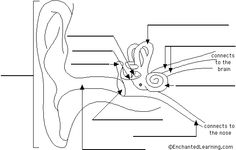
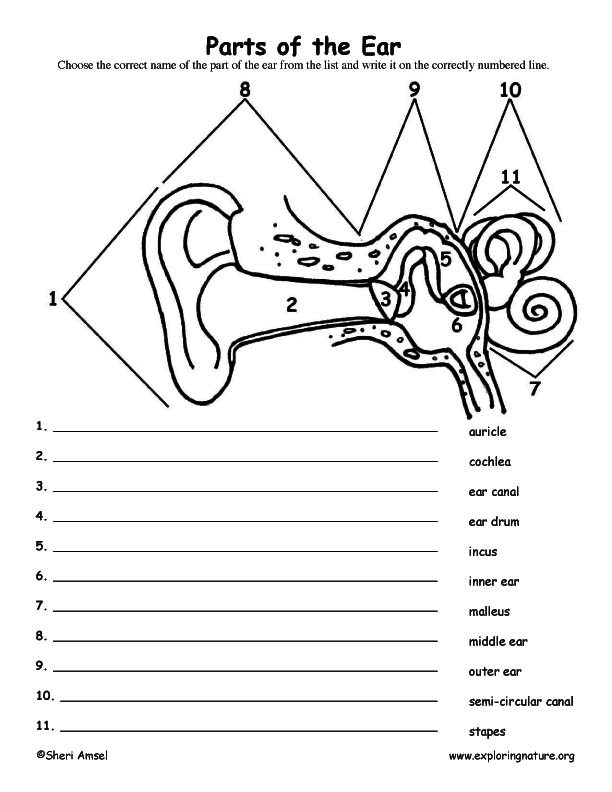
Inner Ear Diagram Worksheet
The inner ear diagram worksheet is a helpful educational tool for students studying biology or anatomy. This worksheet provides a comprehensive and informative visual representation of the various structures within the inner ear, allowing students to label and identify each entity accurately. With clear and concise descriptions, the inner ear diagram worksheet caters specifically to students who seek a better understanding of the subject matter in a self-paced and engaging manner.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
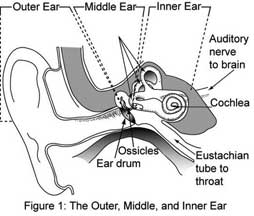
What is the function of the cochlea?
The function of the cochlea is to transform sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. This process allows us to hear and perceive different pitches and volumes of sound. The cochlea is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear that contains hair cells responsible for detecting sound waves and sending signals to the brain via the auditory nerve.
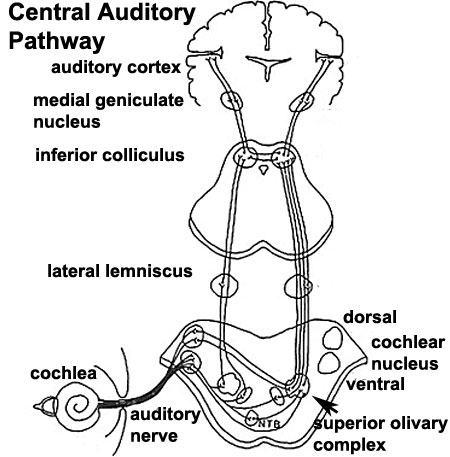
What role does the semicircular canals play in the inner ear?
The semicircular canals, along with the otolithic organs, help provide the sense of balance and spatial orientation by detecting changes in head rotation and angular acceleration. These canals are filled with fluid and hair cells that sense movement, sending signals to the brain to help maintain balance and stabilize vision during movement.
What is the purpose of the vestibule in the inner ear?
The purpose of the vestibule in the inner ear is to detect linear acceleration and the orientation of the head in relation to gravity. It contains structures called the utricle and saccule, which are responsible for sensing changes in head position and acceleration, helping to maintain balance and equilibrium.
What are the hair cells and what is their function?
Hair cells are sensory receptors located in the inner ear that are responsible for detecting sound waves and converting them into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. Their function is to help us hear and maintain balance by detecting movement and fluid pressure within the ear. These specialized cells play a crucial role in our sense of hearing and orientation in space.
How does the round window function in the inner ear?
The round window in the inner ear serves as a pressure-relief valve, allowing for the displacement of fluid within the cochlea when sound waves enter the ear. This movement of fluid helps maintain the proper function of the delicate structures within the inner ear, such as the cochlea and the hair cells responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
What is the significance of the oval window in the inner ear?
The oval window in the inner ear is significant because it serves as the connection point between the middle ear and the inner ear, specifically the cochlea. It is covered by the stapes bone and helps to transmit sound vibrations from the middle ear to the cochlea, where they are converted into nerve impulses that are then interpreted by the brain as sound. The oval window plays a crucial role in the process of hearing and amplifying sound signals within the ear.
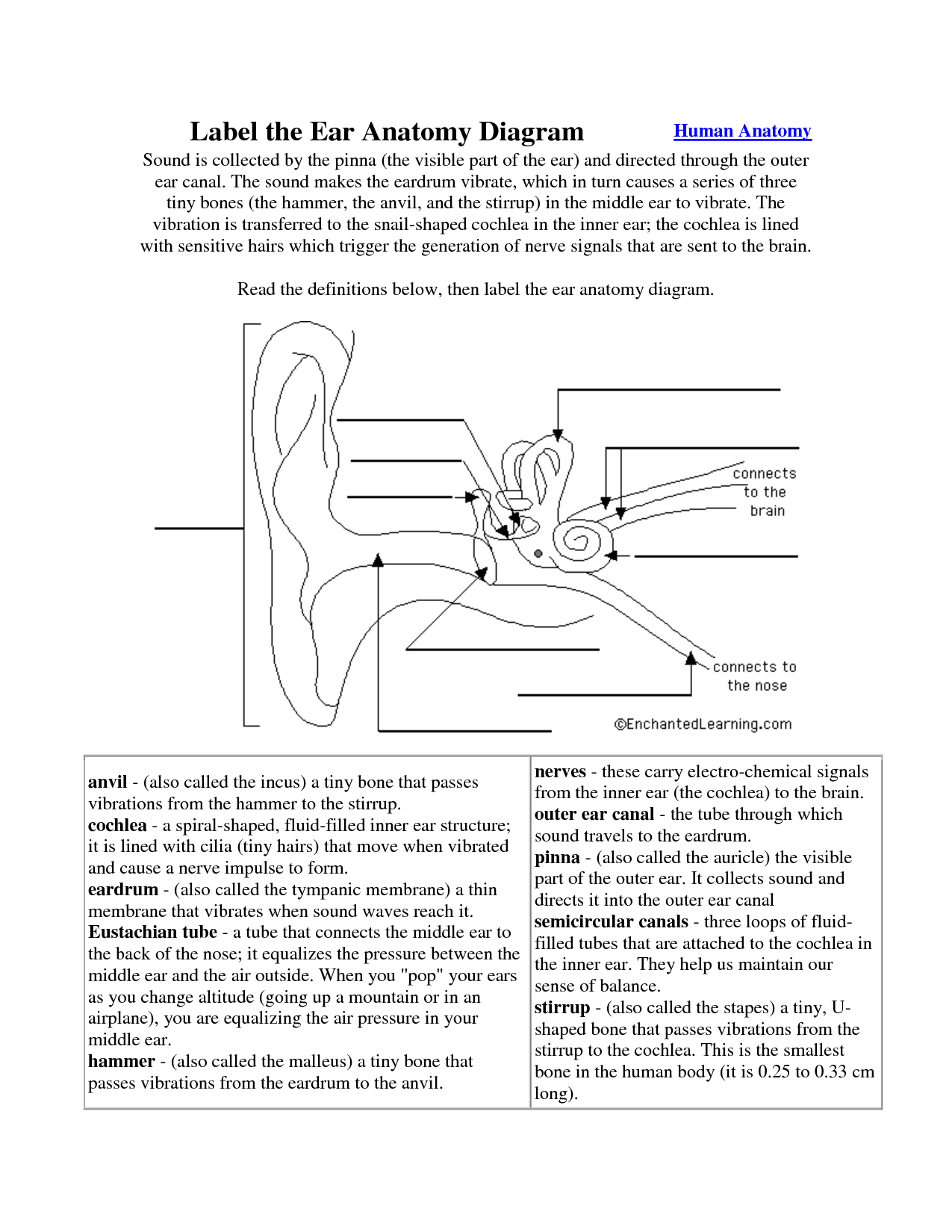
What is the relationship between the cochlear nerve and the inner ear?
The cochlear nerve is a branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain. It plays a crucial role in transmitting auditory information from the cochlea of the inner ear to the brain, where sound signals are processed and interpreted.
How does the endolymph contribute to the functioning of the inner ear?
Endolymph is a fluid-filled structure within the inner ear that plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and proper functioning of the inner ear. It helps transmit sound vibrations and head movements to the sensory cells, allowing for the detection of sound and balance. The movement of endolymph in the inner ear is essential for stimulating hair cells in the cochlea and the vestibular system, which ultimately sends signals to the brain for processing sound and maintaining equilibrium.
What is the purpose of the utricle and saccule in the inner ear?
The utricle and saccule are parts of the vestibular system in the inner ear that are responsible for detecting linear acceleration and head position. They help the brain maintain balance, sense changes in position and movement, and stabilize vision during motion by sending signals to the brain about the body's orientation in space.
How does the inner ear contribute to our sense of balance and hearing?
The inner ear plays a crucial role in our sense of balance and hearing. Within the inner ear, the vestibular system helps us maintain our balance by sensing movement and orientation of the head, which is important for coordination and stability. It contains fluid-filled semicircular canals that detect rotational movements and otolithic organs that detect linear movements. Additionally, the cochlea in the inner ear is responsible for hearing. Sound waves entering the ear cause vibrations in the cochlea which are then converted into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for interpretation, allowing us to hear and perceive sounds. Thus, the inner ear contributes significantly to both our sense of balance and hearing.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments