Human Eye Worksheet
The human eye worksheet is a helpful tool for students studying anatomy and physiology or anyone interested in learning more about how the eyes function. This worksheet is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the various structures and functions of the eyes, allowing learners to deepen their understanding of this complex sensory organ.
Table of Images 👆
- Eye Anatomy Coloring Page
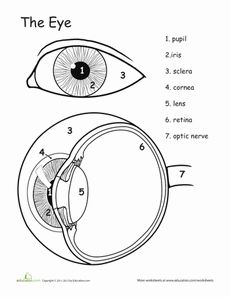
- Human Eye Anatomy Diagram Worksheet
- The Vision and Eye Anatomy Worksheet Answers
- Printable College Anatomy Worksheets
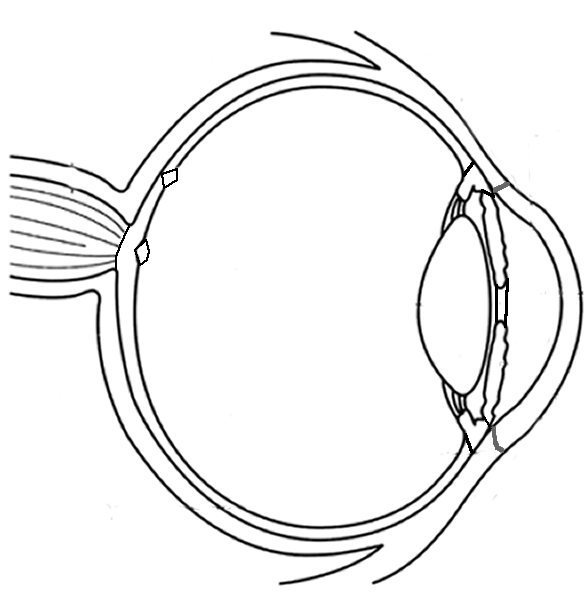
- Human Eye Diagram
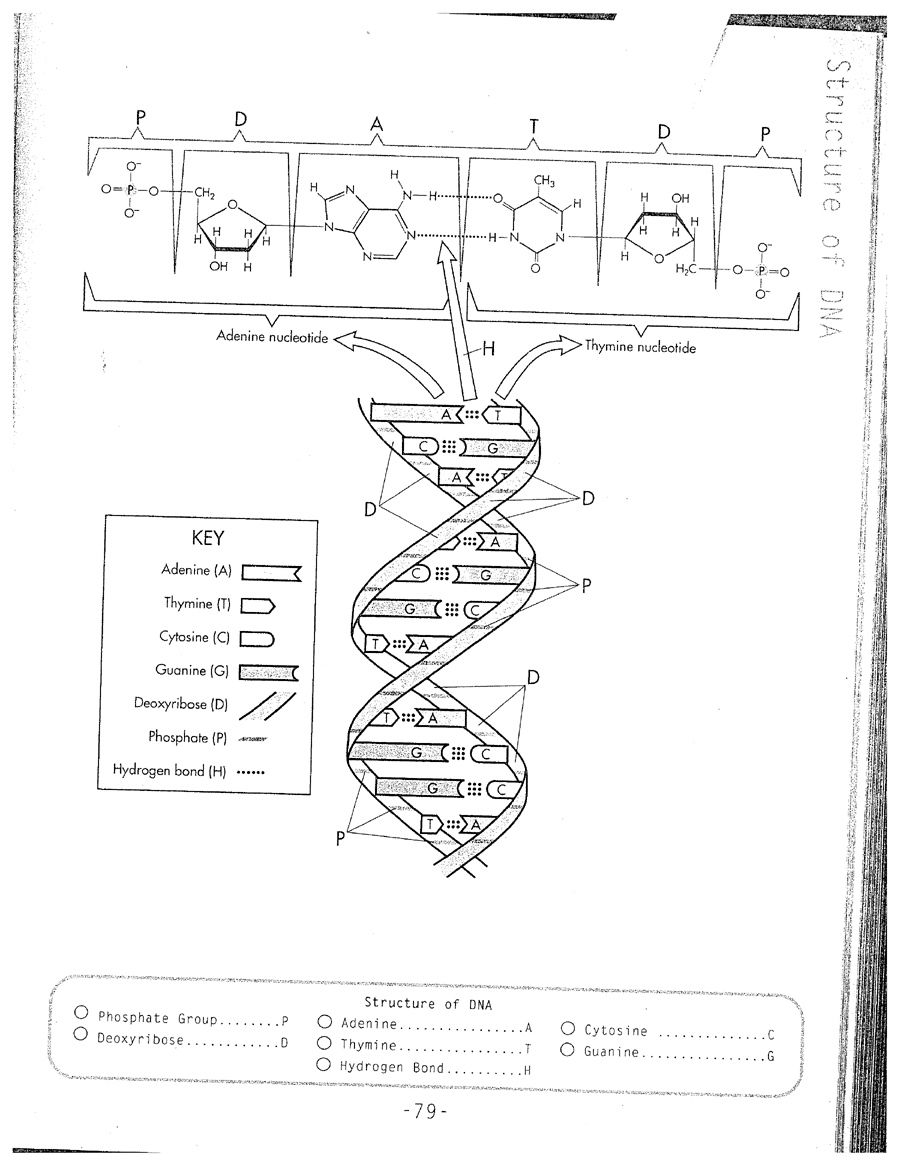
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- Human Eye Anatomy Coloring Page
- Brain Human Body Worksheet
- Biology Cell Organelles Worksheet
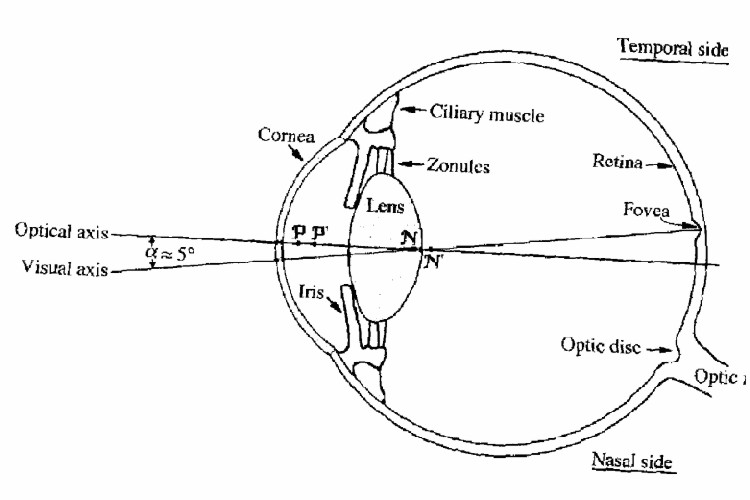
- Eye Diagram Nearsightedness
- Neuron Anatomy Activity Answers
- Ears Eyes Nose Mouth Printable Worksheets
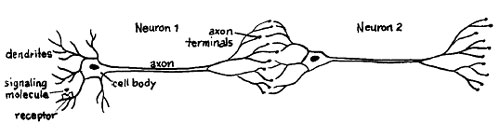
- Synapse Between Two Neurons Diagram
- Robot Outline Template
- Bikini Bottom Genetics 2 Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
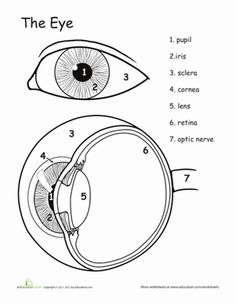
What is the human eye?
The human eye is a complex sensory organ that allows for the perception of light, shapes, colors, and depth. It consists of various structures including the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and optic nerve that work together to capture and process visual information, which is then transmitted to the brain for interpretation.
What are the main parts of the eye?
The main parts of the eye include the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve, and vitreous humor. The cornea is the clear outer covering, the iris is the colored part that controls the size of the pupil, the lens focuses light onto the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells that send signals through the optic nerve to the brain for processing. The vitreous humor is a gel-like substance that helps maintain the shape of the eye.
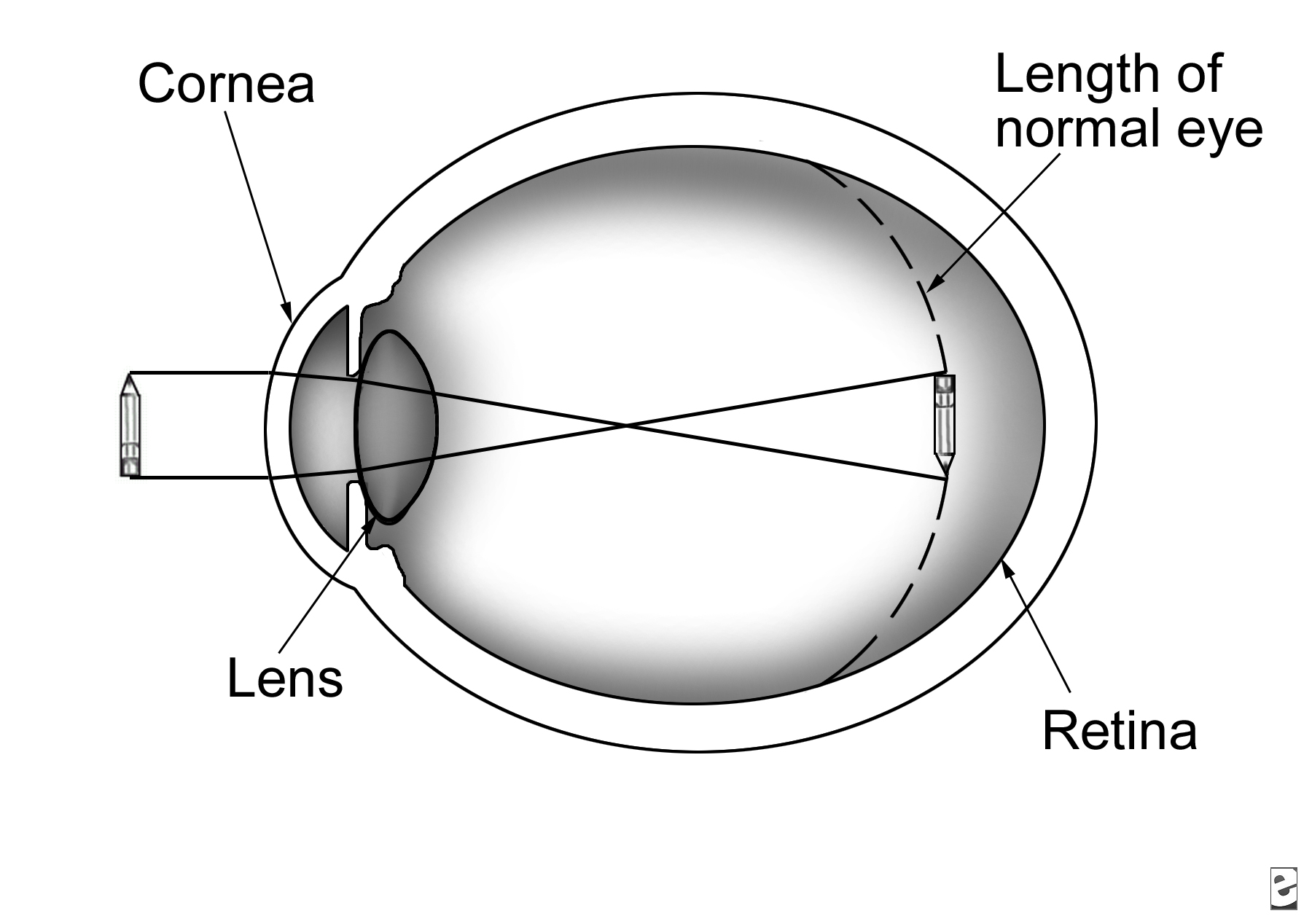
How does the cornea work?
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that works to refract light entering the eye, allowing it to focus on the retina at the back of the eye. It plays a crucial role in the eye's ability to bend and focus light accurately, helping to create clear vision. Additionally, the cornea acts as a protective barrier, shielding the eye from dust, germs, and other harmful substances.
What is the function of the iris?
The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye through the pupil. It can adjust the size of the pupil to control the amount of light that reaches the retina, helping to protect the eye from bright light and regulate visual clarity in different lighting conditions.
How does the lens focus light?
The lens focuses light through a process called refraction, which occurs when light passes from one medium (air) into another (such as glass in the lens). As the light travels from air to the lens, it bends at the surface of the lens due to the change in density, causing the light rays to converge or diverge depending on the type of lens (convex or concave). This bending of light helps to bring the light rays into focus at a specific point, creating a clear image.
What is the purpose of the retina?
The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused, convert the light into neural signals, and send those signals to the brain for visual recognition and processing. It contains specialized cells called photoreceptors (rods and cones) that play a crucial role in capturing and processing light to create visual images.
How do the rods and cones of the retina contribute to vision?
Rods and cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina that play a crucial role in vision. Rods are responsible for vision in low light conditions and detecting motion, while cones are responsible for color vision and visual acuity in brighter light. Rods contain a pigment called rhodopsin that is sensitive to light, allowing them to detect even small amounts of light, while cones contain different pigments that are responsive to specific wavelengths of light, enabling color vision. Together, rods and cones work to convert light stimuli into electrical signals that are then transmitted to the brain for visual processing, ultimately enabling us to see and perceive our surroundings.
What is the role of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. It serves as the primary conduit for sensory input related to vision, allowing the brain to process and interpret visual stimuli.
How does the brain interpret visual information received from the eye?
The brain interprets visual information received from the eye through a complex process that involves the transmission of electrical signals from the retina to the visual cortex located in the occipital lobe at the back of the brain. These signals are then processed, analyzed, and integrated with previous knowledge and experiences to construct a coherent visual perception. The brain also uses mechanisms such as edge detection, motion detection, color processing, and depth perception to make sense of the visual information received from the eye.
How does the process of vision contribute to depth perception?
The process of vision contributes to depth perception by using various visual cues such as binocular disparity, motion parallax, and relative size to interpret the distance of objects from the viewer. The brain combines information from both eyes to create a sense of depth and distance, allowing us to perceive the three-dimensional world accurately. This integration of visual data helps us navigate our environment and interact with objects in a spatially aware manner.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments