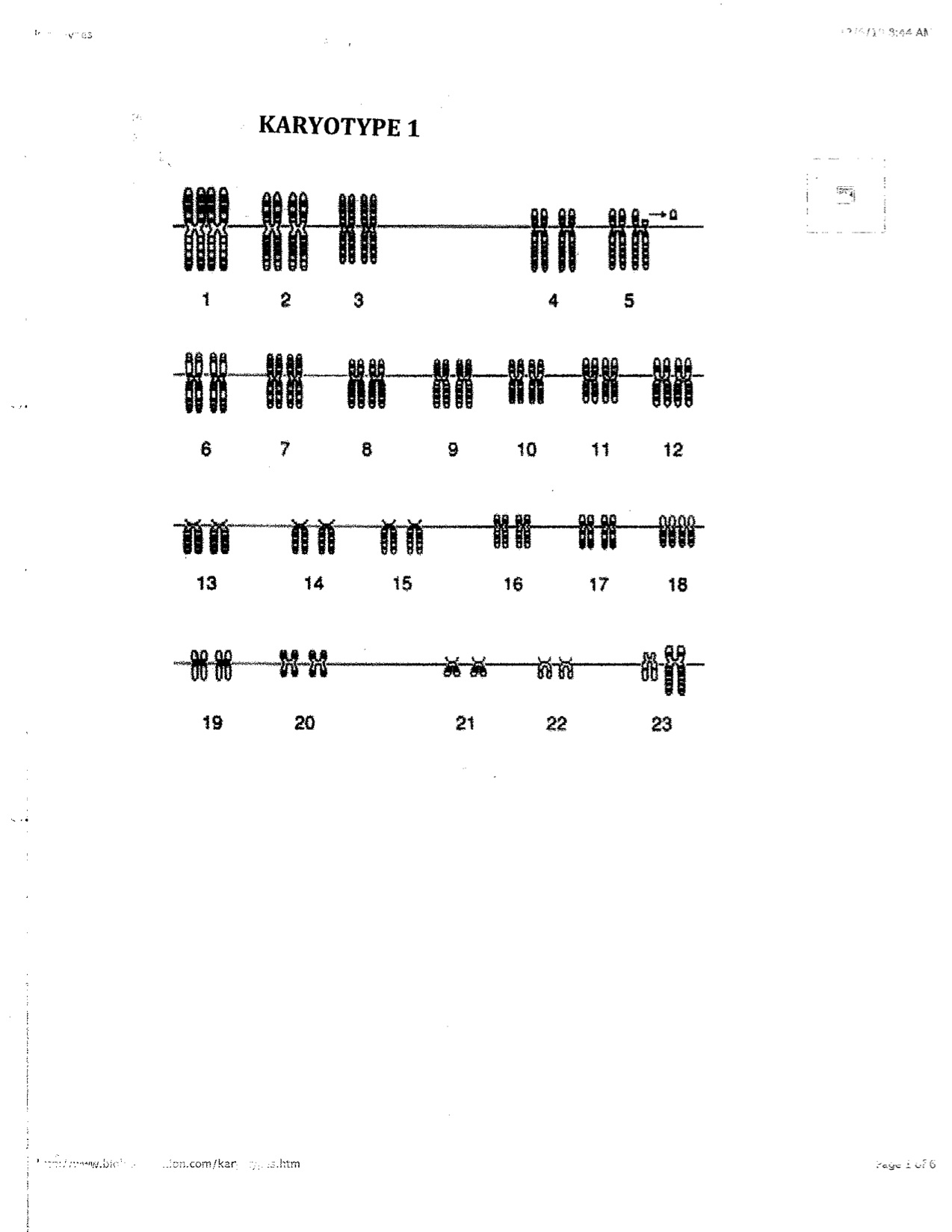
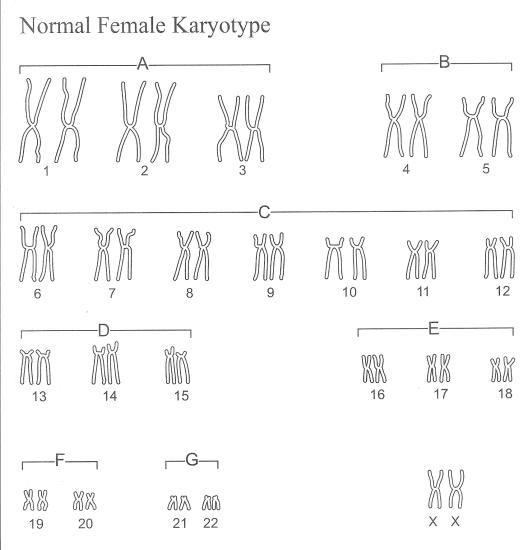
- Karyotype
- Karyotype Human Chromosomes
- Human Karyotype Worksheet
- Biology Karyotype Worksheet Answer Key
- Human Karyotype Worksheet
- Chromosome Karyotype Worksheet
- Triple X syndrome
- Human Chromosome Karyotype Worksheet
- Karyotype Worksheet and Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
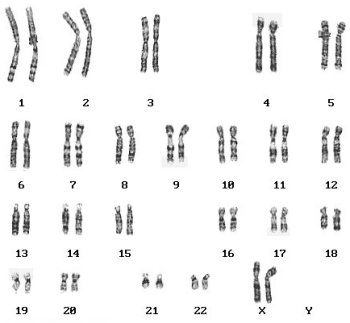
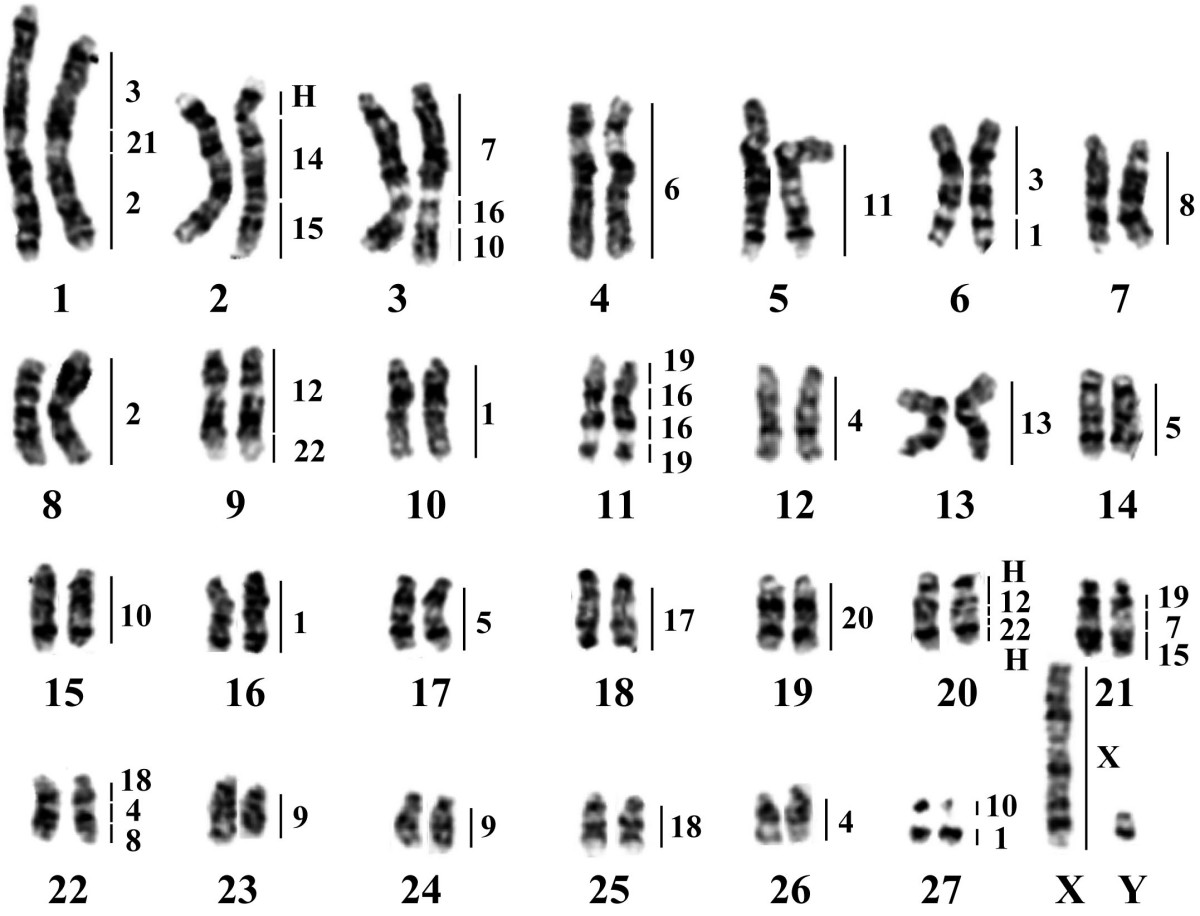
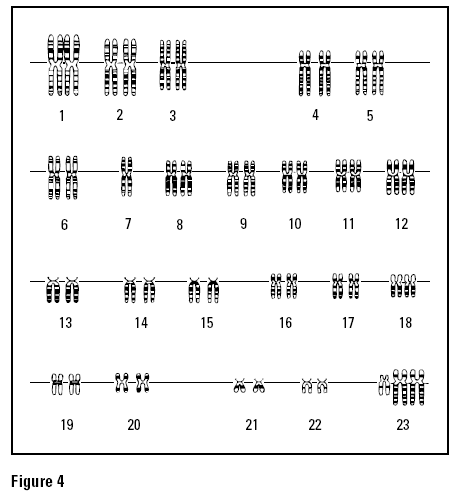
What is a karyotype?
A karyotype is a test that displays the chromosomes found in an individual's cells. It is a way to analyze the number, size, and shape of chromosomes in order to detect any abnormalities or genetic disorders. A karyotype can provide valuable information for diagnosing certain medical conditions and understanding genetic variations.
How are karyotypes useful in genetic analysis?
Karyotypes are useful in genetic analysis because they provide a comprehensive visual representation of an individual's chromosomes, allowing scientists to assess chromosomal structure, number, size, and any abnormalities present. By analyzing these karyotypes, researchers can identify genetic disorders, chromosomal abnormalities, and potential disease risks. Karyotyping is particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome, as well as in guiding reproductive decisions and personalized treatment plans based on an individual's chromosomal profile.
What are the key components of a karyotype?
A karyotype is a test that displays an individual's complete set of chromosomes. The key components of a karyotype include a visual representation of an individual's chromosomes arranged in pairs from largest to smallest, with specific attention to the number, size, and shape of each chromosome. This allows for the identification of any abnormalities, such as missing or extra chromosomes, translocations, or other structural changes that may be indicative of genetic disorders or diseases.
How can chromosomal abnormalities be detected through karyotyping?
Chromosomal abnormalities can be detected through karyotyping by analyzing a sample of the person's cells, typically obtained from a blood sample. The chromosomes are stained and arranged in order of size, allowing geneticists to examine the number, size, and structure of the chromosomes. Any missing or extra chromosomes, as well as any structural abnormalities such as deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations, can be identified through karyotyping, which allows for the diagnosis of genetic disorders caused by chromosomal abnormalities.
What is the difference between a normal and abnormal karyotype?
A normal karyotype refers to a complete set of chromosomes in a cell that is typical for a species, with the correct number and structure of chromosomes. An abnormal karyotype, on the other hand, refers to any deviation from this normal set-up, such as missing or extra chromosomes, translocations, deletions, or duplications. Abnormal karyotypes can be associated with genetic disorders, developmental abnormalities, or increased risk of certain health conditions.
What are the different types of chromosomal abnormalities?
There are several types of chromosomal abnormalities, including deletions (loss of a portion of a chromosome), duplications (extra copies of a portion of a chromosome), inversions (reversal of a portion of a chromosome), translocations (exchange of genetic material between non-homologous chromosomes), and aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes, such as trisomy or monosomy). These abnormalities can result in genetic disorders and developmental issues.
How can karyotype analysis be used in diagnosing genetic disorders?
Karyotype analysis can be used in diagnosing genetic disorders by examining a person's chromosomes to identify any abnormalities or variations in number, size, shape, or structure. This analysis allows healthcare professionals to detect genetic conditions such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome, which are characterized by specific chromosomal abnormalities. By comparing a patient's karyotype to a normal one, medical professionals can pinpoint the underlying genetic cause of a disorder, enabling accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Can karyotyping be used to determine the gender of an individual?
Yes, karyotyping can be used to determine the gender of an individual. By analyzing the chromosomes present in a sample, karyotyping can identify whether the individual has two X chromosomes (female) or one X and one Y chromosome (male), providing information about the individual's gender.
How is karyotyping performed?
Karyotyping is performed by first obtaining a sample of cells, typically from a blood sample or amniotic fluid in prenatal testing. The cells are then cultured in a lab to stimulate cell division and prepare them for analysis. Next, the cells are treated to stop the cell cycle at a specific stage so the chromosomes can be viewed and photographed. The chromosomes are then sorted and arranged based on their size, banding pattern, and other characteristics to create a visual map of an individual's full set of chromosomes. This process allows for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders.
Are there any limitations or drawbacks to karyotype analysis?
Some limitations of karyotype analysis include the inability to detect small genetic abnormalities or mutations, the requirement of actively dividing cells for analysis, limitations in detecting mosaicism or rearrangements that may not be visible on a standard karyotype, and the potential for misinterpretation of results due to technical errors or sample contamination. Additionally, karyotyping may not provide the level of detail needed for a comprehensive genetic diagnosis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.








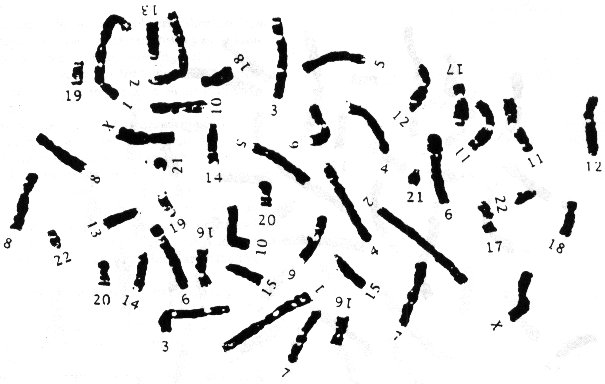















Comments