Human Evolution Worksheet
Are you interested in delving deeper into the fascinating world of human evolution? If so, you're in luck! An entity-focused and comprehensive human evolution worksheet is here to provide you with a structured and informative learning experience. This worksheet is designed for students studying anthropology or anyone who has a keen interest in human history and wants to expand their knowledge on the subject.
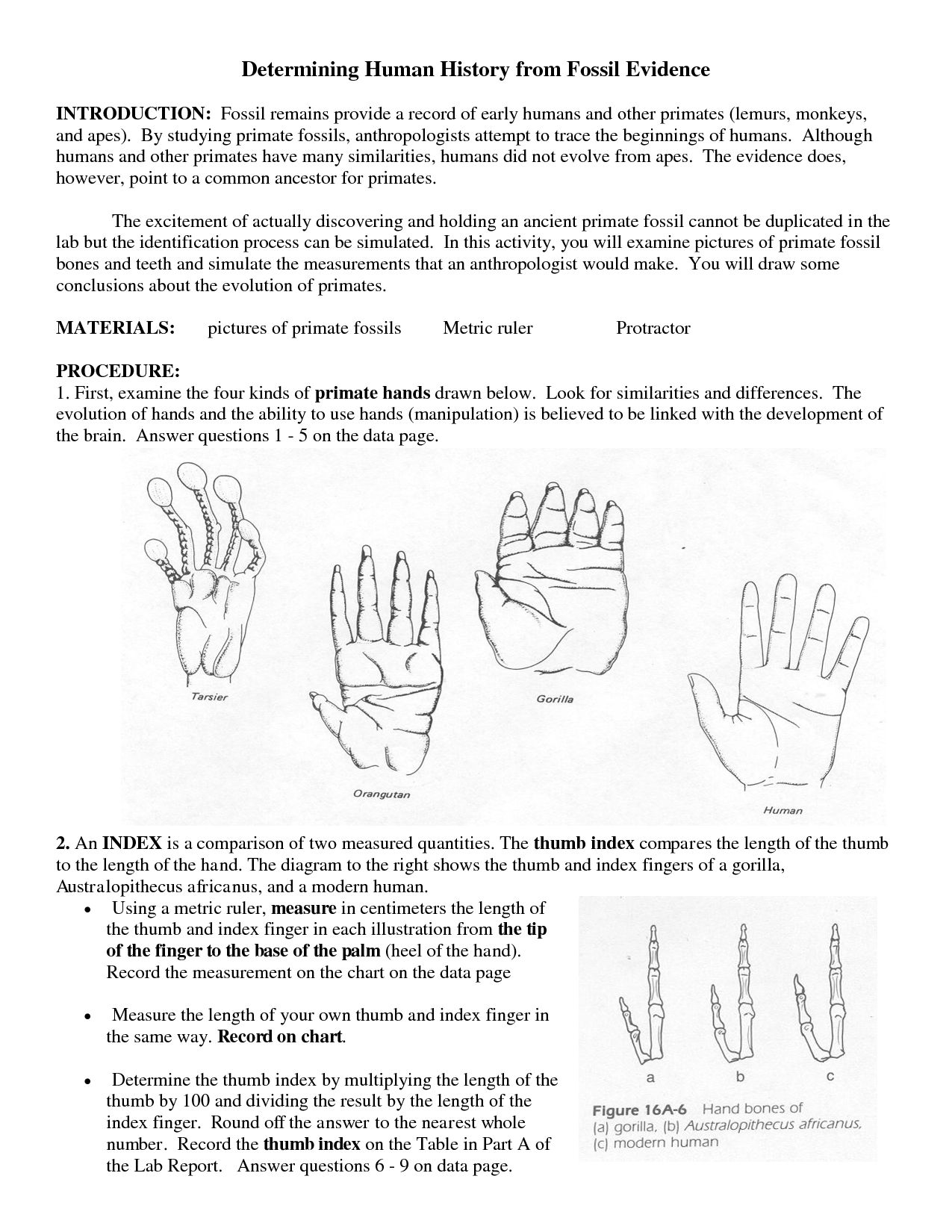
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
When did human evolution begin?
Human evolution is believed to have begun around 6 to 7 million years ago when the first ancestors of modern humans diverged from their common ancestor with chimpanzees. This marked the beginning of the evolutionary process that eventually led to the emergence of Homo sapiens as the dominant species on Earth.
What were the earliest known human ancestors?
The earliest known human ancestors were hominins, such as Ardipithecus ramidus and Australopithecus afarensis, which lived between 4 to 7 million years ago. These species were bipedal primates that eventually evolved into the genus Homo, which includes modern humans.
What traits distinguish Homo sapiens from other species?
Some of the key traits that distinguish Homo sapiens from other species include complex language abilities, advanced cognitive skills, the use and creation of complex tools, the development of social structures and cooperation, and the ability to adapt and innovate in a variety of environments. Additionally, Homo sapiens have a unique capacity for symbolic thought, cultural development, and the transmission of knowledge across generations, which has allowed for the incredible diversity and adaptability of our species.
How did bipedalism evolve in humans?
Bipedalism in humans evolved over millions of years through a process of natural selection and adaptation. It is believed to have originated in response to environmental changes, such as the transition from forests to savannas, which required early human ancestors to travel longer distances on two legs to better navigate their surroundings, search for food, and avoid predators. Over time, this adaptation became advantageous, leading to the development of anatomical features that support efficient bipedal locomotion, such as changes in the structure of the pelvis, legs, and feet.
What were the advantages of early humans' increased brain size?
The advantages of early humans' increased brain size were improved cognitive abilities like problem-solving, tool-making, communication, and social cooperation. This led to better adaptation to the environment, increased chances of survival, and eventually the development of complex societies and cultural advancements.
How did the development of tools influence human evolution?
The development of tools significantly influenced human evolution by enabling our ancestors to access new resources, create shelter, hunt more effectively, and protect themselves. This increased efficiency in securing food and creating a safer environment promoted brain development, cognitive abilities, and social interactions. Over time, these advancements contributed to the evolution of larger brains and the emergence of more sophisticated behaviors, ultimately shaping the path towards modern humans and our continued technological progress.
When and where did Homo sapiens first appear?
Homo sapiens first appeared in Africa around 300,000 years ago.
How did early humans adapt to different environments?
Early humans adapted to different environments through a variety of means, such as developing different physical characteristics like skin color and body shapes to suit the climate, creating tools and weapons for hunting and gathering food, developing social structures to cooperate and share resources, and utilizing fire for warmth, cooking, and protection. These adaptations allowed early humans to thrive in diverse environments and eventually spread across the globe.
What evidence suggests that early humans practiced social behaviors?
Evidence suggests that early humans practiced social behaviors through various elements such as burial rituals, cave paintings, and tools found in archaeological sites. Burial rituals indicate that early humans had a concept of the afterlife and cared for their deceased, showing social bonds and a sense of community. Cave paintings demonstrate a shared cultural and symbolic language, suggesting group communication and cooperation. Tools found in sites like Olduvai Gorge show evidence of collaboration and division of labor within early human groups, indicating social organization and cooperation among individuals.
What factors contributed to the extinction of other human species, such as Neanderthals?
There are several factors that contributed to the extinction of other human species like Neanderthals, including competition for resources with modern humans, interbreeding, possibly leading to genetic assimilation, environmental changes, and possibly diseases brought by modern humans. These factors combined likely played a role in the decline and eventual extinction of Neanderthals and other human species.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments