Heat Loss Worksheet
Are you a student or professional seeking to deepen your understanding of heat loss calculations? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore the importance of worksheets in accurately predicting and minimizing heat loss.
Table of Images 👆
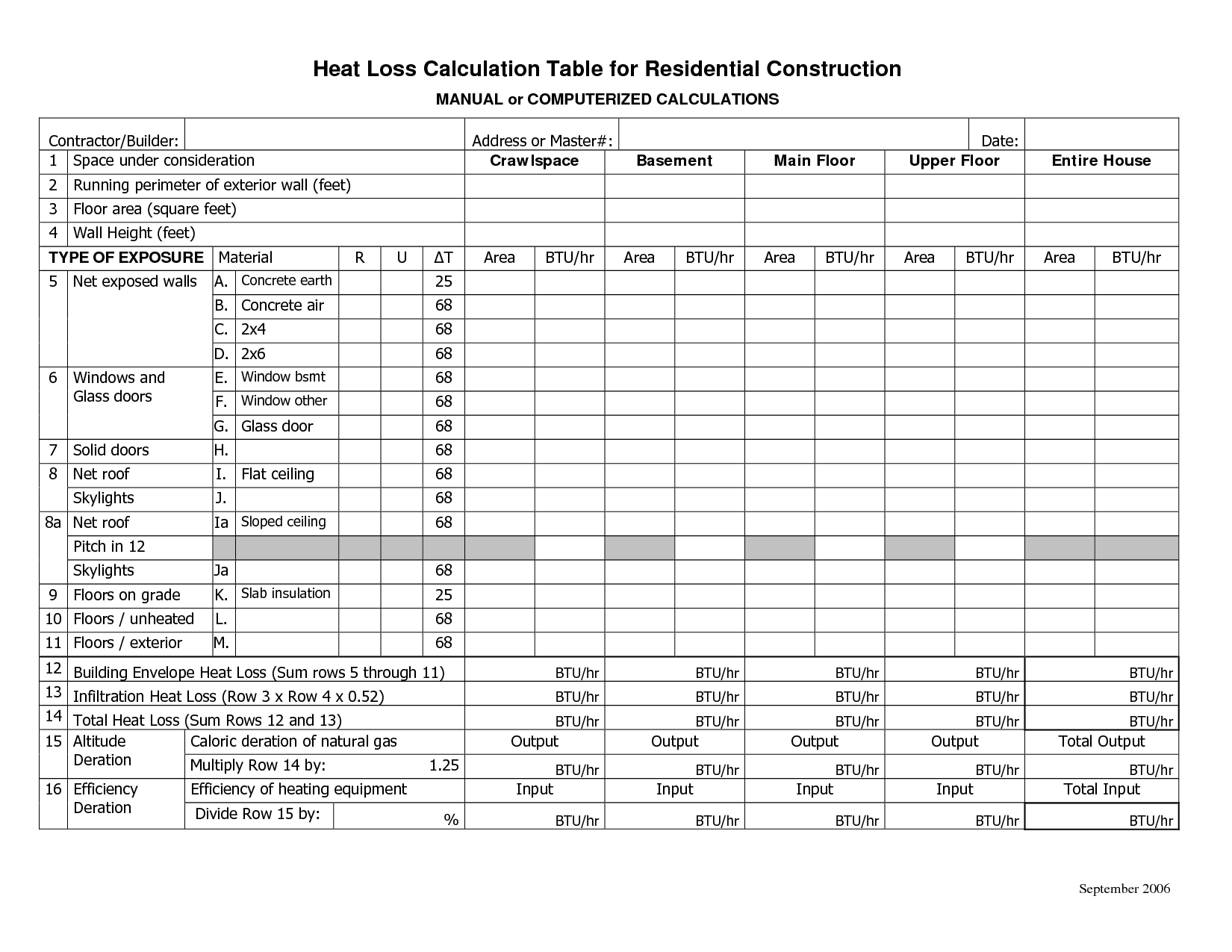
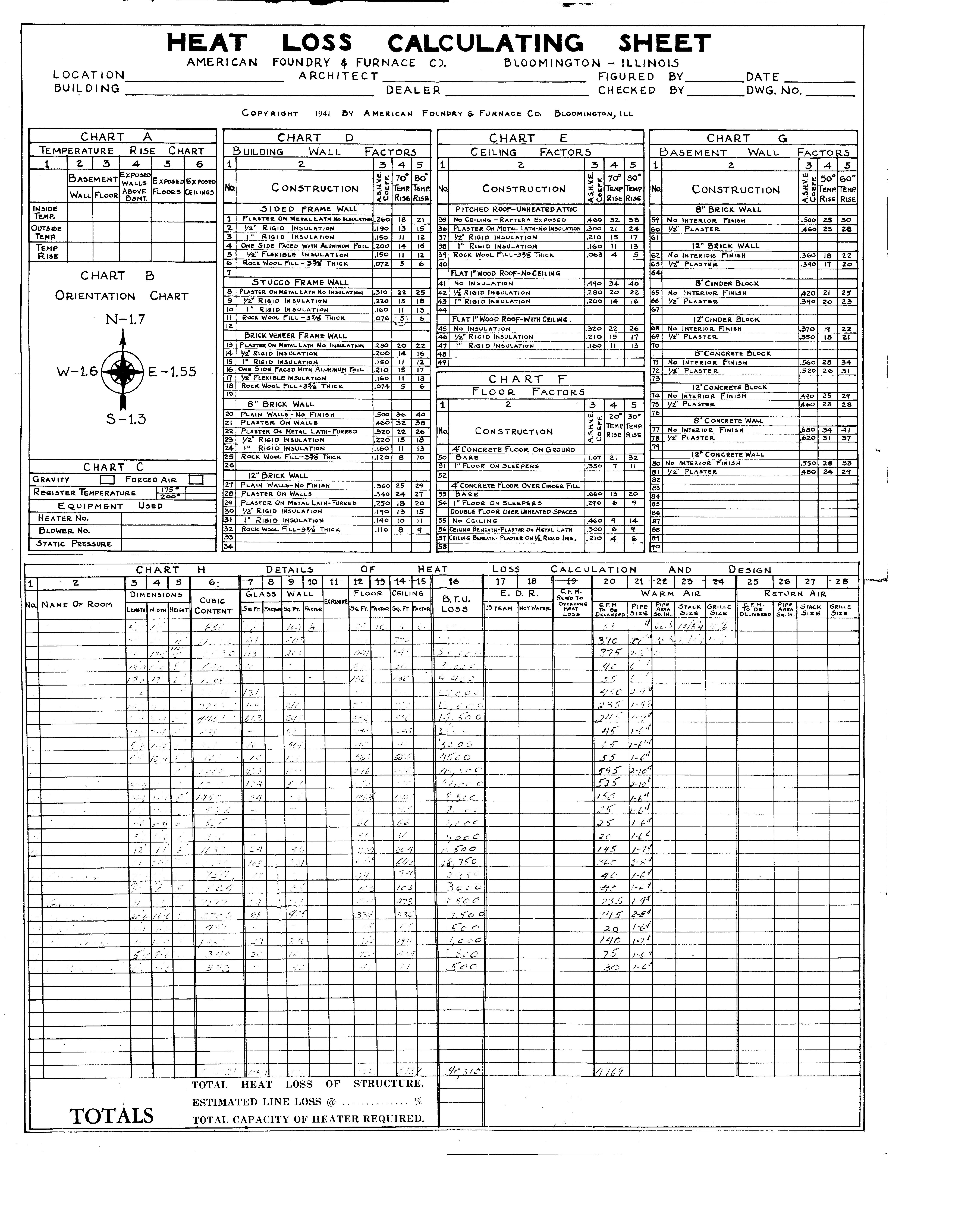
- Residential Heat Loss Calculation Sheet
- Heat Load Calculation Worksheet
- Heat Loss Calculation Worksheet
- Basic Forms of Energy Worksheets
- Heat Loss Calculation Worksheet
- Thermal Energy Worksheet Heat and Temperature
- Heat Loss Calculation Worksheet
- Thermal Convection Equation Heat Transfer
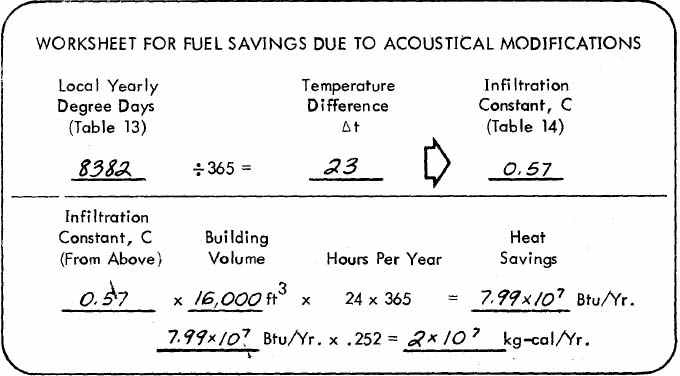
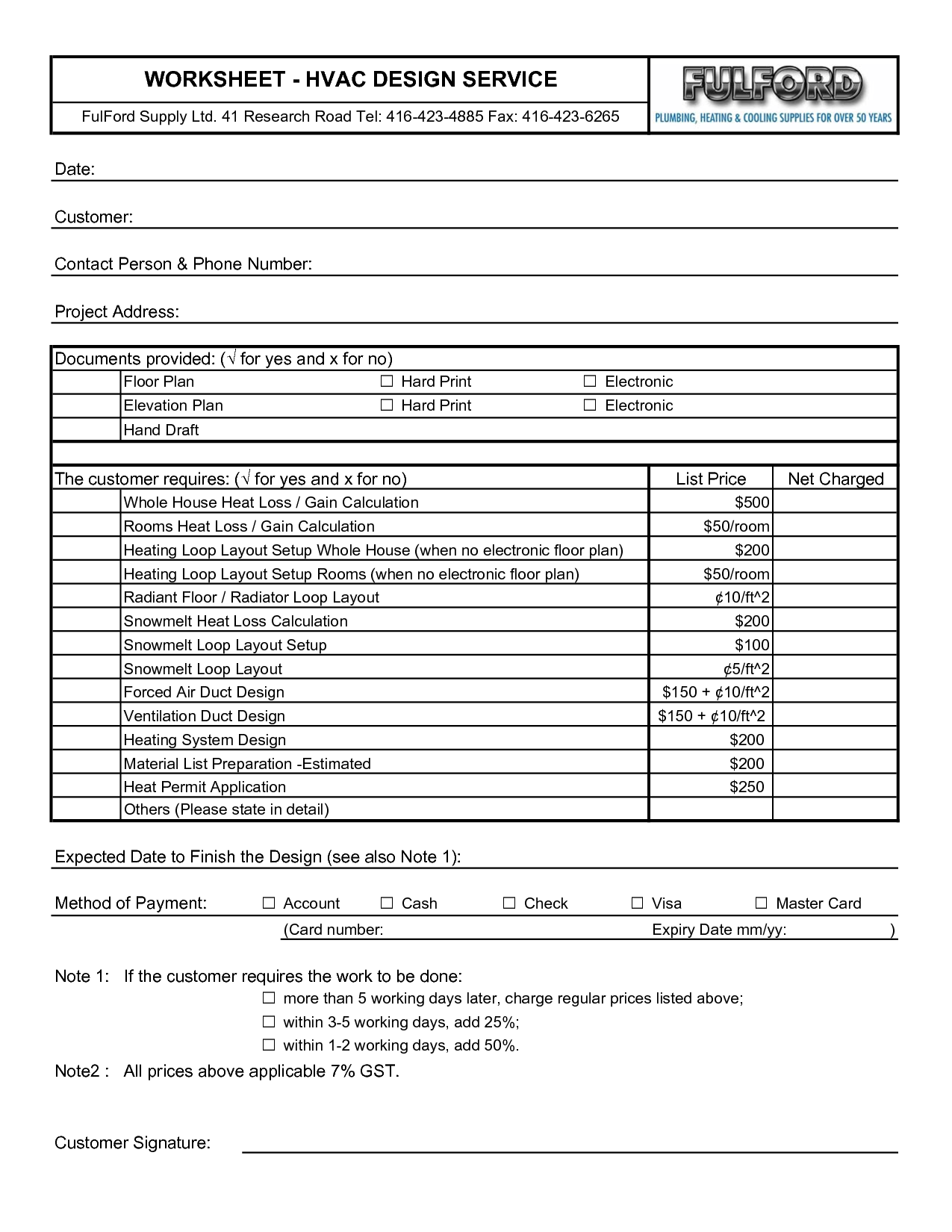
- Boiler Heat Loss Calculation Worksheet
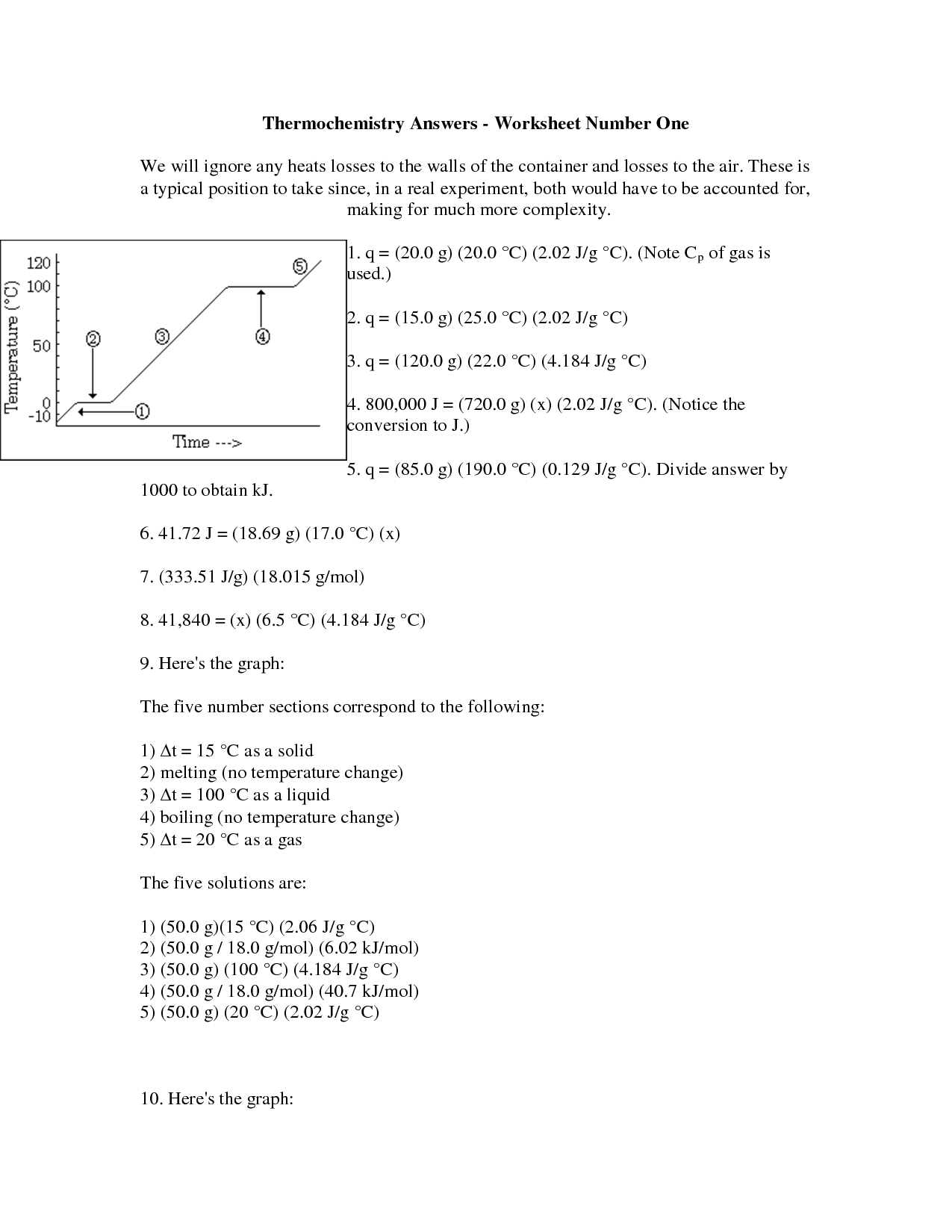
- Chemistry Heating Curve Worksheet Answers
- Heat Transfer Worksheet Answer Key
- Geothermal Heat Pump Sizing Calculator
- Convection Heat Transfer Equation for Pipe
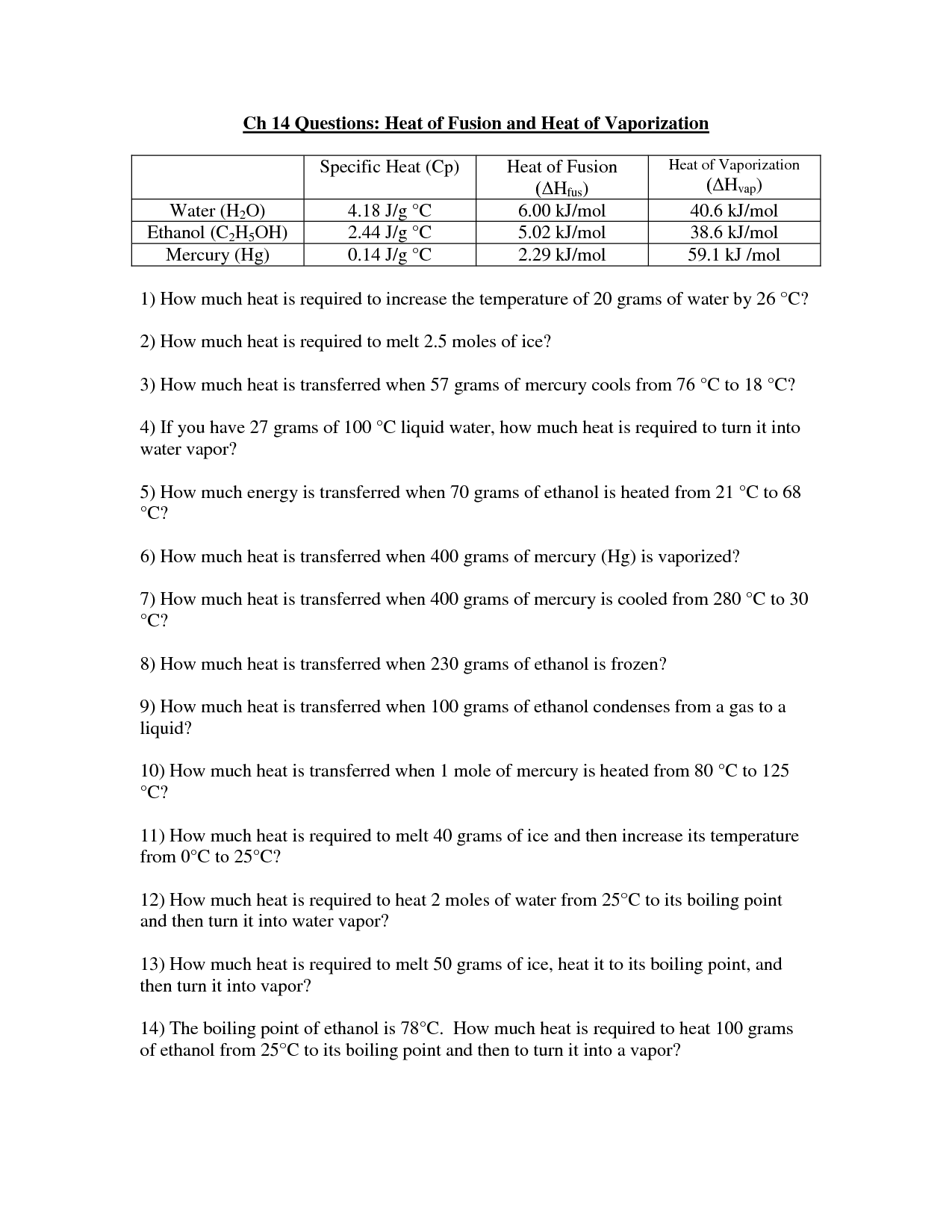
- Specific Heat Calculations Worksheet
- Heat Transfer Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is heat loss?
Heat loss refers to the transfer of thermal energy from a warmer substance to a cooler substance or environment. It occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. This process leads to a decrease in the temperature of the warmer substance as thermal energy is dissipated to its surroundings.
What are the factors that affect heat loss?
Some factors that affect heat loss include the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings, the surface area of the object, the material of the object, the presence of insulation, air movement (convection), and humidity levels. Additionally, the length of time the object is exposed to these factors can also impact the rate of heat loss.
How is heat transferred through conduction?
Heat is transferred through conduction by direct contact between particles in a material. When a substance is heated, its particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate, colliding with neighboring particles and transferring heat energy through this process. This transfer continues until thermal equilibrium is reached, and the substance's temperature becomes uniform. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals, transfer heat more efficiently through conduction due to their closely packed atoms and free electrons that facilitate rapid energy transfer.
How does convection contribute to heat loss?
Convection contributes to heat loss by transferring heat through the movement of fluids or gases. As air or water next to a warm surface is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, carrying heat energy away from the surface. Cooler, denser air or water then moves in to replace the rising warm fluid, repeating the process and facilitating the transfer of heat to the surrounding environment. This continuous movement and exchange of fluids aid in the dissipation of heat, resulting in heat loss from the warmer object or surface.
What role does radiation play in heat loss?
Radiation is one of the mechanisms by which heat is lost from an object. When an object is at a higher temperature than its surroundings, it emits thermal radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves. This radiation carries away heat energy from the object, causing it to cool down. For example, the Earth loses heat through radiation into space, especially at night when there is no direct sunlight warming the surface. Heat loss through radiation is more significant for objects at high temperatures and in a vacuum or space environment where there is no medium for conduction or convection.
How does insulation reduce heat loss?
Insulation reduces heat loss by creating a barrier that hinders the transfer of heat between the inside and outside of a building. The material used in insulation traps air pockets that act as a buffer, slowing down the movement of heat energy through conduction, convection, and radiation. This helps maintain a more stable temperature inside the building by preventing excessive heat loss in cold weather and heat gain in warm weather.
What are common sources of heat loss in buildings?
Common sources of heat loss in buildings include leaky windows and doors, poorly insulated walls and roofs, gaps and cracks in the building envelope, lack of air sealing, inadequate insulation, and heat loss through floors and foundations. Other sources include inefficient heating systems, poor maintenance of HVAC systems, and lack of proper ventilation. All of these factors can contribute to higher energy bills and reduced comfort levels in buildings.
How does air infiltration impact heat loss?
Air infiltration can significantly impact heat loss in a building by allowing warm air to escape and cool air to enter. When cold outside air infiltrates a building, it displaces the warm air inside, forcing the heating system to work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature. This increased workload results in higher energy consumption and ultimately higher heating costs. Proper insulation and air sealing measures can help reduce air infiltration and minimize heat loss, making a building more energy-efficient and comfortable.
How can windows and doors contribute to heat loss?
Windows and doors can contribute to heat loss through poor insulation and air leakage. If windows and doors are old or not properly sealed, cold air can seep in and warm air can escape, leading to increased energy consumption and higher heating bills. Additionally, single-pane windows or thin glass provide less insulation than double or triple-pane windows, further exacerbating heat loss. Properly insulating and sealing windows and doors can help mitigate heat loss and improve energy efficiency in a building.
What are some strategies to minimize heat loss in homes?
To minimize heat loss in homes, you can implement strategies such as ensuring proper insulation in walls, floors, and ceilings; sealing any drafty areas around windows, doors, and vents; using energy-efficient windows and doors; maintaining your heating system regularly; controlling humidity levels; and using heavy curtains or blinds to keep heat in during winter months. Additionally, adjusting your thermostat to a comfortable yet energy-efficient temperature and using programmable thermostats can also help reduce heat loss and save on energy costs.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






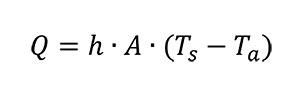
















Comments