Greater than Less than Fraction Worksheets
Are you searching for educational resources to aid your child's understanding of greater than and less than fractions? Look no further! We have curated a collection of comprehensive worksheets that focus on this key mathematical concept, perfect for elementary and middle school students.
Table of Images 👆
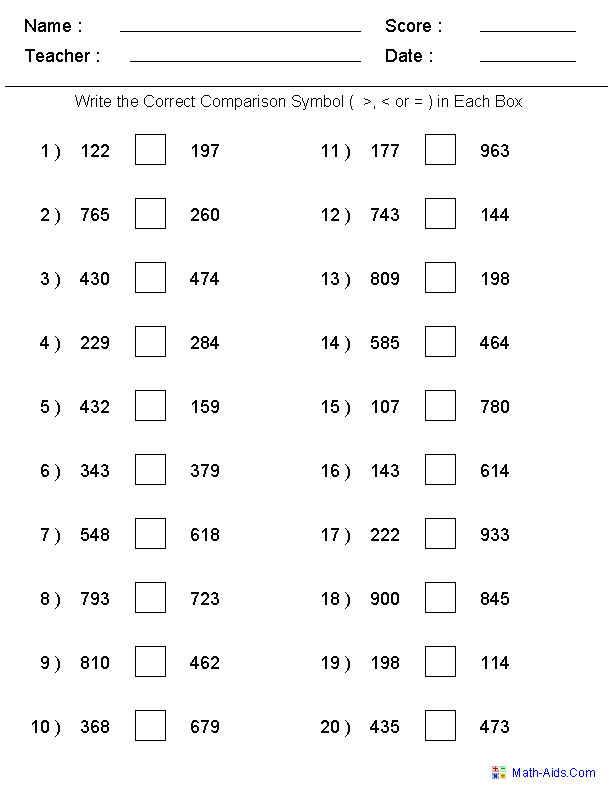
- Integers Greater than Less than Worksheets
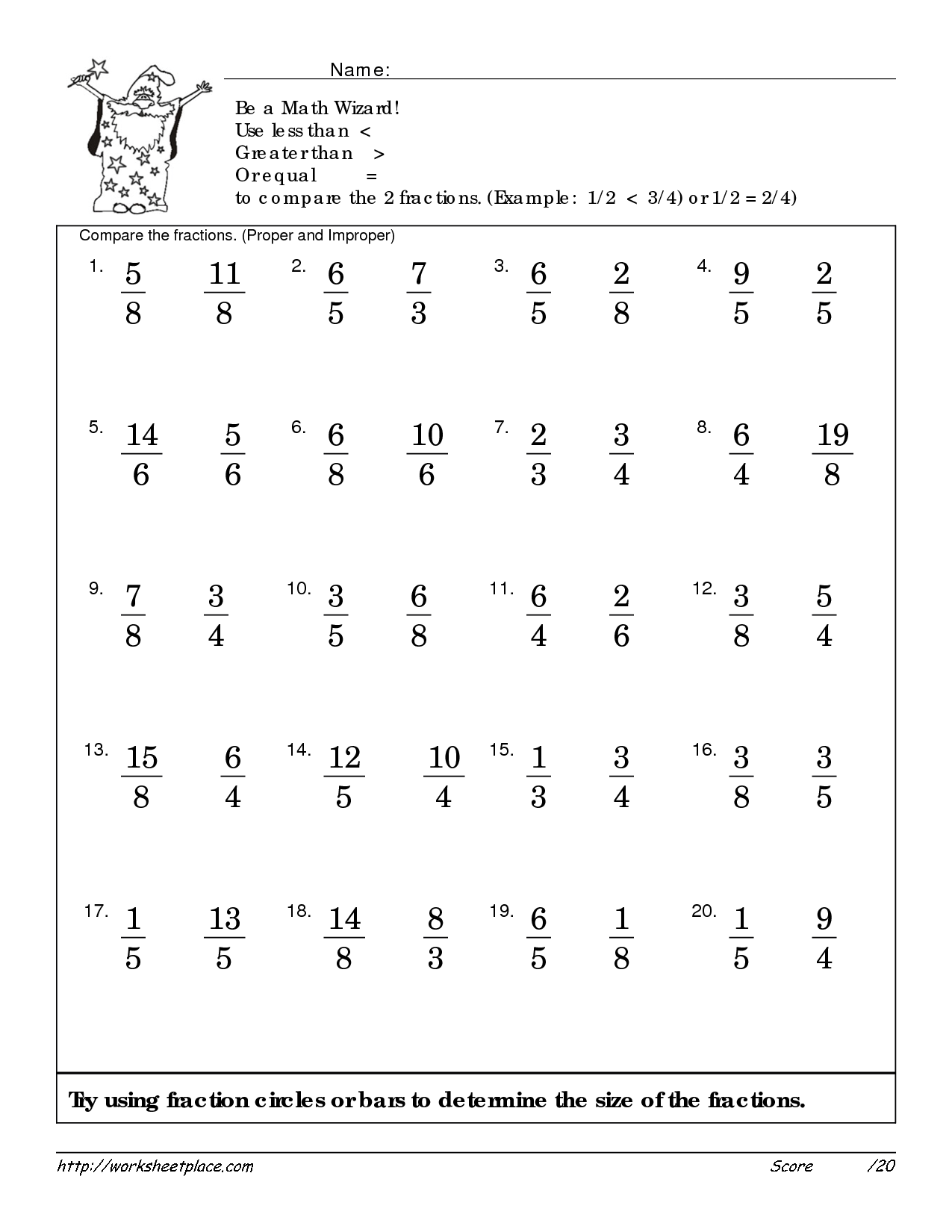
- Fractions Greater or Less than 1 2
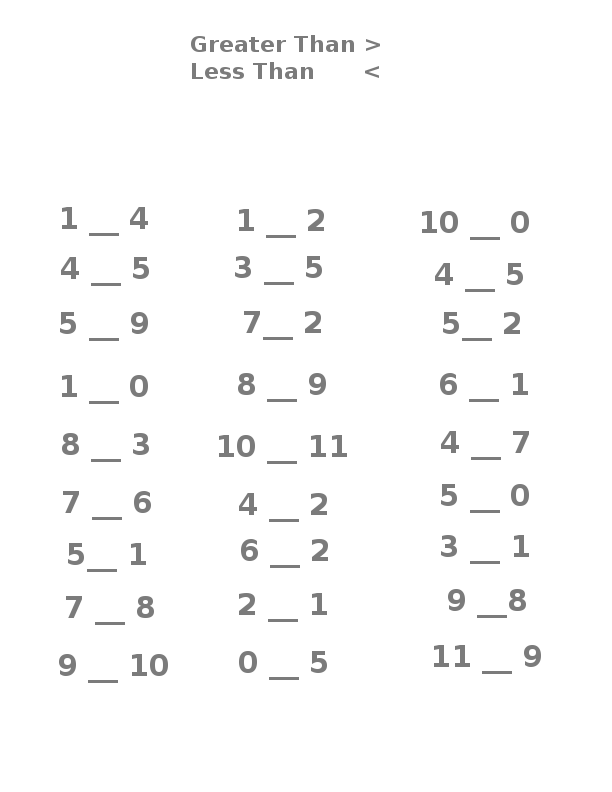
- Greater than Less than Worksheets
- Greater than Less than Math Worksheets
- More than Less than Worksheets First Grade
- Comparing Decimals Worksheet
- Greater than or Less than Fraction Worksheets
- Greater Less than Worksheets 2nd Grade Math
- Greater than Less than Worksheets
- Integer Greater than Less Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a fraction in the context of greater than/less than worksheets?
In the context of greater than/less than worksheets, a fraction is a number that represents a part of a whole. Fractions are used to compare quantities or parts of a whole to determine which is greater or less than the other. Students often need to convert fractions to a common denominator before comparing them in greater than/less than exercises on worksheets.
How do you determine if one fraction is greater than another?
To determine if one fraction is greater than another, you can cross-multiply the fractions to find a common denominator, then compare the numerators. If the numerator of the first fraction multiplied by the denominator of the second fraction is greater than the numerator of the second fraction multiplied by the denominator of the first fraction, then the first fraction is larger. If the values are equal, then the fractions are equal in value.
What is the significance of the numerator in a fraction when comparing with another fraction?
The numerator in a fraction represents the number of equal parts being considered, while the denominator represents the total number of parts that make up a whole. When comparing fractions, a larger numerator indicates a larger quantity of the same-sized parts being considered, making the fraction greater in value. It shows the relationship between the parts being compared in terms of quantity or size.
How does the denominator affect the comparison between fractions?
The denominator of a fraction plays a critical role in determining the size and value of the fraction. A larger denominator indicates that the fraction represents a smaller value, while a smaller denominator suggests a larger value. When comparing fractions, denominators should be the same to make accurate comparisons. If the denominators are different, you can find a common denominator by simplifying or converting the fractions to have the same base, enabling you to compare them easily.
Can fractions with different denominators be compared using the greater than/less than symbols?
Yes, fractions with different denominators can be compared using the greater than (>) or less than (<) symbols. To compare such fractions, they must first be converted to equivalent fractions with a common denominator. Once the fractions have the same denominators, you can directly compare the numerators to determine which fraction is greater or lesser.
Are there any special rules for comparing fractions with the same numerator?
Yes, when comparing fractions with the same numerator, the fraction with the smaller denominator is the larger fraction. This is because the smaller the denominator, the larger the value of the fraction. For example, ? is larger than ¼ because 3 is smaller than 4. So, when comparing fractions with the same numerator, focus on the denominators to determine which fraction is larger.
What do you do when the denominators of two fractions are different and you need to compare them?
When comparing fractions with different denominators, you need to find a common denominator. To do this, you can either find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators or multiply the denominators together to find a common denominator. Once you have the fractions with the same denominator, you can compare them by looking at their numerators. The fraction with the larger numerator is greater, and the fraction with the smaller numerator is lesser.
What is the role of common denominators in comparing fractions?
The role of common denominators in comparing fractions is to make it easier to determine which fraction is larger or smaller. By finding a common denominator for two or more fractions, you can ensure that the fractions have the same base for comparison. This allows you to directly compare the numerators of the fractions to see which one is greater or lesser, making it simpler to determine the relationship between the fractions.
How can improper fractions be compared using greater than/less than symbols?
Improper fractions are compared by converting them into mixed numbers first. The whole numbers of the mixed numbers are compared first. If they are equal, then the fractions are compared. If the fractions are still different, they can be converted to have the same denominator to make comparison easier. The greater than (>) or less than (<) symbols can then be used to show which fraction is larger or smaller.
Is it necessary to simplify fractions before comparing them?
No, it is not necessary to simplify fractions before comparing them. Comparison of fractions can be done by finding common denominators or converting them into decimal form to easily determine which fraction is greater or less than the other without simplification.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




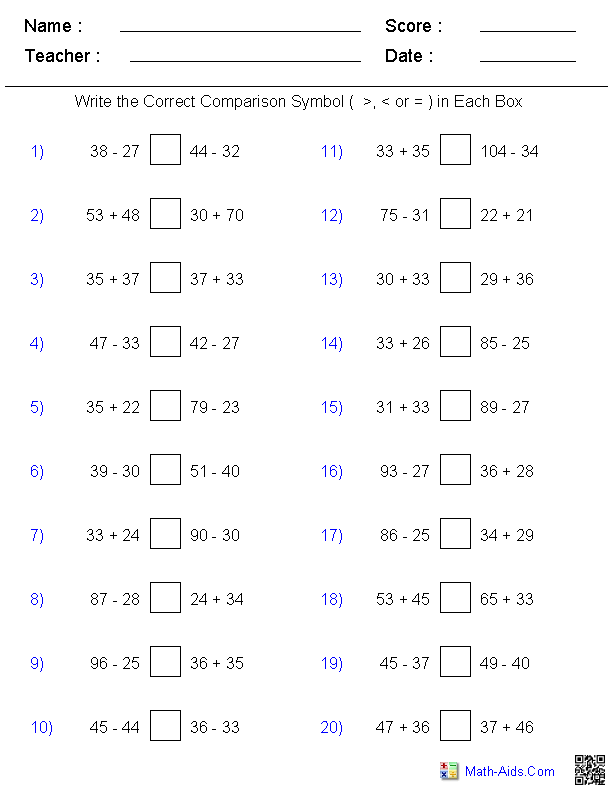

















Comments