Heart Labeling Worksheet
The Heart Labeling Worksheet is a valuable learning tool for biology students who are studying the human circulatory system. This worksheet provides a clear and concise visual representation of the heart, allowing students to practice and reinforce their understanding of its various parts and functions.
Table of Images 👆
- Label Heart Diagram Worksheet
- Blank Heart Diagram Worksheet
- Heart Diagram to Label Worksheet Printable
- Human Eye Coloring Page
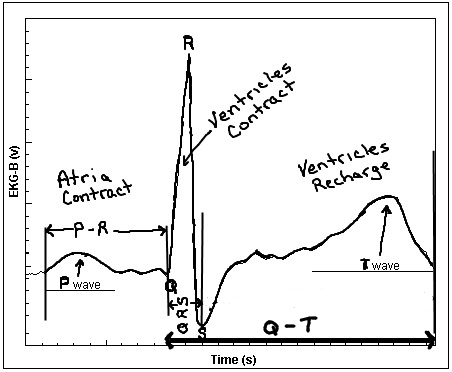
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
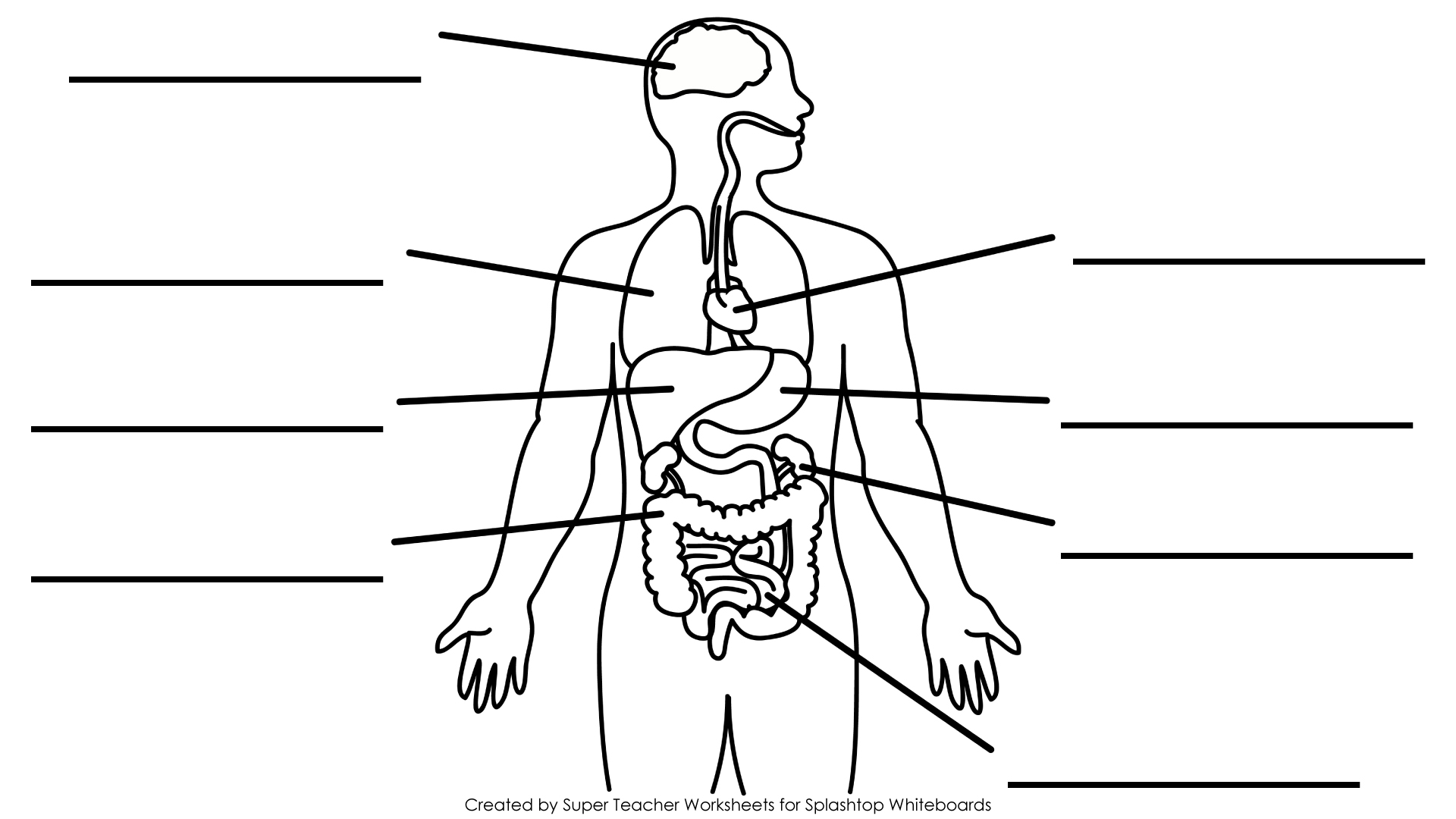
- Blank Human Body Organs Diagram
- Vertebra Bone Anatomy Worksheet
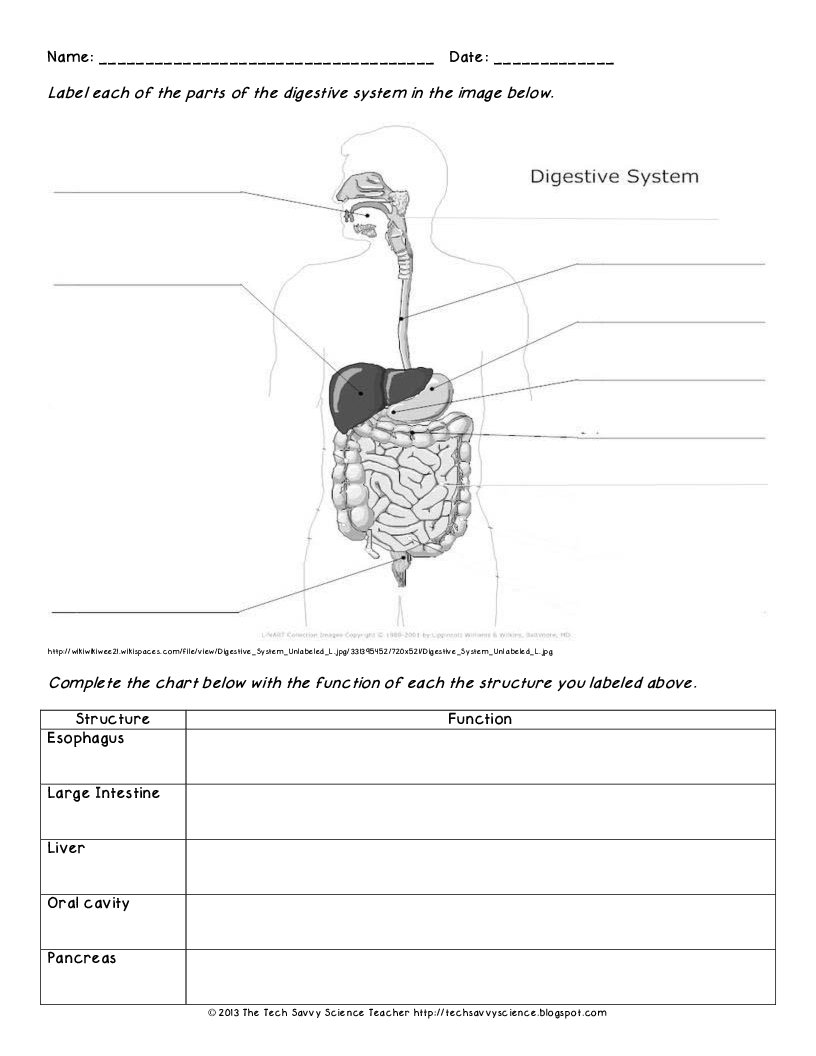
- Human Body Systems Worksheets
- Muscular System Worksheets
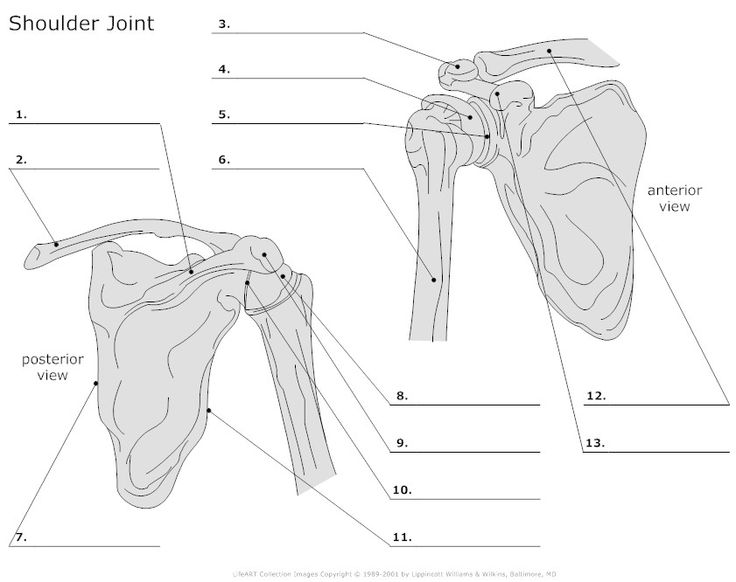
- Shoulder Joint Unlabeled
- Label Body Parts Worksheets
- ECG Diagram Labeled
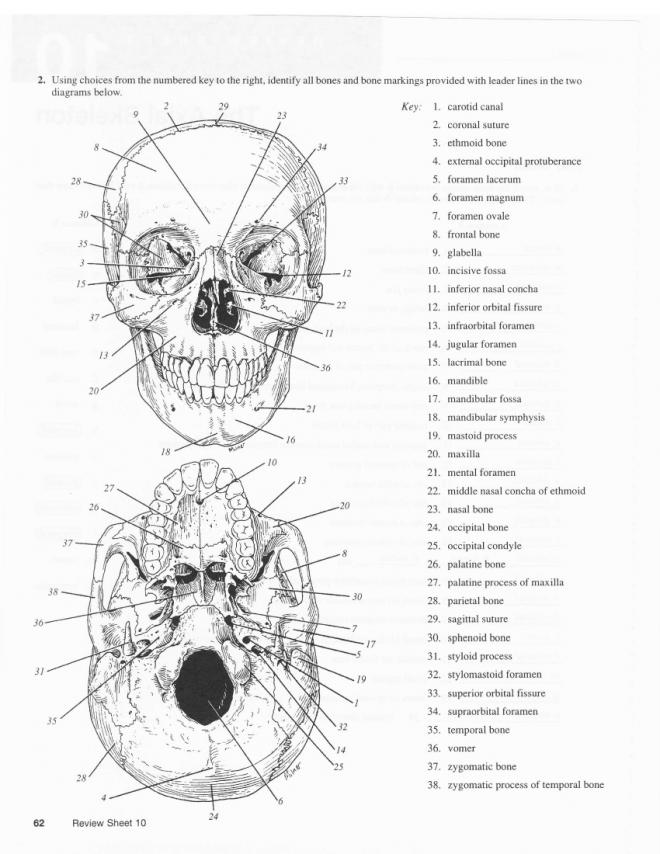
- Bone Markings Identify Skeleton
- Brain Nervous System Worksheet
- Brain Nervous System Worksheet
- Brain Nervous System Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the heart?
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products. It plays a vital role in the circulatory system, ensuring that all parts of the body receive the necessary resources to function properly.
Where is the heart located in the body?
The heart is located in the chest cavity, slightly left of the center of the chest, between the lungs and behind the sternum.
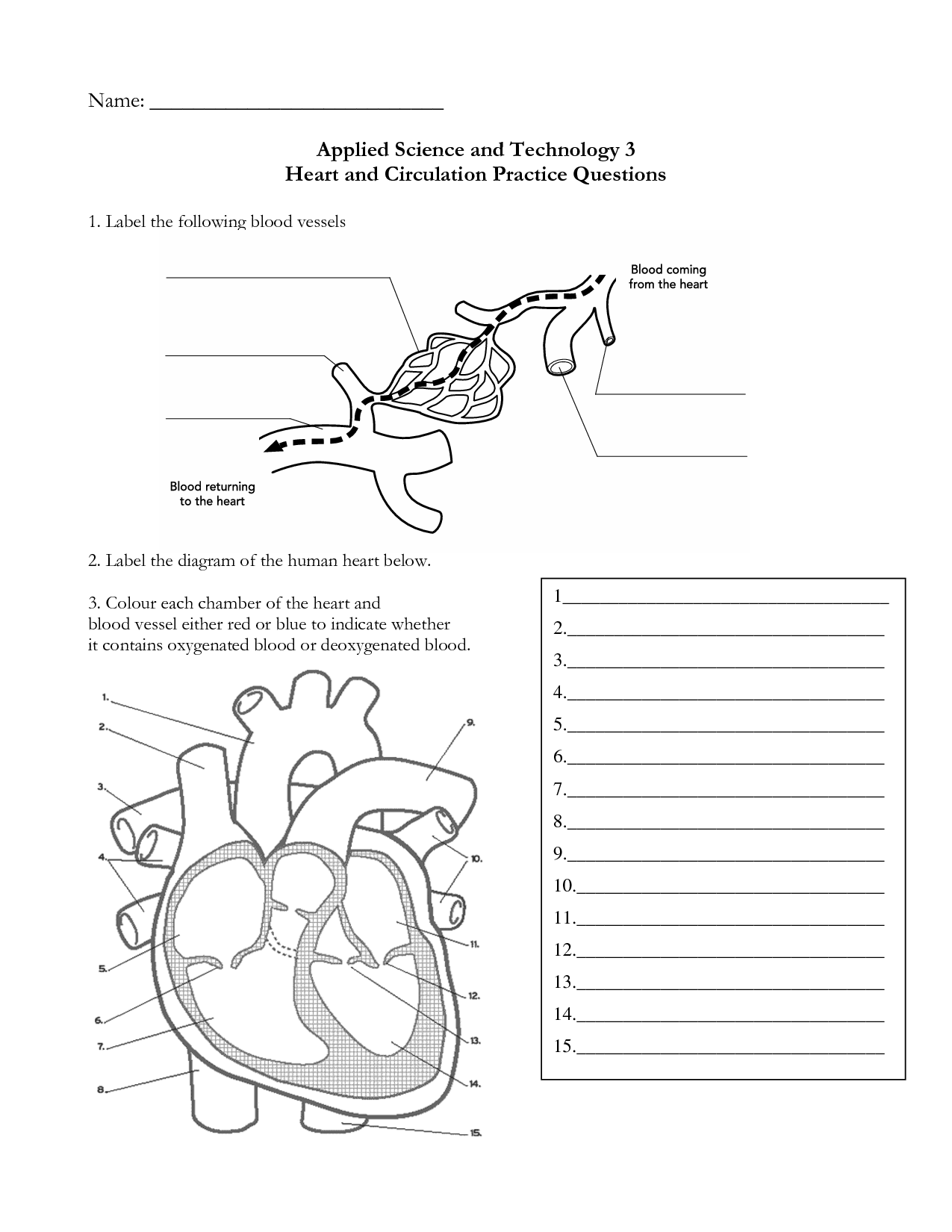
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria receive blood from the body and lungs, while the ventricles pump blood out to the body and lungs. These chambers work together to efficiently pump oxygenated blood throughout the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
What are the main blood vessels connected to the heart?
The main blood vessels connected to the heart are the aorta, which carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body, and the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation. Additionally, the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava bring deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower parts of the body back to the heart.
What is the purpose of the heart valves?
The purpose of heart valves is to regulate the flow of blood through the heart by ensuring that blood flows in one direction and prevents backflow. There are four valves in the heart: the tricuspid valve, the pulmonary valve, the mitral valve, and the aortic valve. These valves open and close in coordination with the heart's contractions, allowing blood to move from one chamber to another and eventually out to the body.
What is the function of the left ventricle?
The main function of the left ventricle is to pump oxygen-rich blood from the lungs out to the rest of the body through the aorta. This chamber of the heart is responsible for maintaining systemic circulation, ensuring that oxygenated blood is delivered to all the tissues and organs of the body.
How does oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow through the heart?
Oxygenated blood enters the heart from the lungs via the pulmonary veins and flows into the left atrium. From there, it passes through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle, which then pumps it out through the aorta to deliver oxygen to the rest of the body. Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart from the body through the vena cavae and enters the right atrium. It then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery for oxygenation before returning to the heart as oxygenated blood.
What is the role of the coronary arteries?
The coronary arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, ensuring that the heart has the necessary nutrients and oxygen to function properly. These arteries play a crucial role in maintaining the heart's ability to pump blood throughout the body effectively and are essential for overall heart health and function.
What is the pericardium and what is its function?
The pericardium is a double-layered membrane that surrounds the heart and the roots of the great blood vessels. Its main function is to protect and support the heart by holding it in place and preventing it from overexpanding. It also helps to maintain the heart's position in the chest cavity, lubricates its movements, and acts as a barrier against infection and inflammation.
How does the heart maintain its own rhythm?
The heart maintains its rhythm through its intrinsic electrical conduction system, which is made up of specialized cells that generate and conduct electrical impulses. This system includes the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. The SA node, located in the right atrium, is known as the heart's natural pacemaker and initiates each heartbeat by sending out an electrical signal. This signal then travels through the rest of the conduction system, causing the heart muscle to contract in a coordinated manner, allowing for the rhythmic pumping of blood throughout the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments