Heat Worksheet for 3rd Grade
Worksheets are an invaluable resource for 3rd grade students to reinforce and practice various concepts. When it comes to learning about heat, a well-designed worksheet can be an excellent tool to engage young minds and help them grasp the concept of this fundamental scientific entity. Whether it's identifying sources of heat or understanding the different ways it can be transferred, a heat worksheet can provide focused practice and ensure a thorough understanding of the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Light and Heat Energy Worksheets
- Temperature Worksheets 4th Grade
- Second Grade Measurement Worksheets
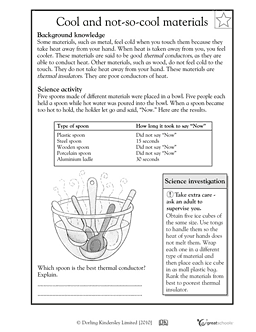
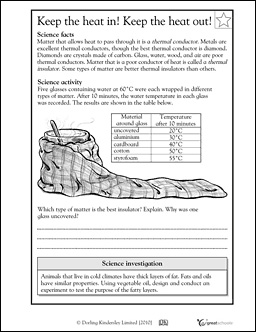
- Heat Conductor and Insulator Worksheets 3rd Grade
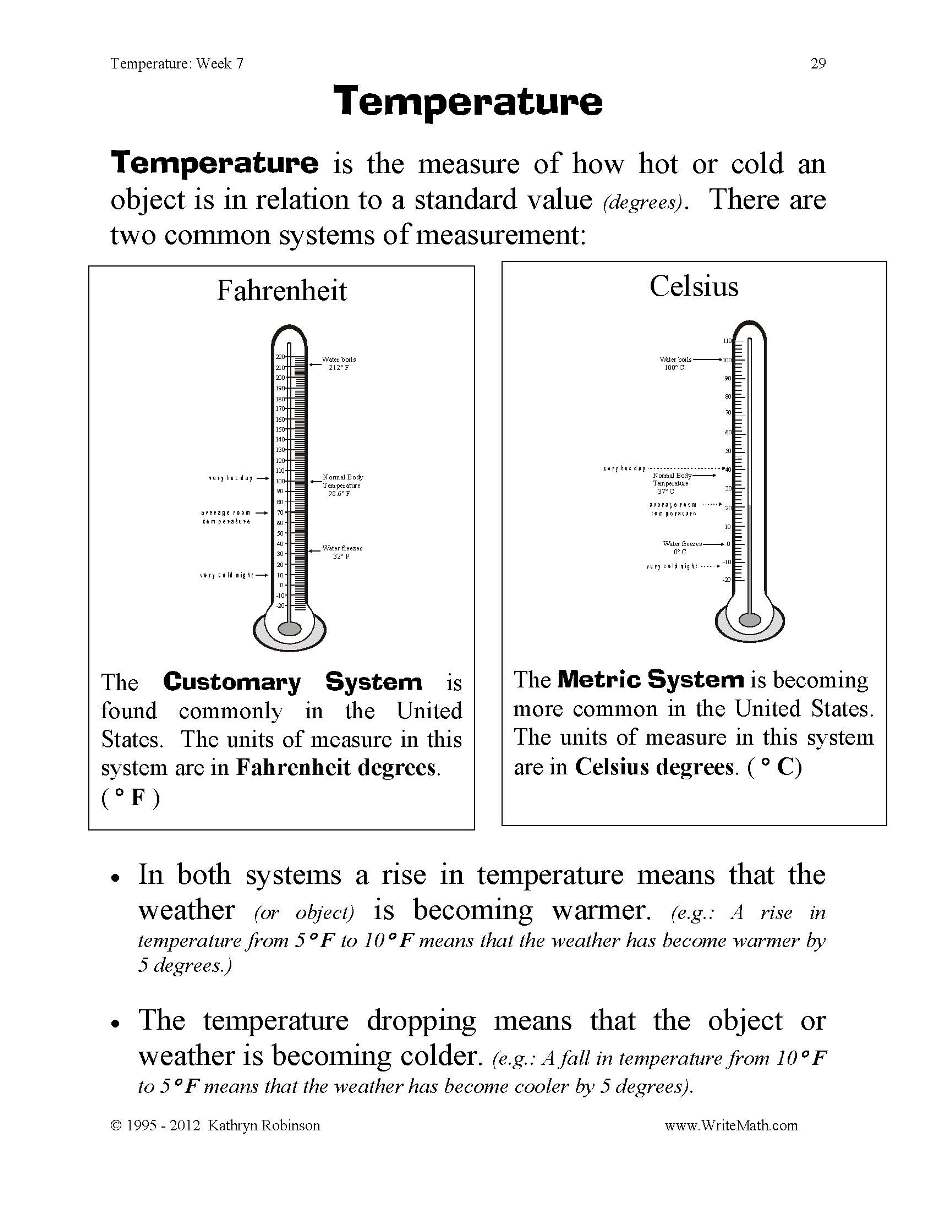
- Temperature Worksheets 4th Grade
- Heat Conductor and Insulator Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Division Worksheets 3rd Grade
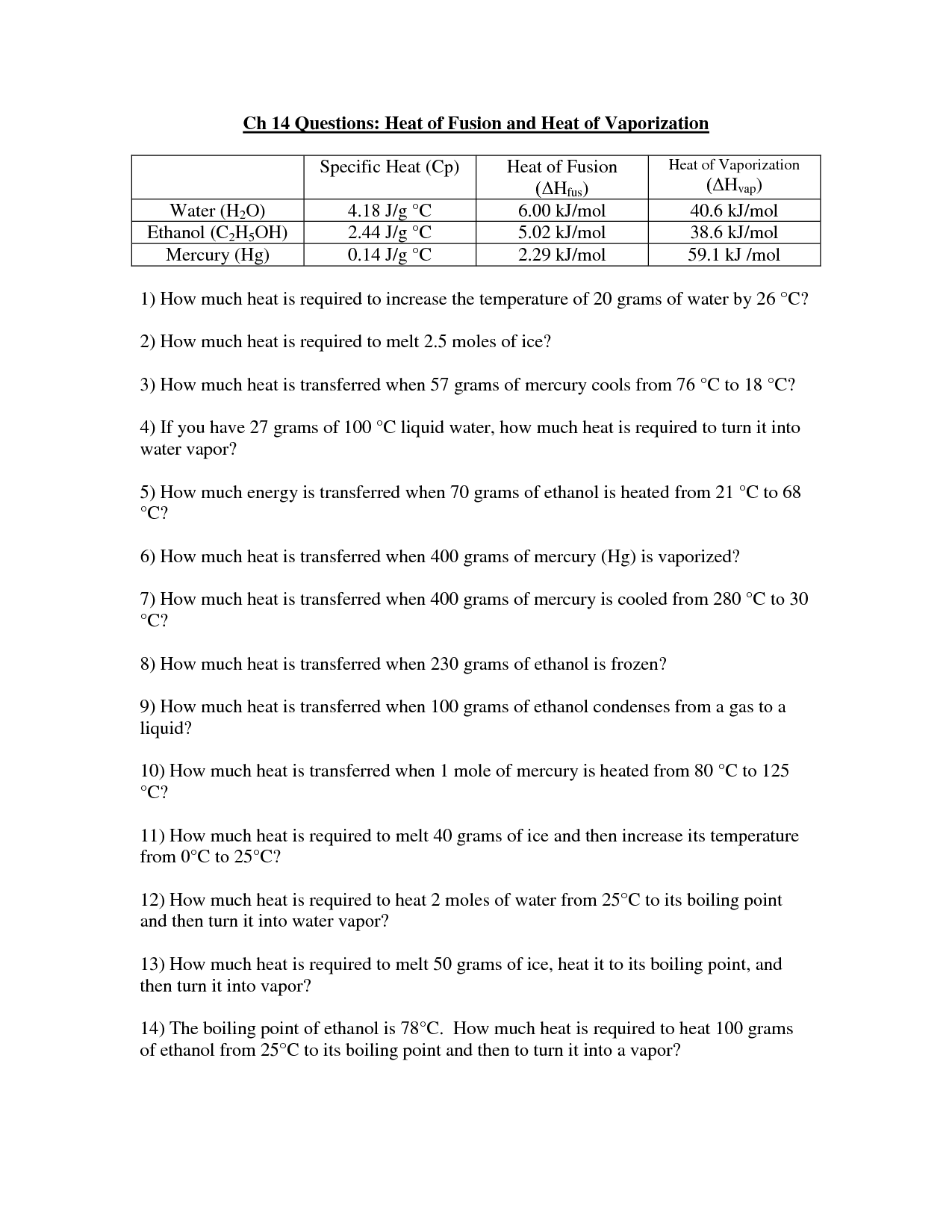
- Heat and Thermal Energy Worksheet
- Third Grade Science Worksheets
- Third Grade Addition Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Thermometer Worksheets
- Thermal Energy Worksheet Heat and Temperature
- Temperature Thermometer Worksheets
- Reading Temperature Worksheets
- Science Worksheets Light Energy and Heat
More 3rd Grade Worksheets
3rd Grade Math WorksheetsTelling Time Worksheets 3rd Grade
Time Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Energy Worksheets 3rd Grade Science
Multiplication Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Math Division Worksheets Printable
Short Reading Comprehension Worksheets 3rd Grade
Soil Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Cursive Writing Worksheets for 3rd Grade
What is heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between different objects or systems due to temperature differences. It can be generated by various processes such as combustion, radiation, or mechanical work, and is typically measured in units of joules or calories. Heat plays a crucial role in many natural phenomena and human activities, influencing temperature changes, physical states of matter, and chemical reactions.
How does heat move from one object to another?
Heat moves from one object to another through three main processes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat is transferred through direct contact between two objects with different temperatures. Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids or gases, where warmer parts rise and cooler parts sink, creating a circulation pattern. Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, without the need for a medium, such as in the case of the sun warming the Earth. These processes work together to distribute heat energy and maintain thermal equilibrium between objects.
What are some sources of heat?
Some sources of heat include the sun, fire, electricity, friction, hot springs, geothermal energy, chemical reactions, and nuclear reactions.
How do animals stay warm in the cold?
Animals stay warm in cold environments through a variety of adaptations, such as growing thicker fur, feathers or blubber, huddling together for warmth, decreasing blood flow to peripheral body parts, and increasing metabolic rate to generate heat. Some animals also have specialized behaviors like shivering and seeking out sheltered areas to conserve body heat and maintain their core temperature.
How does heat affect different materials?
Heat affects different materials in various ways depending on their composition. For example, metals expand when heated, making them malleable and easier to work with. Plastics can melt or deform under heat, changing their shape and properties. Organic materials like wood or paper can char or burn when exposed to high temperatures. Ceramics can become more brittle or crack due to thermal stress. In general, heat can alter the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of materials, sometimes irreversibly.
What happens when a substance gets heated?
When a substance is heated, its particles absorb energy, gaining kinetic energy and moving faster. This increase in kinetic energy causes the particles to move farther apart, leading to an expansion of the substance. In solids, heating can cause the particles to vibrate more vigorously, eventually breaking the bonds and turning the substance into a liquid. Further heating can turn the liquid into a gas as the particles gain enough energy to break free from each other.
What are some examples of heat transfer?
Some examples of heat transfer include conduction, where heat is transferred through direct contact between materials, convection, which involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids or gases, and radiation, where heat is emitted by a source and travels through space without the need for a medium.
How can we measure heat?
Heat can be measured using a thermometer, which detects the temperature of a substance or an environment. Thermometers work by either expanding a liquid (such as mercury) or changing the electrical resistance of a metal in response to heat, allowing us to quantify how hot or cold something is in units such as Celsius or Fahrenheit. Additionally, infrared thermometers are often used to measure heat from a distance by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object, providing a non-contact way to determine temperature.
What are some ways we can stay cool in hot weather?
Some ways to stay cool in hot weather include staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, wearing light-colored and loose-fitting clothing, staying in the shade or indoors during the hottest part of the day, using fans or air conditioning to cool down, taking cool showers or baths, and using cold packs or wet towels to lower body temperature. Additionally, avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat hours and applying sunscreen to protect your skin can also help you stay cool in hot weather.
How is heat used in everyday life?
Heat is used in everyday life for various purposes, such as cooking food, warming buildings, heating water for showers and baths, drying clothes, and sterilizing medical equipment. It is also utilized in industrial processes, such as melting metals, generating electricity, and manufacturing products like glass and ceramics. Additionally, heat is essential for transportation, as it powers engines in vehicles and airplanes. Overall, heat plays a crucial role in numerous aspects of daily life, making it an indispensable resource for human comfort, convenience, and economic activities.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments