High School Physical Science Worksheets
If you are a high school student or teacher looking for a wide variety of resources to reinforce your understanding of physical science concepts, then these high school physical science worksheets are just what you need.
Table of Images 👆
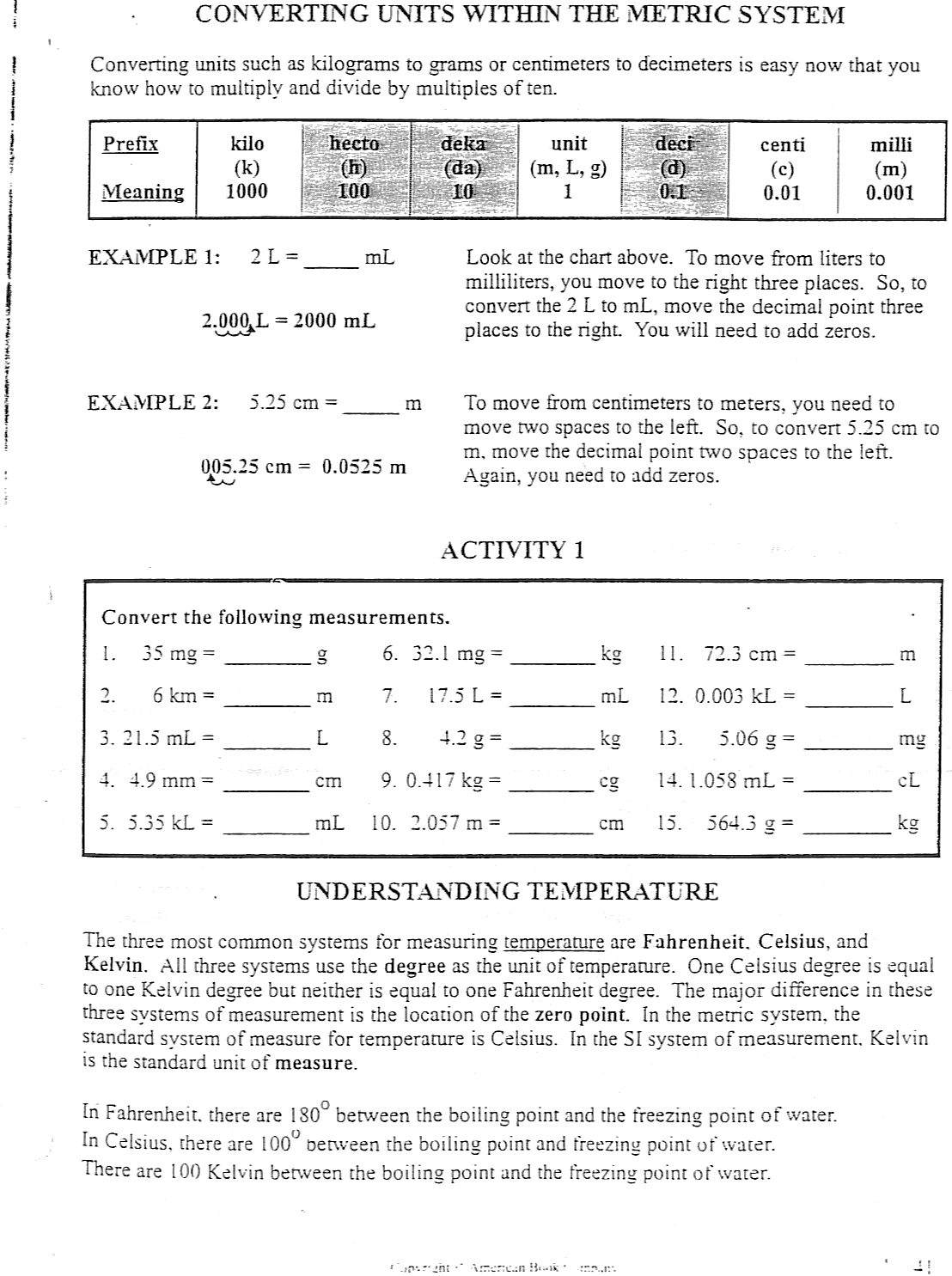
- Metric Conversion Worksheets High School
- Physical Evidence Forensic Science Worksheet
- Physical Science Newtons Laws Worksheet Answers
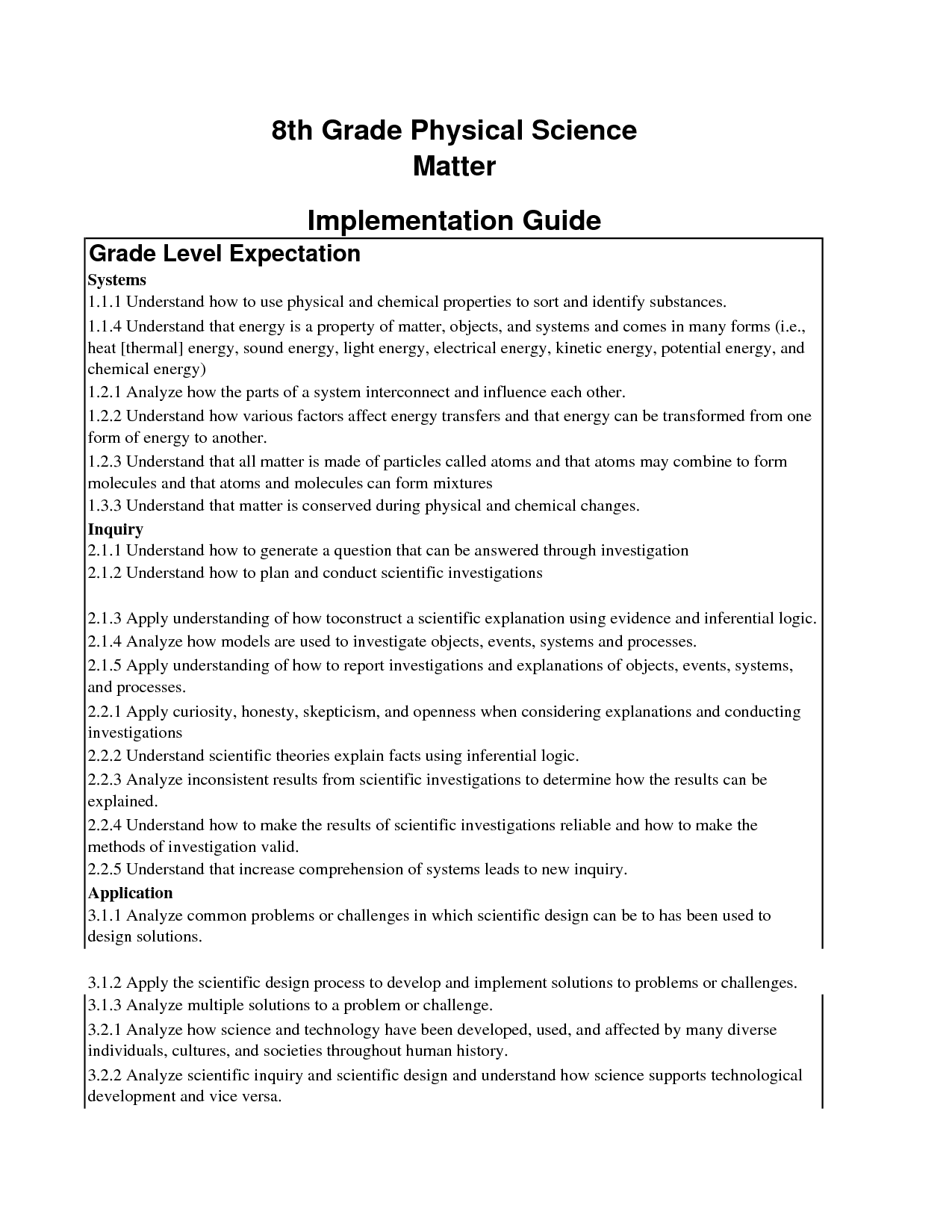
- High School Science Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- 8th Grade Physical Science Worksheet Answers
- Forensic Science Worksheet Answers
- Holt Science Spectrum Worksheets Answers
- Forensic Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Safety Worksheets High School
- Bohr Model Worksheet Answers
- Physics Conversions Worksheets
- 9th Grade School Worksheets
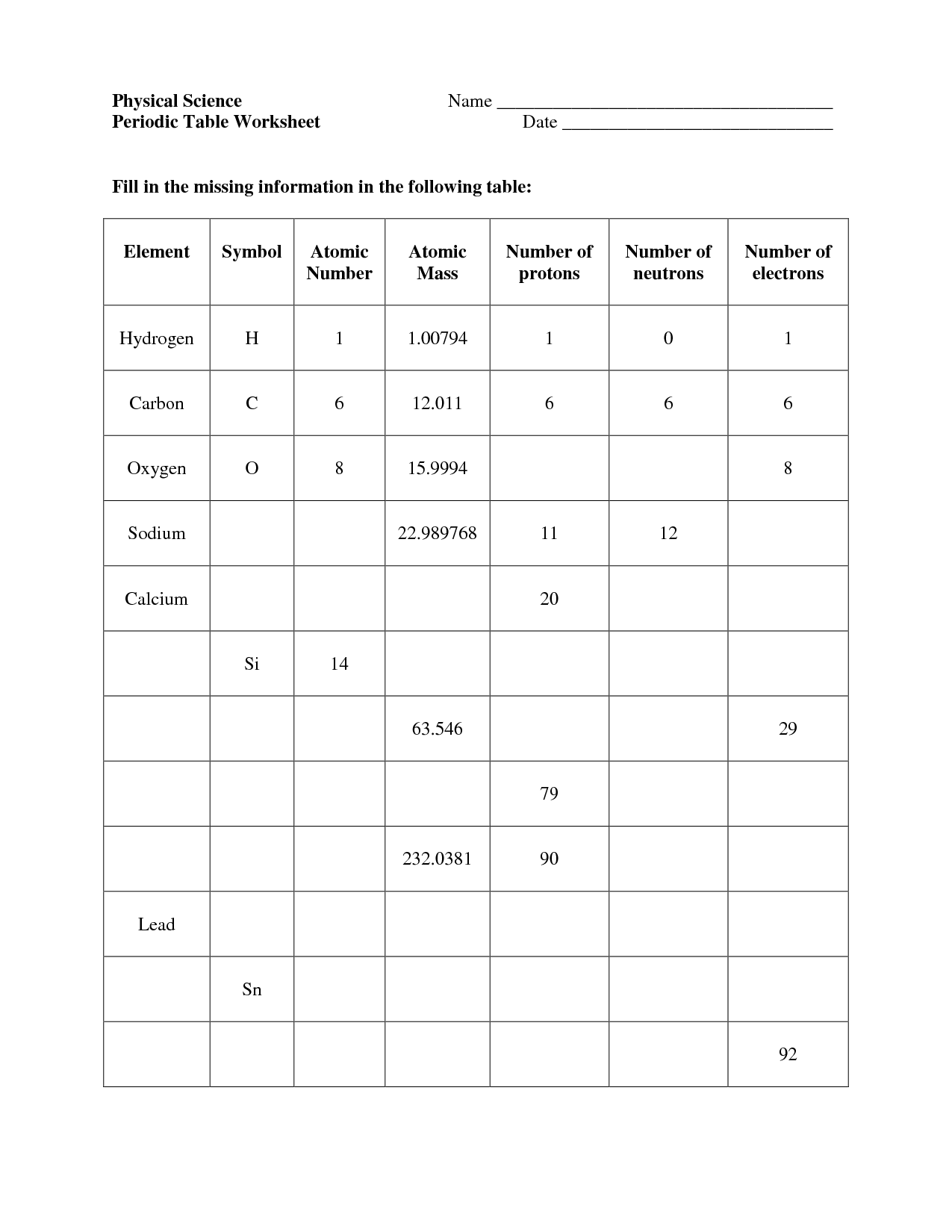
- Periodic Table 8th Grade Worksheets
- Bohr Atomic Model Worksheet Middle School
- Periodic Table Worksheet Fill In
- Earth Science Worksheets High School
- Bohr Model Worksheets Middle School
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
Define matter and provide three examples.
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Some examples of matter include water, air, and iron.
Explain the difference between physical and chemical changes.
Physical changes involve simple alterations in the physical state or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as melting, freezing, or breaking apart. In contrast, chemical changes result in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties due to rearrangement of atoms and molecules, such as burning, rusting, or reacting with other substances.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its significance.
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process through which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen. Using the pigment chlorophyll, plants absorb sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through a series of reactions in the chloroplasts of their cells. This process is crucial for the survival of various living organisms, as it provides oxygen for respiration and serves as the primary source of energy for plants and other organisms in the food chain. Photosynthesis plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's atmosphere and climate by removing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
What are the three laws of motion proposed by Sir Isaac Newton?
Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion are: 1) An object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force (law of inertia); 2) The force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma); and 3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Explain the concept of energy and provide three examples of different types.
Energy is the ability to do work or cause changes in a system. It can exist in various forms, such as mechanical energy (like the motion of a moving object), thermal energy (from heat), and electrical energy (from the flow of electrons in a circuit). Other examples of energy types include chemical energy (stored in molecules), nuclear energy (from atomic reactions), and light energy (from electromagnetic radiation).
Discuss the difference between series and parallel circuits.
In a series circuit, components are connected one after another in a single path, resulting in the same current flowing through each component. If one component fails or is removed, the entire circuit is broken. In contrast, a parallel circuit has multiple branches where each component has its own separate path to the power source. This allows different currents to flow through each component, and if one component fails, it does not necessarily affect the rest of the circuit. Additionally, the total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of all individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance.
Describe the structure of an atom and the roles of its subatomic particles.
Atoms consist of a central nucleus made up of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Protons and neutrons are similar in size and mass, while electrons are much smaller and orbit the nucleus at various energy levels. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons are neutral. Protons determine the element's identity, neutrons stabilize the nucleus, and electrons participate in chemical reactions and bonding with other atoms.
What is the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration according to Newton's second law?
According to Newton's second law of motion, the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is given by the equation F = ma, where F represents the force applied to an object, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration produced. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. In simpler terms, the greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration will be; conversely, the greater the mass of an object, the lower its acceleration will be for a given force.
Explain the concept of density and how it is calculated.
Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume of a substance. It is calculated by dividing an object's mass by its volume. The formula for density is: density = mass / volume. The units of density are typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm^3) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m^3). Objects with high density have more mass packed into a smaller volume, while objects with low density have less mass spread out over a larger volume.
Discuss the different forms of energy transfer and provide examples of each.
Energy can be transferred in various forms, including conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact, such as a metal spoon becoming warm when placed in hot soup. Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids or gases, like boiling water in a pot. Radiation is the transfer of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as sunlight heating the Earth's surface. Each form of energy transfer plays a crucial role in the natural world and our everyday lives.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments